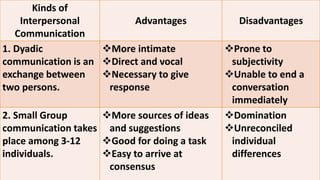
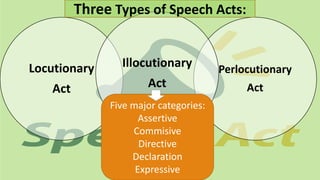
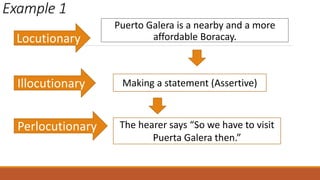
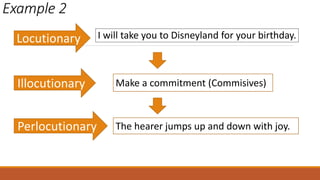
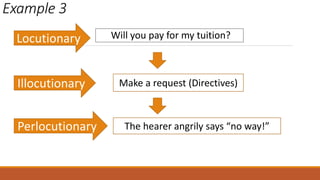
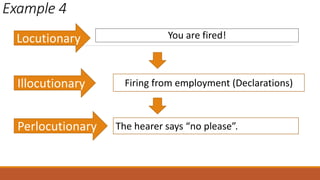
The document discusses different types of speech contexts and styles. It defines four types of speech contexts: intrapersonal, interpersonal, public, and mass communication. Intrapersonal communication occurs within an individual through thinking. Interpersonal communication occurs between individuals through feedback. Public communication addresses a large audience without feedback. Mass communication reaches a wide audience through media. It also outlines five speech styles - intimate, casual, consultative, formal, and frozen - that are appropriate for different contexts and levels of formality.