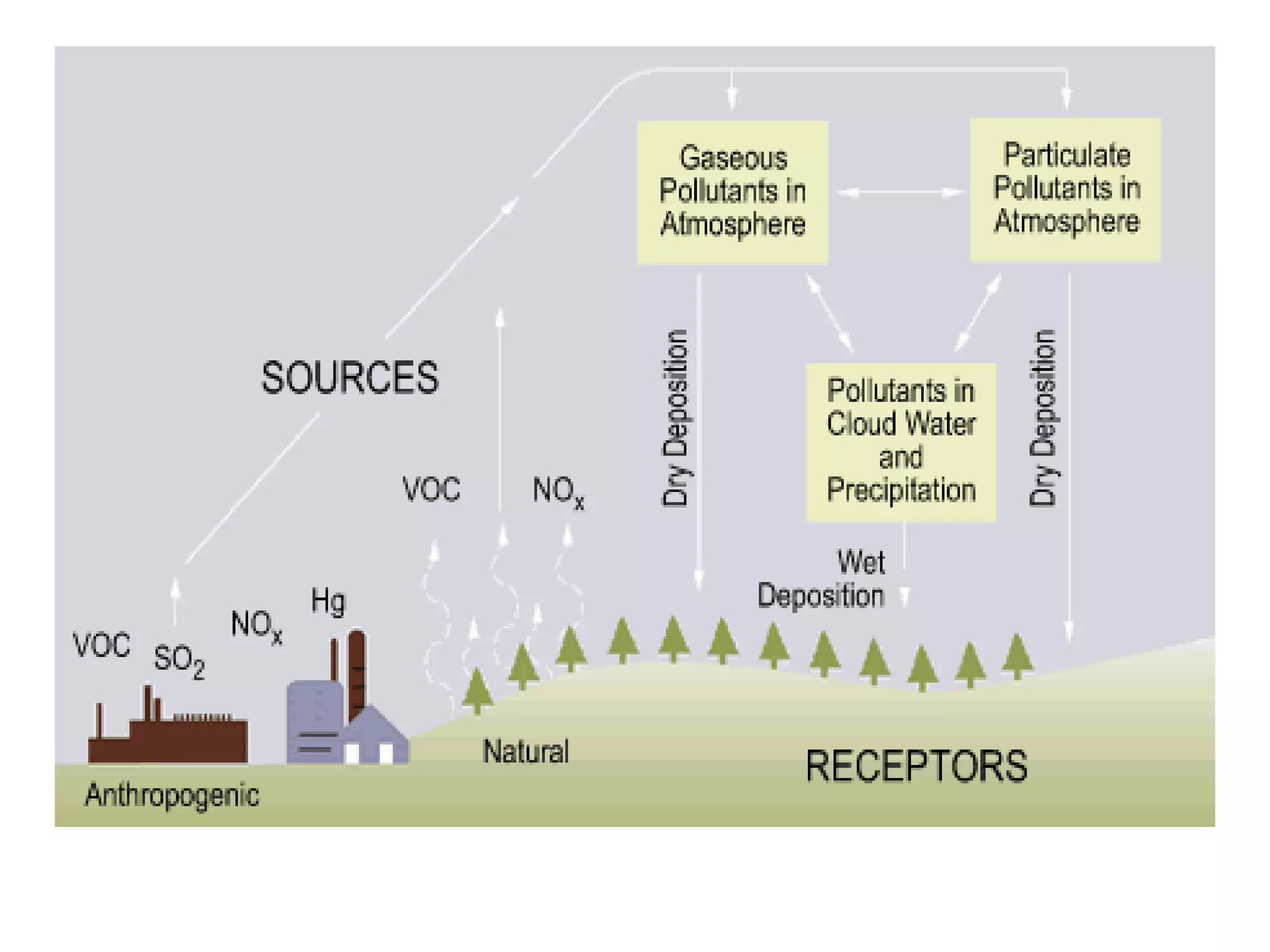
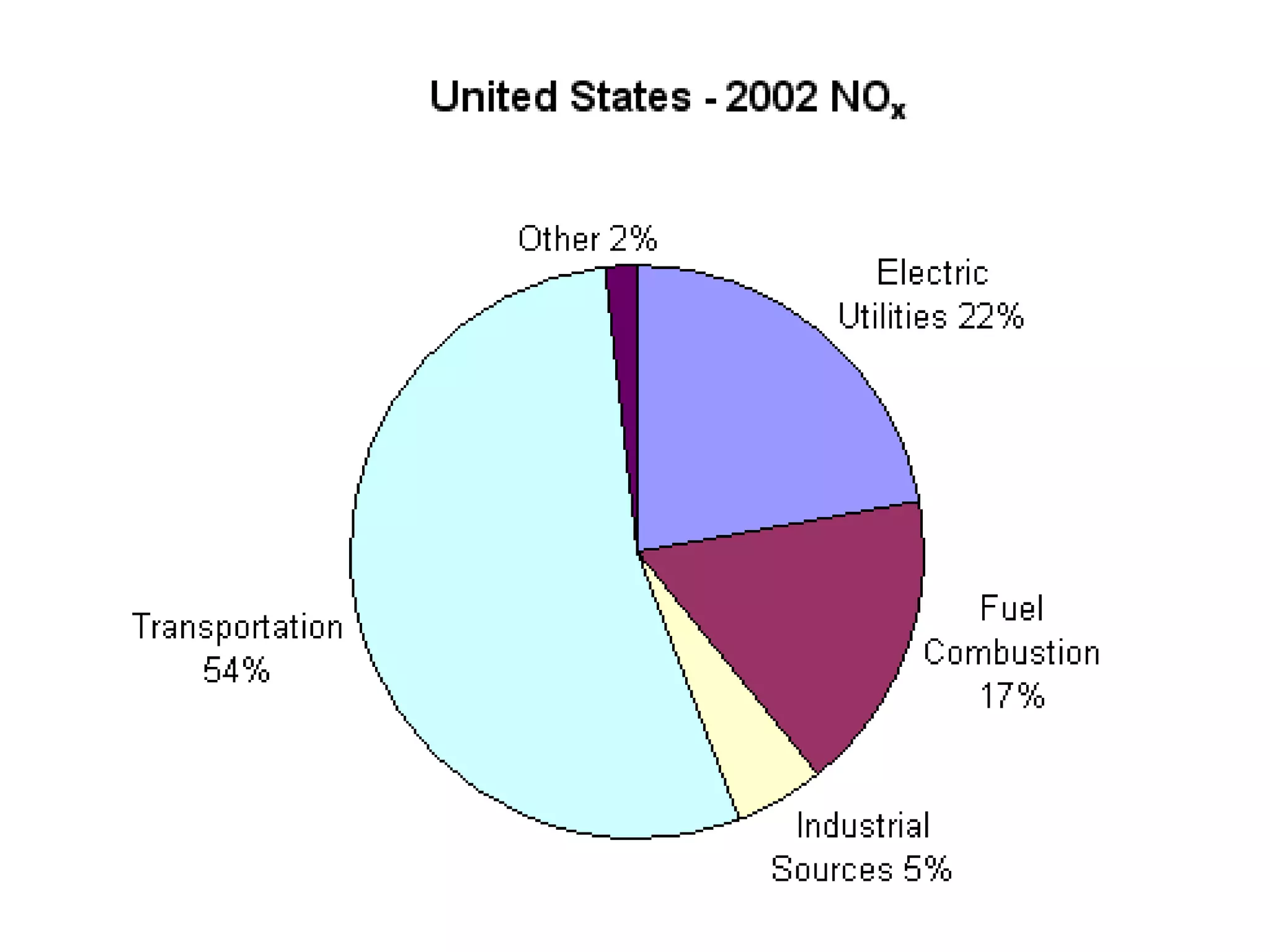
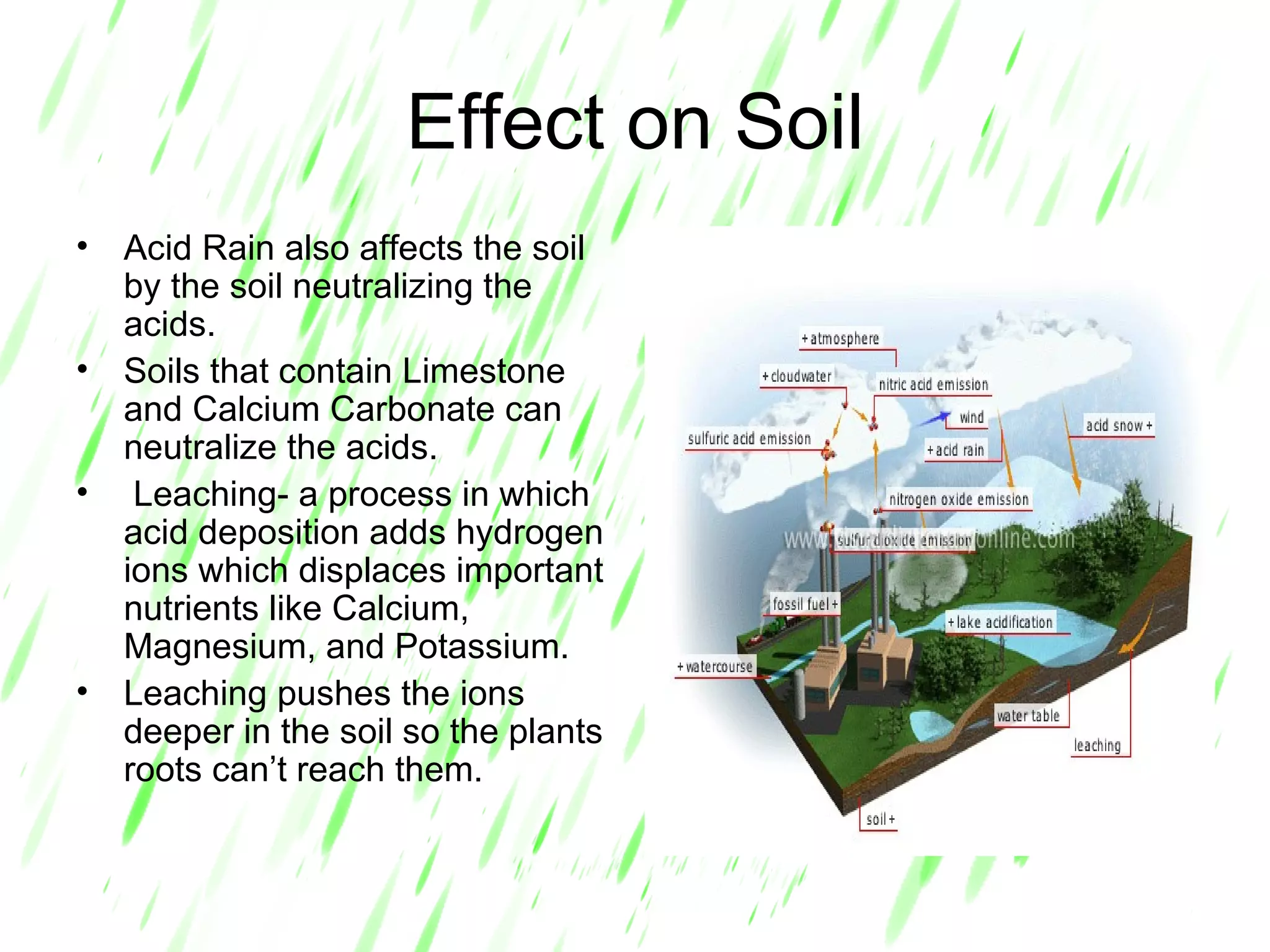
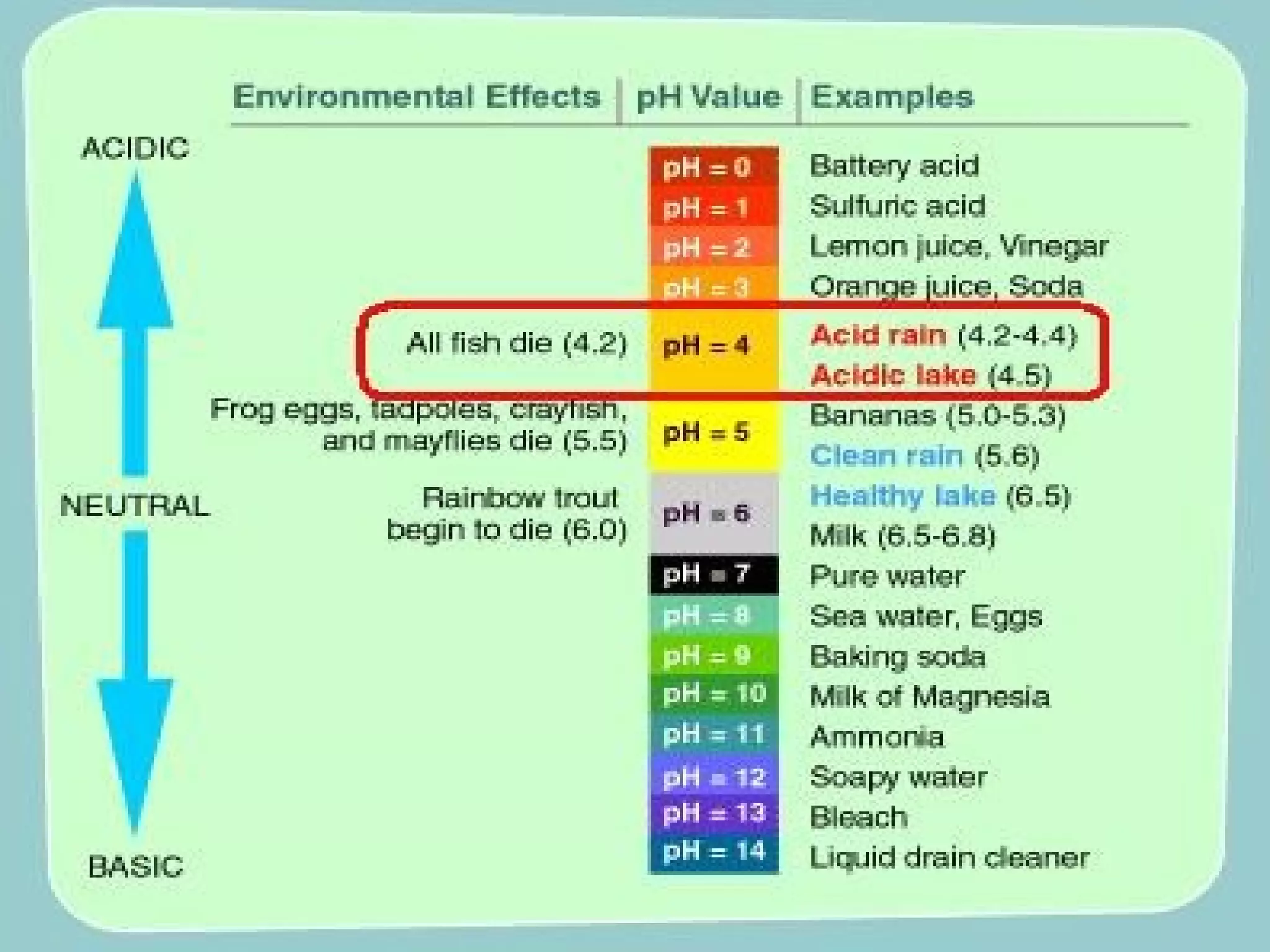
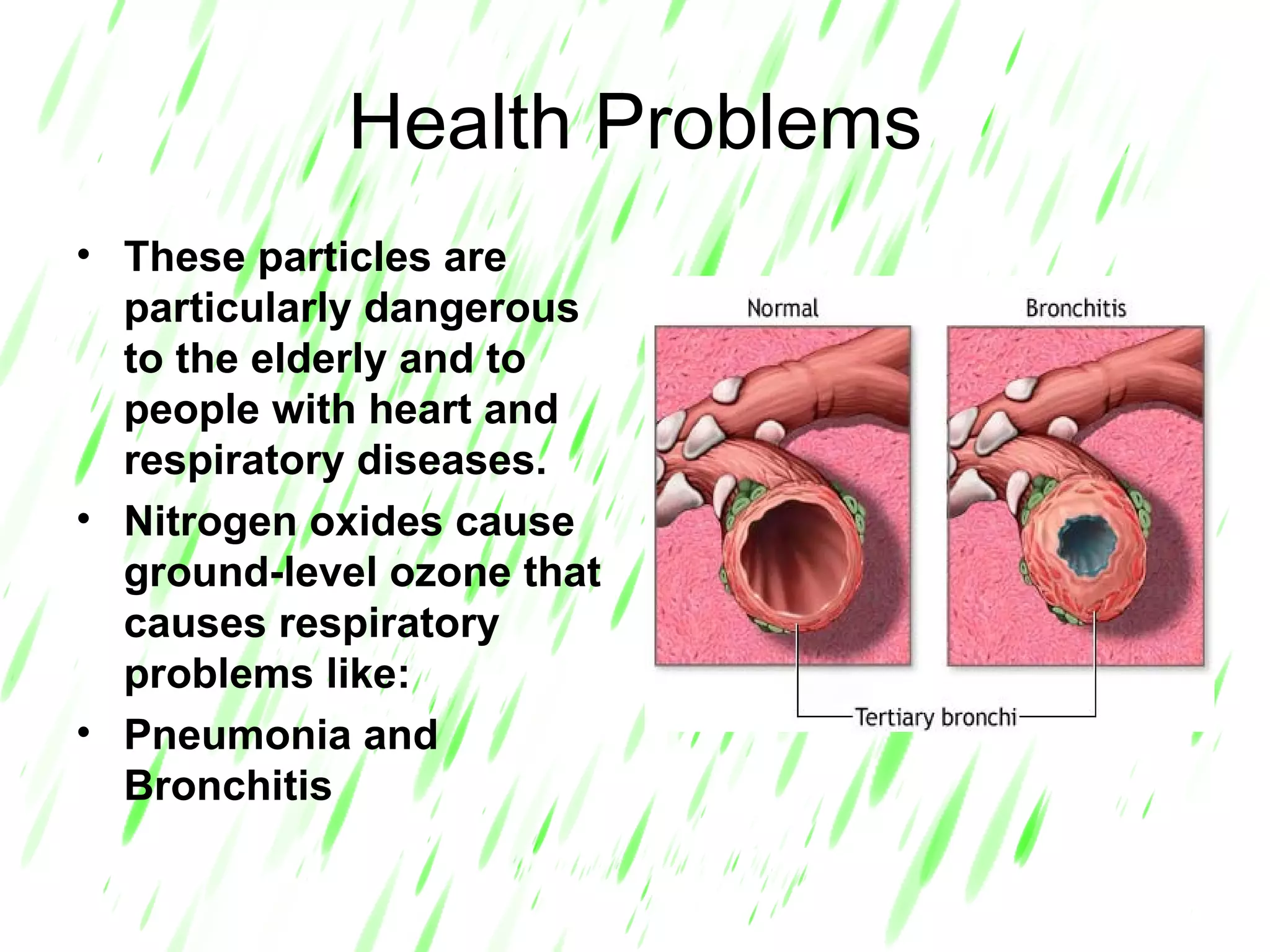
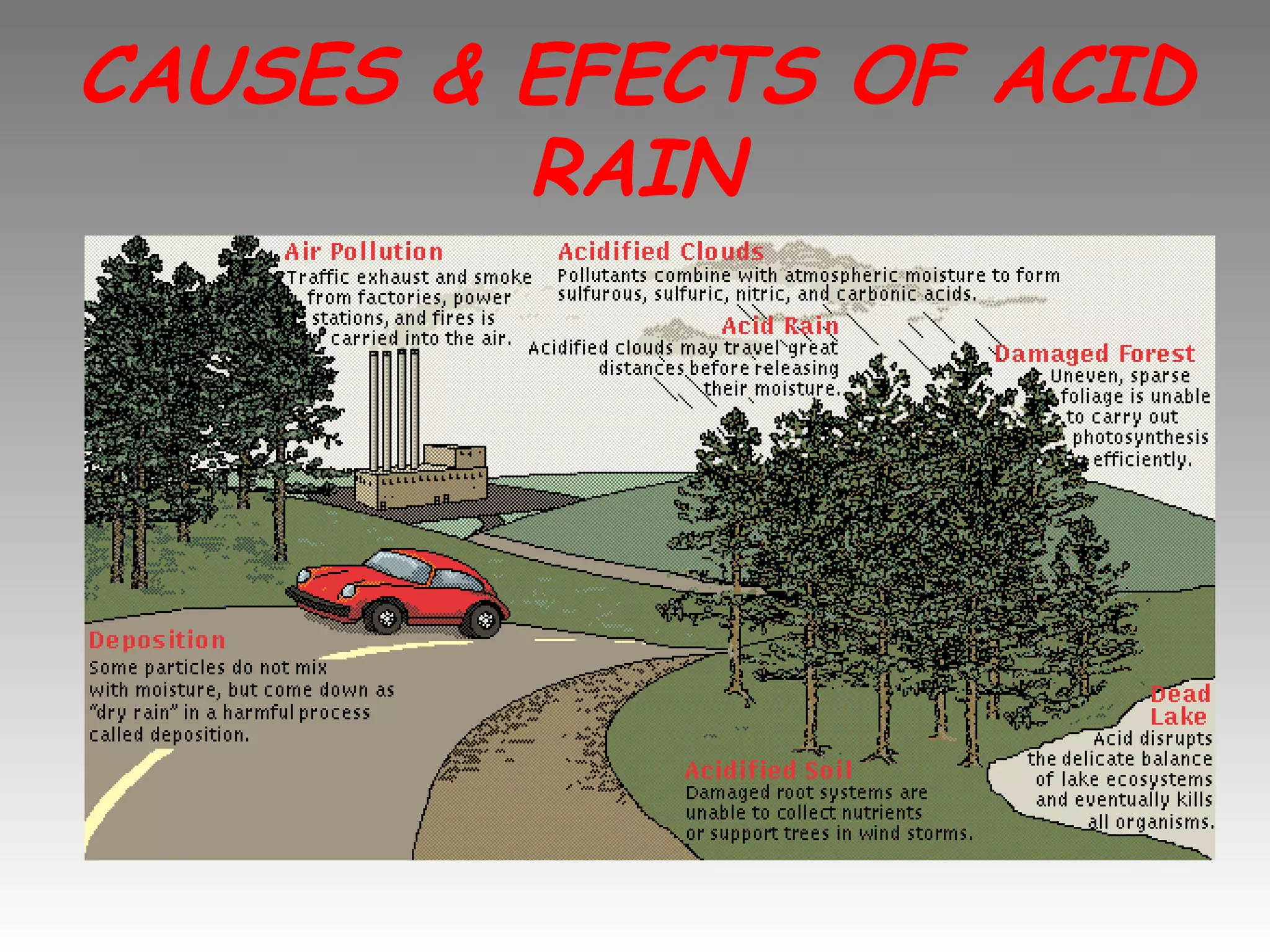
Acid rain is rain that is acidic due to atmospheric pollution such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides from burning fossil fuels. It damages ecosystems, buildings, and human health. To reduce acid rain, countries need to decrease fossil fuel burning by using pollution controls on power plants and vehicles or switching to renewable energy. Individuals can help by conserving energy to decrease demand for fossil fuels.