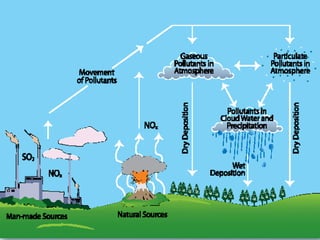
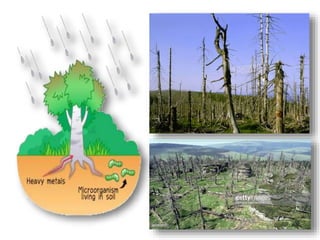
Acid rain is caused by emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides from the burning of fossil fuels. When these gases react with water and other compounds in the atmosphere, they form acids that fall to Earth as rain, snow, or other precipitation. Acid rain harms both aquatic environments and forests by making soils and waters acidic. It damages trees and other plants by leaching nutrients from soils and wearing away leaves, and harms aquatic animals by making waters toxic. Preventing acid rain requires reducing fossil fuel combustion through cleaner industry, alternative energy sources, and individual energy conservation efforts.