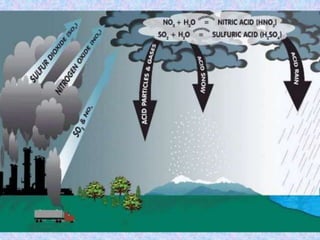
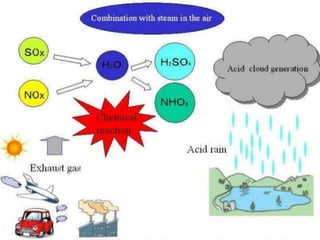
Acid rain is caused by sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions from human sources like power plants and vehicles reacting in the atmosphere and falling to earth as rain, snow, or dry particles with a pH lower than 5.6. It damages aquatic ecosystems, soils, infrastructure, and is linked to health issues. Prevention methods include installing pollution controls on industry smokestacks, transitioning to renewable energy, restoring damaged environments, and international agreements to reduce emissions. Individual actions like conserving energy and choosing low-emissions transportation can also help address the problem.









![Impacts of acid rain
• A] On Aquatic ecosystem
• Both the lower pH and higher aluminum
concentrations in surface water that occur as a
result of acid rain can cause damage to fish and
other aquatic animals.
• At pH lower than 5 most fish eggs will not hatch
and lower pHcan kill adult fish.
• As a result of acidification, fishes suffered
significant changes in mortality, reproductive
failure, reduced growth, skeletal deformities and
increased uptake of heavy metals.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidrain-170512070407/85/Acid-rain-12-320.jpg)

![Cont…
• B] On animals
• Proportion of birds laying defective eggs have
rose from roughly 10% in 1983-1984 to 40%
by 1987/88 (limited in areas of acid rain).
• No snails are found in lakes with a pH of less
than 5.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidrain-170512070407/85/Acid-rain-14-320.jpg)
![Cont…….
• C] On plants
• Acid rain does not usually kill trees directly. It weakens trees by
• slowing up the growth of forests,
• damaging their leaves; cause leaves and needles to turn brown and
fall off & die
• limiting the nutrients available to them, or
• exposing them to toxic substances slowly released from the soil and
• makes them more susceptible to other threats.
• Forests in high mountain regions often are exposed to greater
amounts of acid than other
• It directly reduces the yield of radishes, carrots, broccoli](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidrain-170512070407/85/Acid-rain-15-320.jpg)
![Cont..
• D] Soil
• Soil biology and chemistry can be seriously damaged
by acid rain.
• Some microbes are unable to tolerate changes to low
pH and are killed. The enzymes of these microbes
are denatured (changed in shape so they no longer
function) by the acid
• The hydronium ions of acid rain also
mobilize toxins such as aluminium, and leach away
essential nutrients and minerals such as magnesium
• 2 H+ (aq) + Mg2+ (clay) 2 H+ (clay) + Mg2+ (aq)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidrain-170512070407/85/Acid-rain-16-320.jpg)
![Cont……..
• E] Human health
• Acid rain does not directly affect human health.
The acid in the rainwater is too dilute to have
direct adverse effects
• However, the particulates responsible for acid
rain (sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides) do have
an adverse effect.
• Increased amounts of fine particulate matter in
the air do contribute to heart and lung problems
including asthma and bronchitis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidrain-170512070407/85/Acid-rain-17-320.jpg)
![Cont……..
• F] Damage of Infrastructure:
• accelerates the decay of building materials and paints,
including irreplaceable buildings, statues, and sculptures
that heritage are parts of our nation’s cultural property.
• Acid rain has the unsettling ability to erase and obliterate
stone and metal, the most durable of materials (especially
those made of rocks, such as limestone and marble, that
contain large amounts of calcium carbonate)
• Increases the corrosion rate of metals
• It can downgrade leather and rubber
• It causes carvings and monuments in stones to lose their
features](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidrain-170512070407/85/Acid-rain-18-320.jpg)
![Cont……
• G] The Socioeconomic Consequences of
Acidification
• Acid deposition causes accelerated corrosion,
fracturing, and discoloration of buildings,
structures, and monuments.
• Lower productivity in fisheries, forestry, and
agriculture translates to lower profits and
fewer jobs for some important industries](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidrain-170512070407/85/Acid-rain-19-320.jpg)











