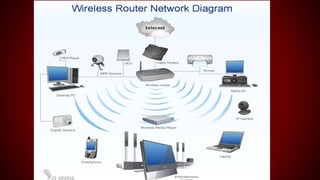
A wireless local area network (WLAN) allows devices to connect to a local network using radio waves instead of cables. WLANs provide connectivity for devices like laptops, phones, and smart appliances over distances of hundreds of feet. Key advantages of WLANs are mobility and easier installation compared to wired networks. However, WLANs also face security risks and reliability issues from signal interference that wired networks do not.