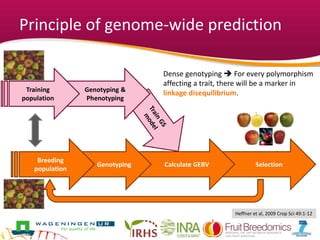
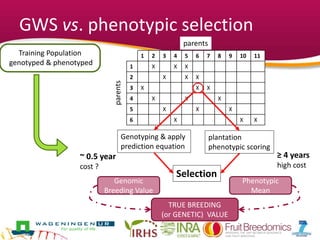
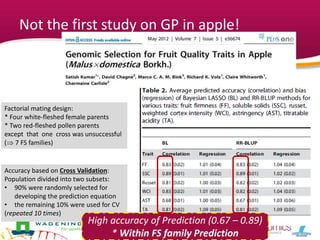
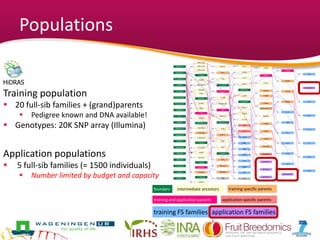
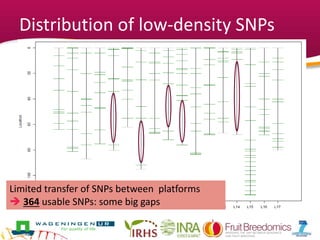
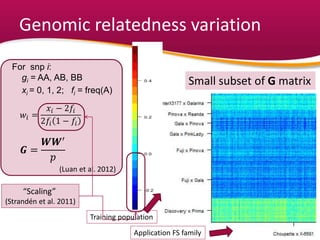
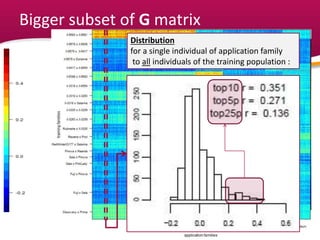
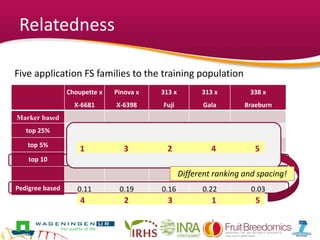
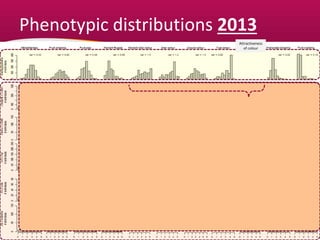
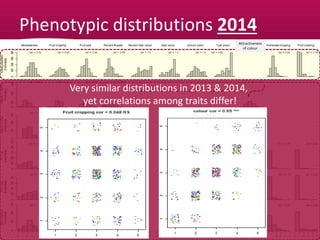
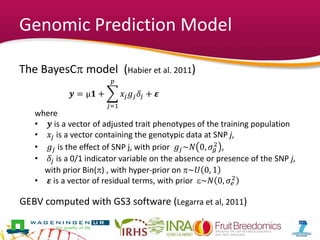
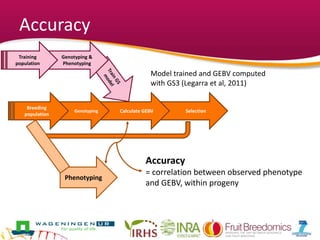
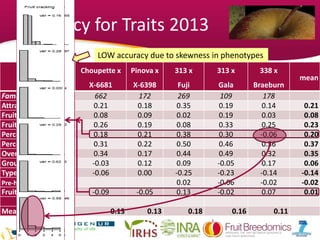
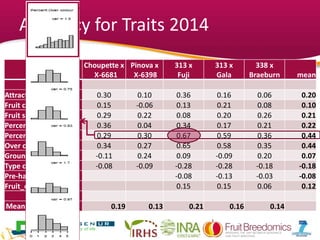
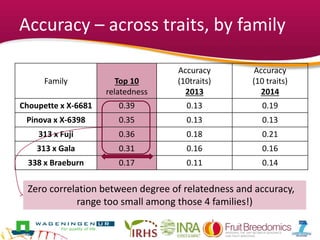
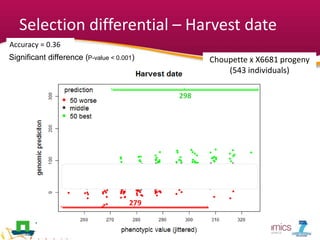
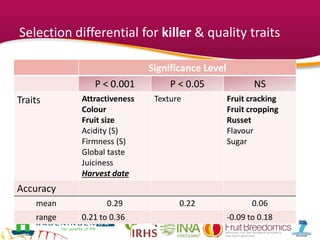
This document summarizes a two-year pilot study on genomic selection in apple breeding. The study involved genotyping and phenotyping a training population of 20 full-sib families and 5 application families. Genomic prediction models were developed and used to calculate genomic estimated breeding values (GEBV) for traits like fruit quality, size, and disease resistance. The accuracy of genomic prediction varied among traits from poor to moderate, and selection differentials based on GEBV were significant for several traits. The study provides a proof of concept for genomic selection in apple breeding but highlights the need for further research on prediction accuracy across multiple years and environments.