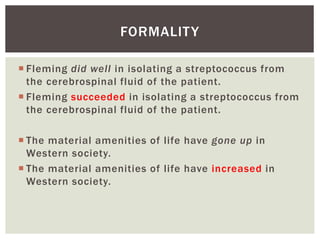
This document discusses the key characteristics of academic writing, including that it is complex, formal, objective, explicit, hedged, and precise. It provides examples of how academic writing uses complex language through higher lexical density. Formality is achieved by avoiding colloquial language and being objective by removing first-person pronouns. Explicitness involves clearly signposting ideas and relationships between parts of the text. Hedging uses cautious language to acknowledge uncertainty, and precision involves using specific details like dates, figures or definitions.