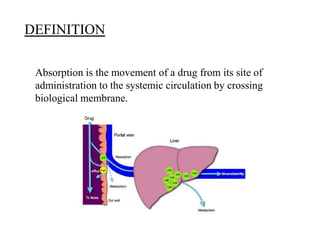
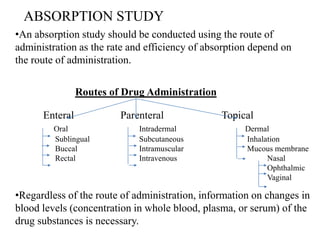
This document discusses factors that affect drug absorption and methods for conducting absorption studies. It defines absorption as a drug crossing a biological membrane from its site of administration into systemic circulation. Factors affecting absorption include drug properties like solubility and molecular size, as well as bodily factors like pH and disease state. Standard absorption studies involve giving subjects single or multiple doses of a drug and collecting blood, urine and other samples to determine pharmacokinetic parameters and evaluate absorption. Key aspects of study design addressed are subject selection, sample collection schedule, and parameters measured like bioavailability and absorption rate.