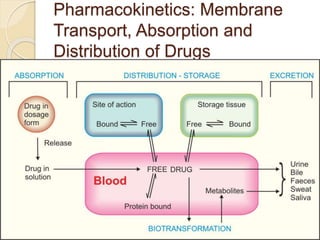
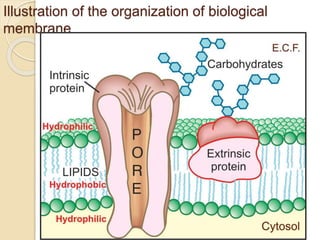
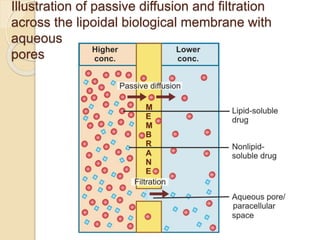
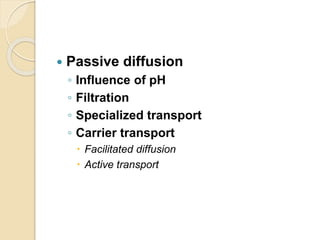
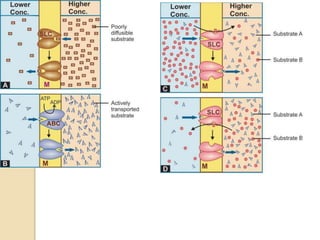
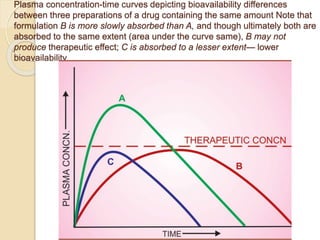
This document discusses pharmacokinetics, which is the quantitative study of how drugs move through the body. It describes how drugs are transported across biological membranes via passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, or active transport. It then discusses absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs. Absorption is affected by factors like solubility, concentration, and route of administration. Distribution depends on lipid solubility, protein binding, and regional blood flow. Drugs undergo biotransformation primarily in the liver and are metabolized to inactive or active forms. Excretion occurs primarily through urine or feces, with some drugs excreted in sweat, saliva, exhaled air, or milk.