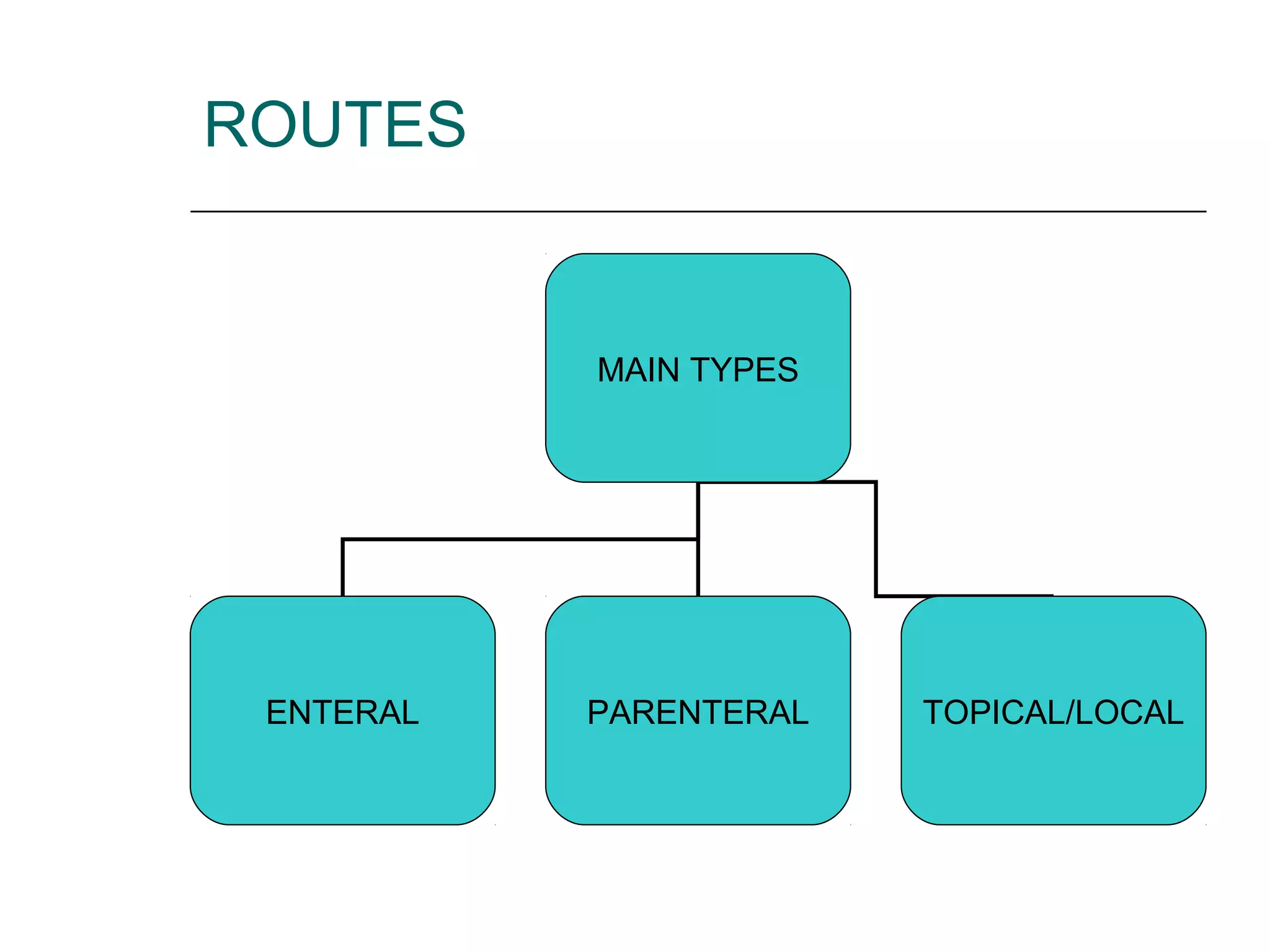
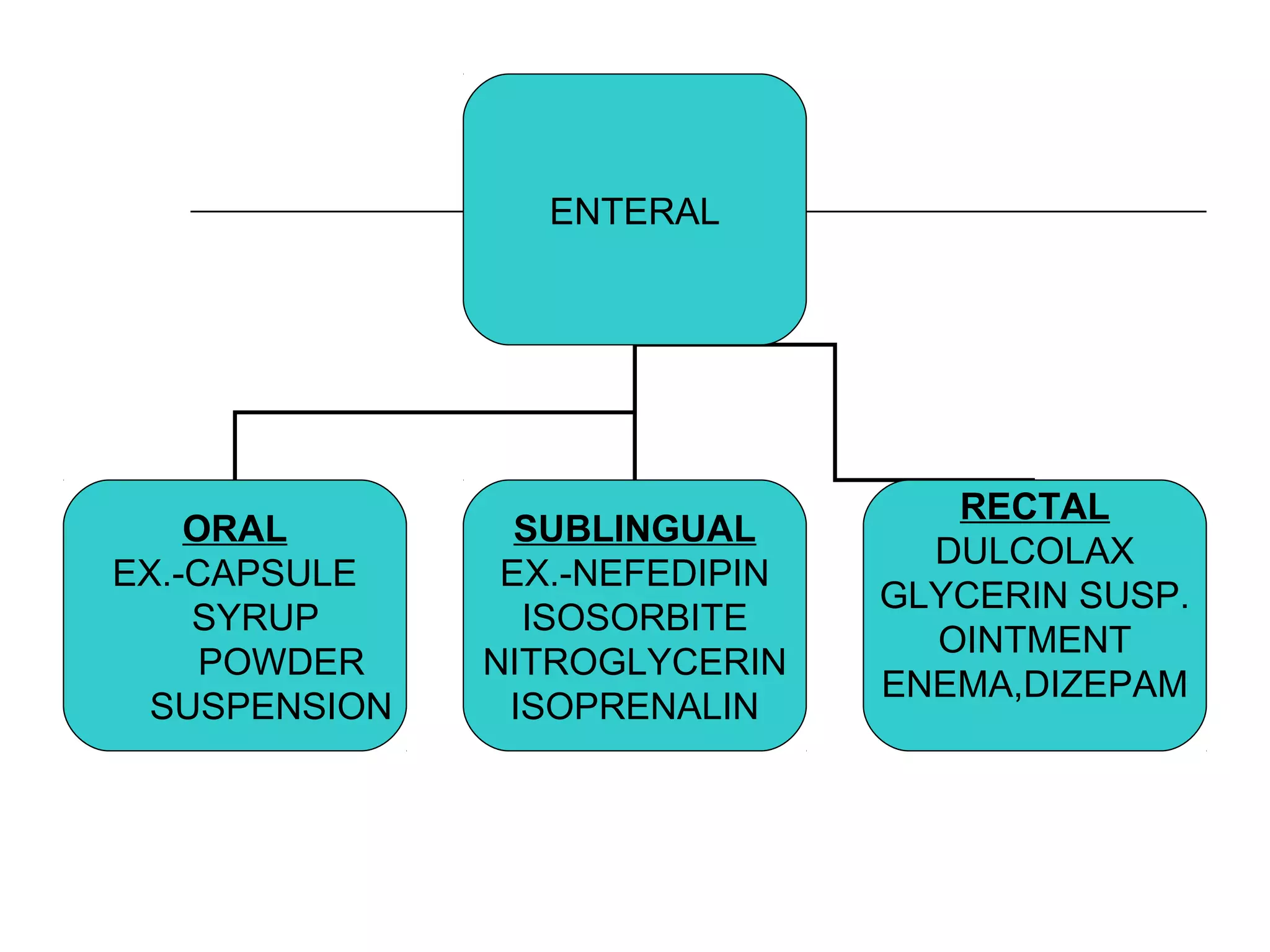
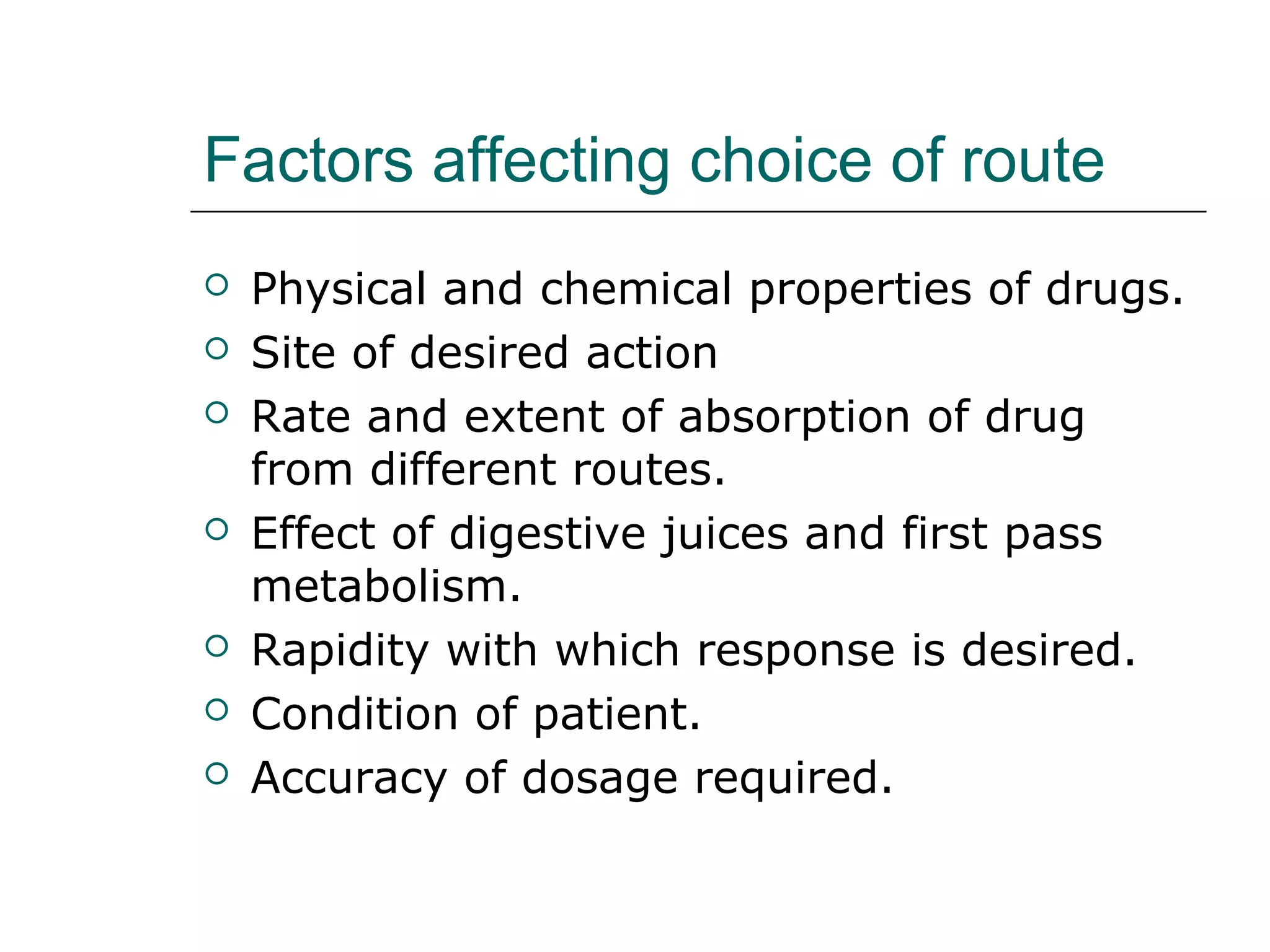
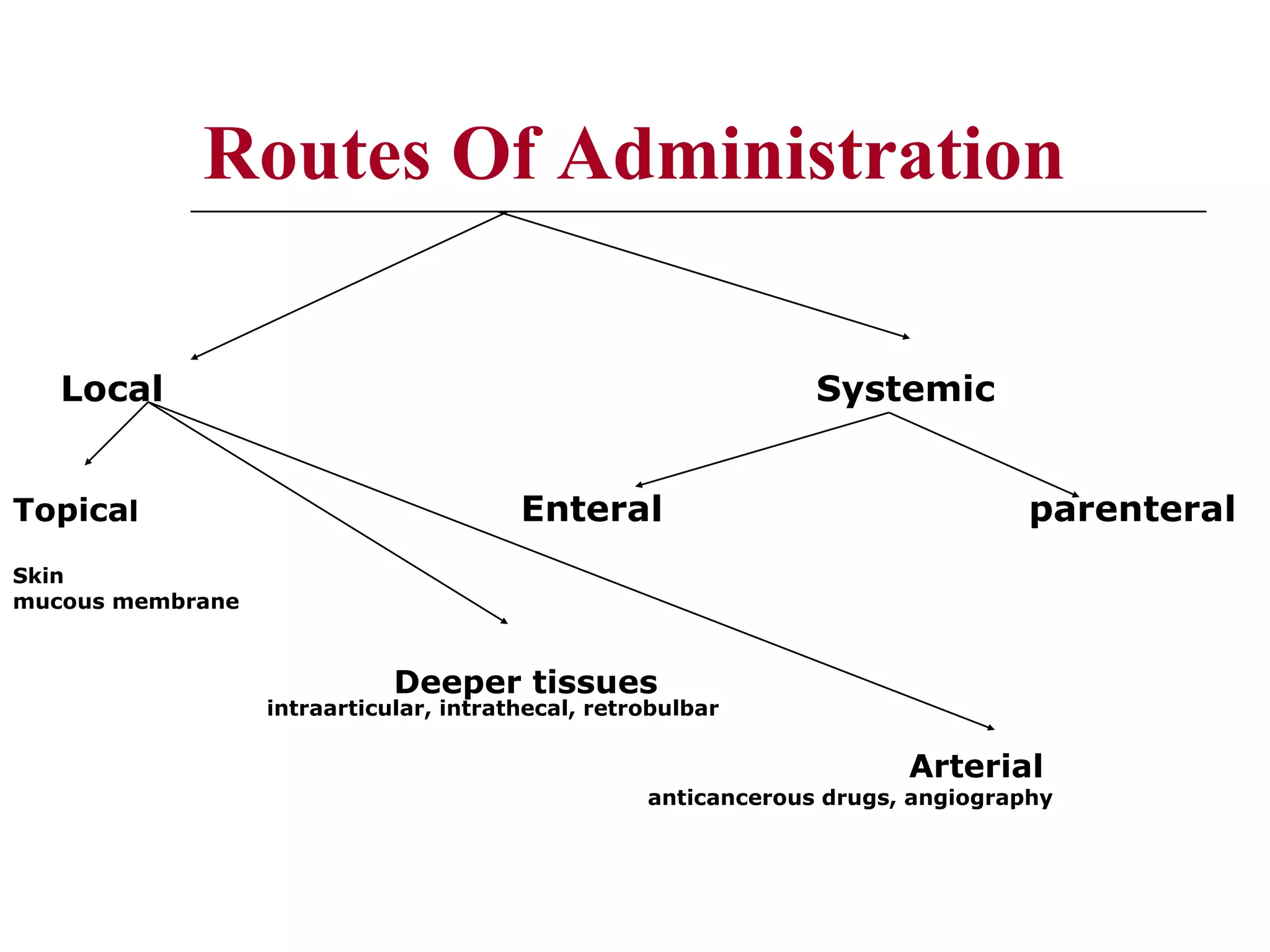
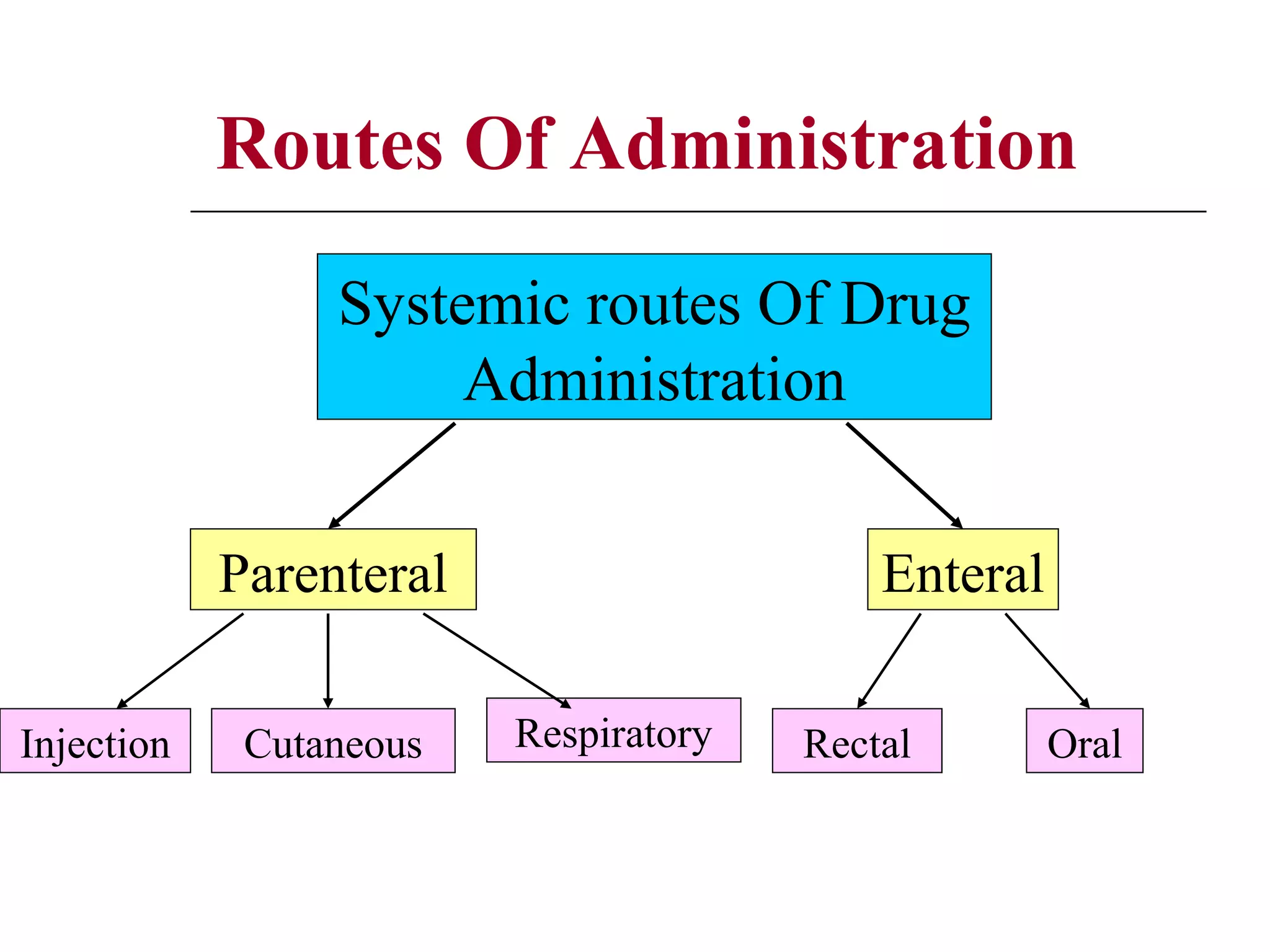
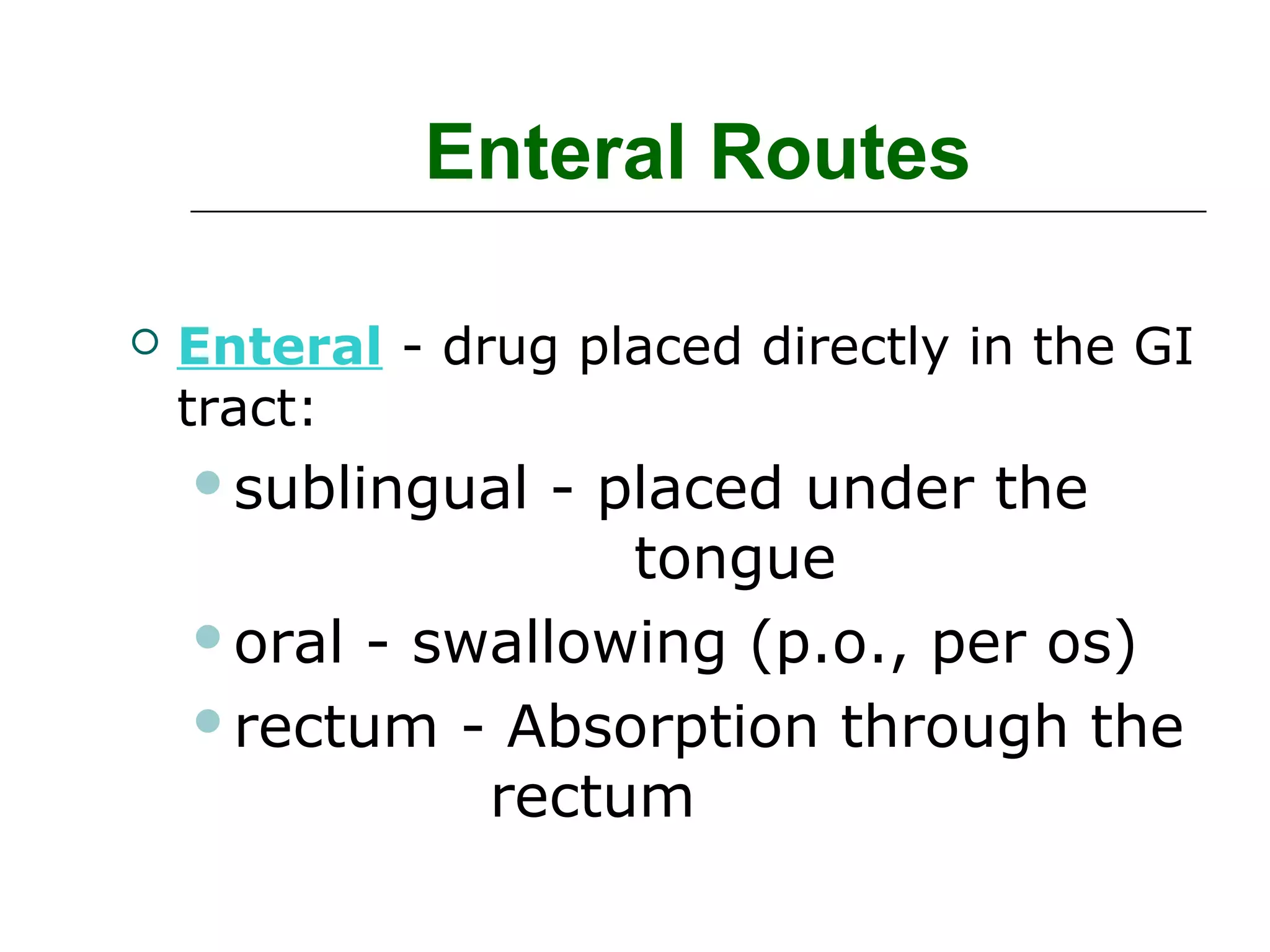
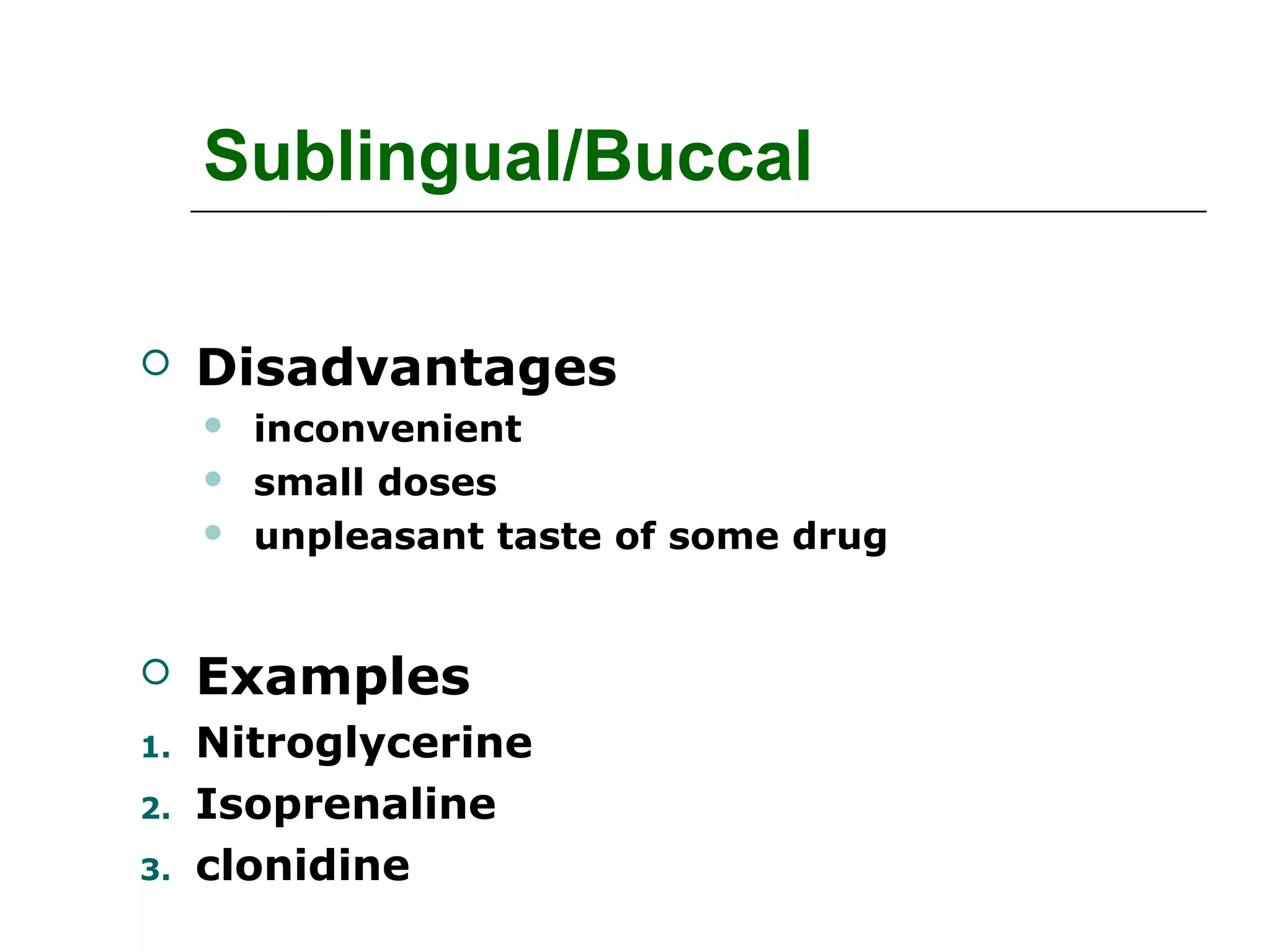
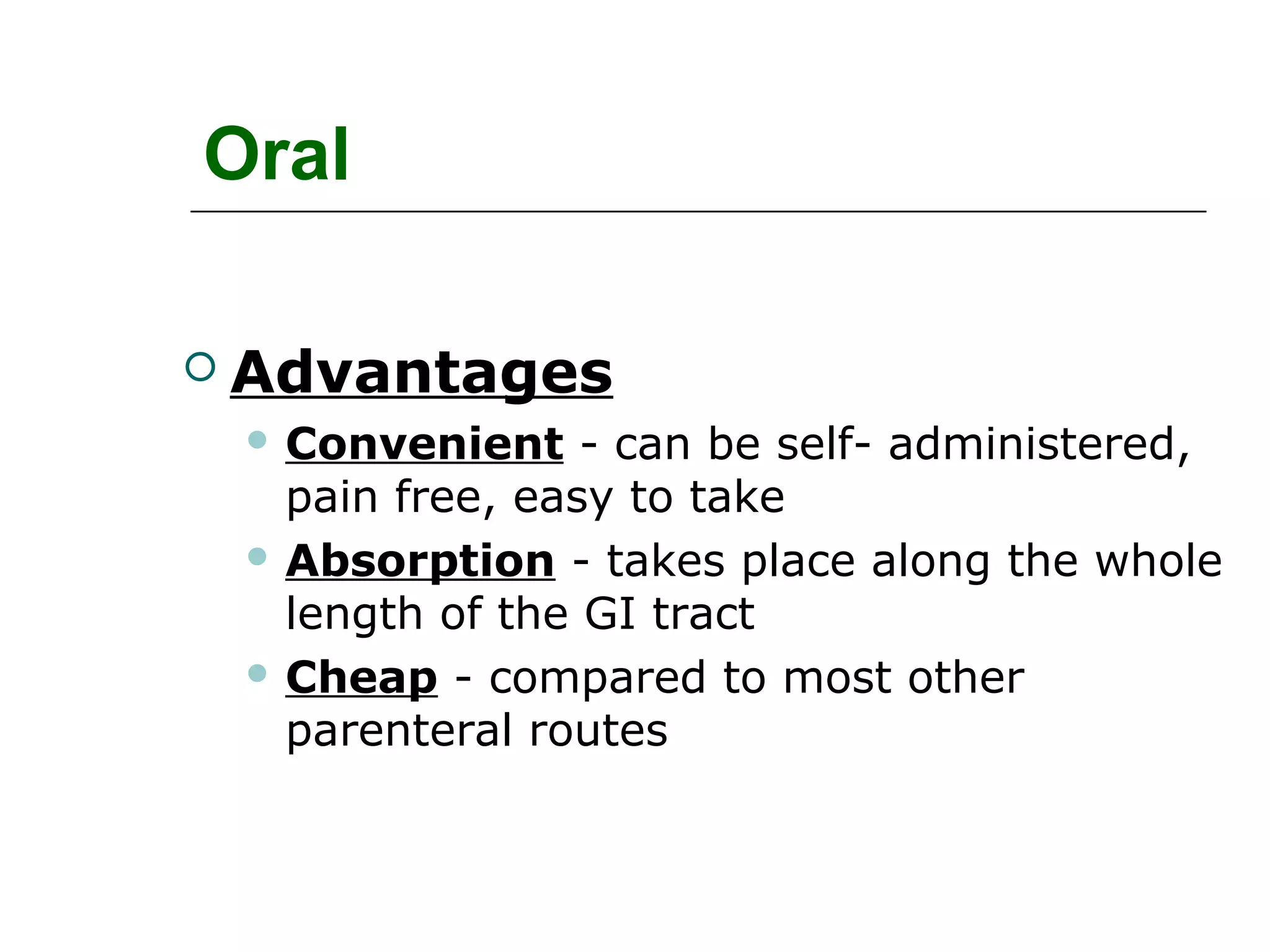
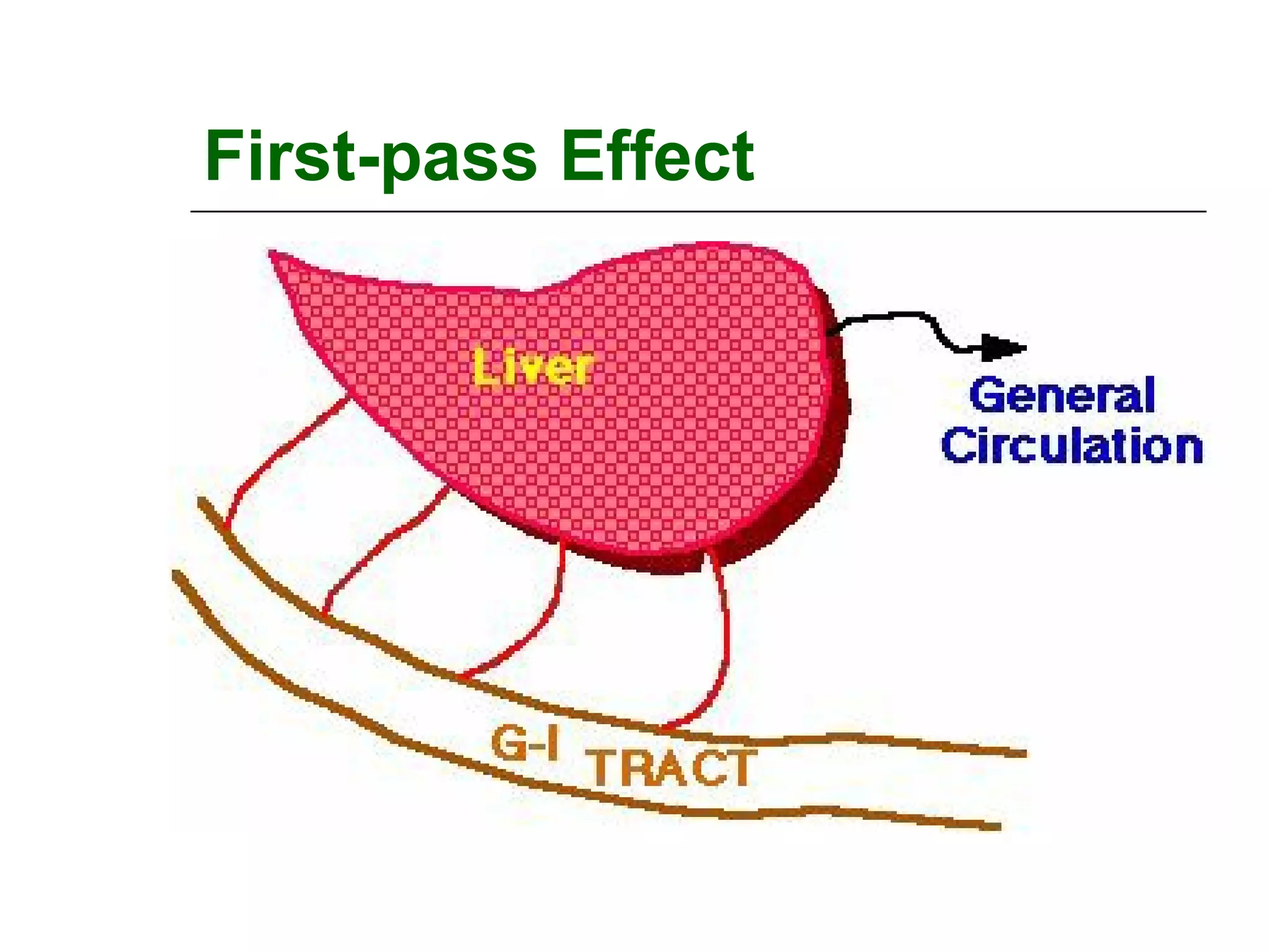
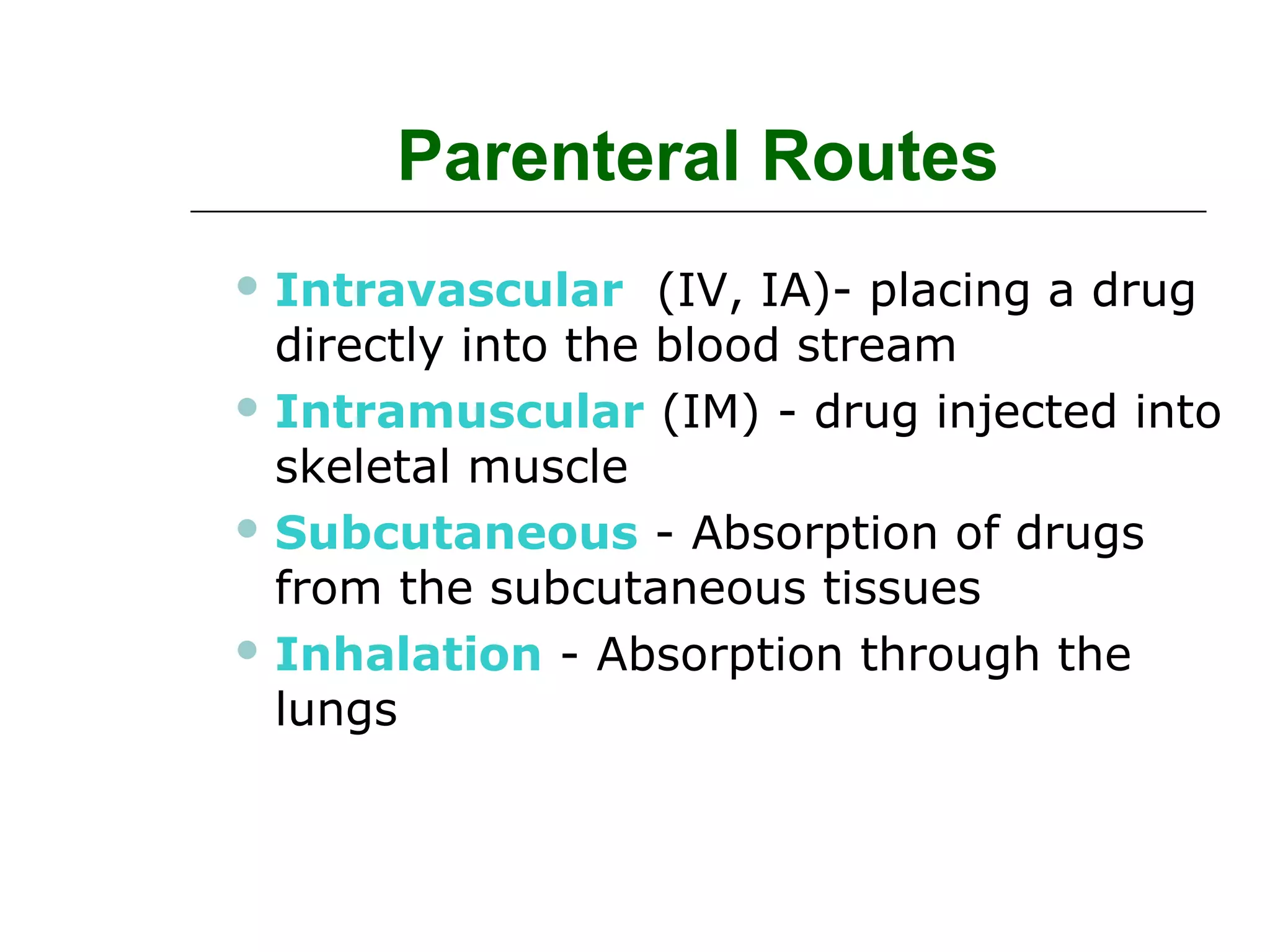
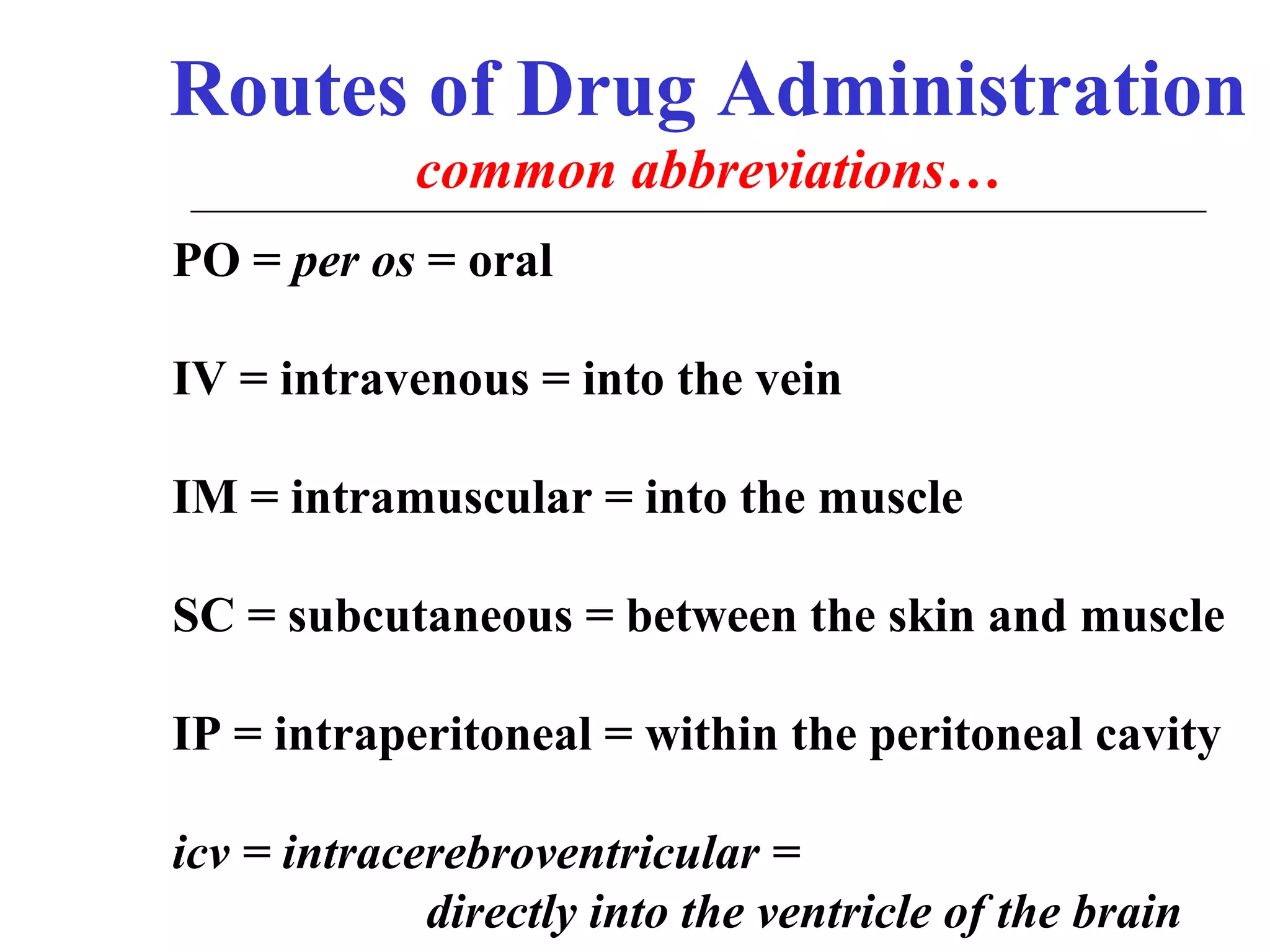
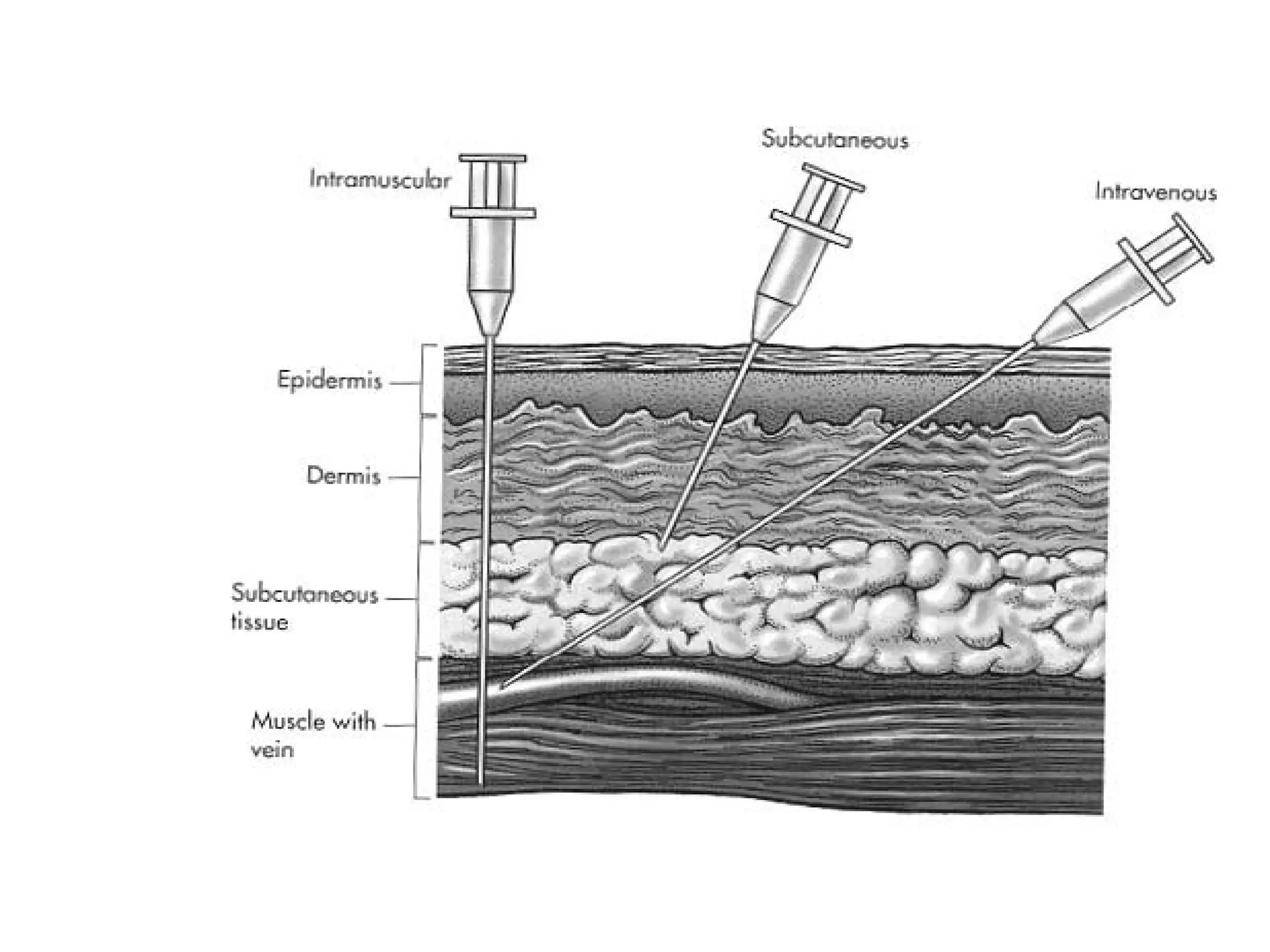
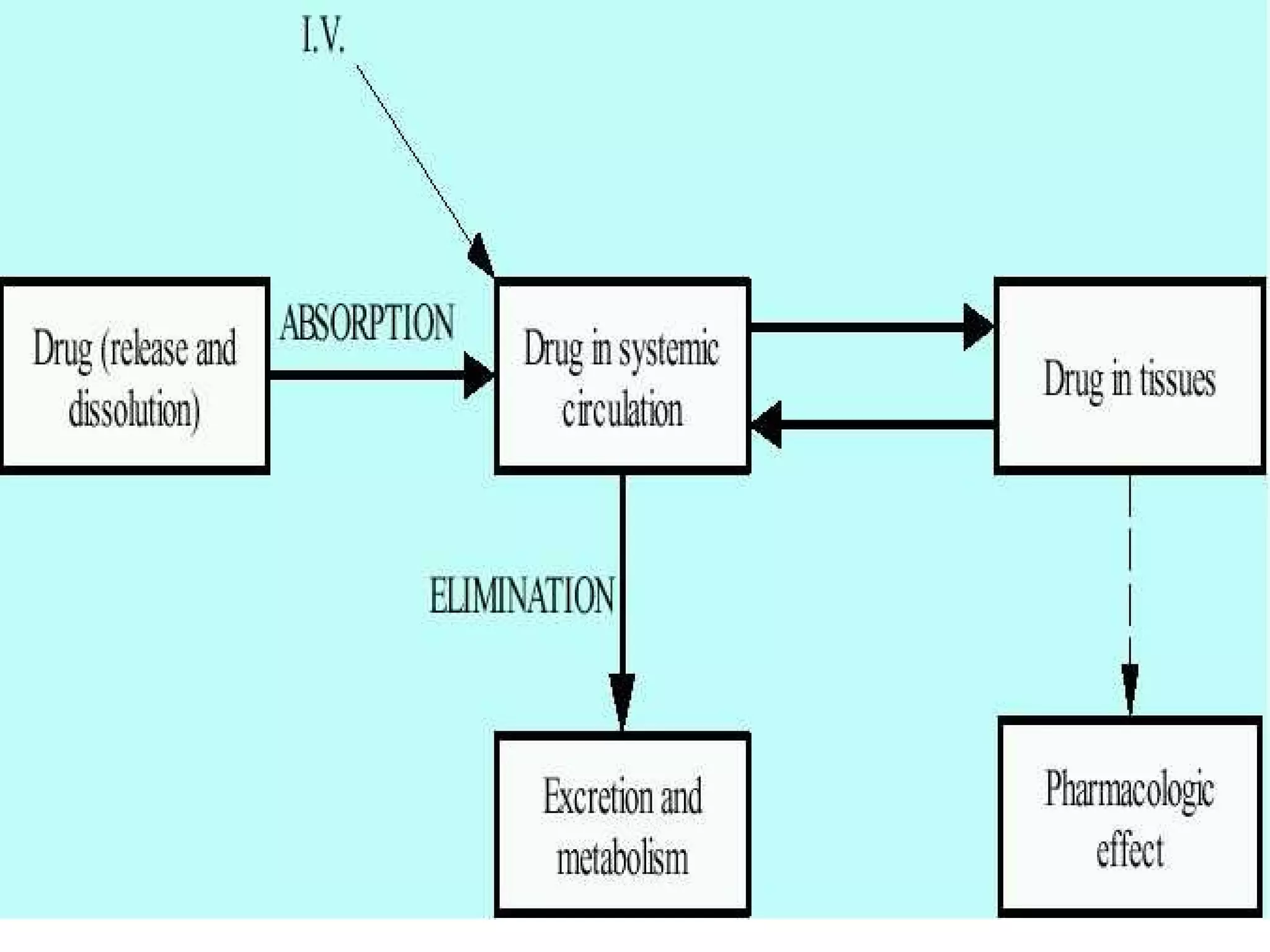
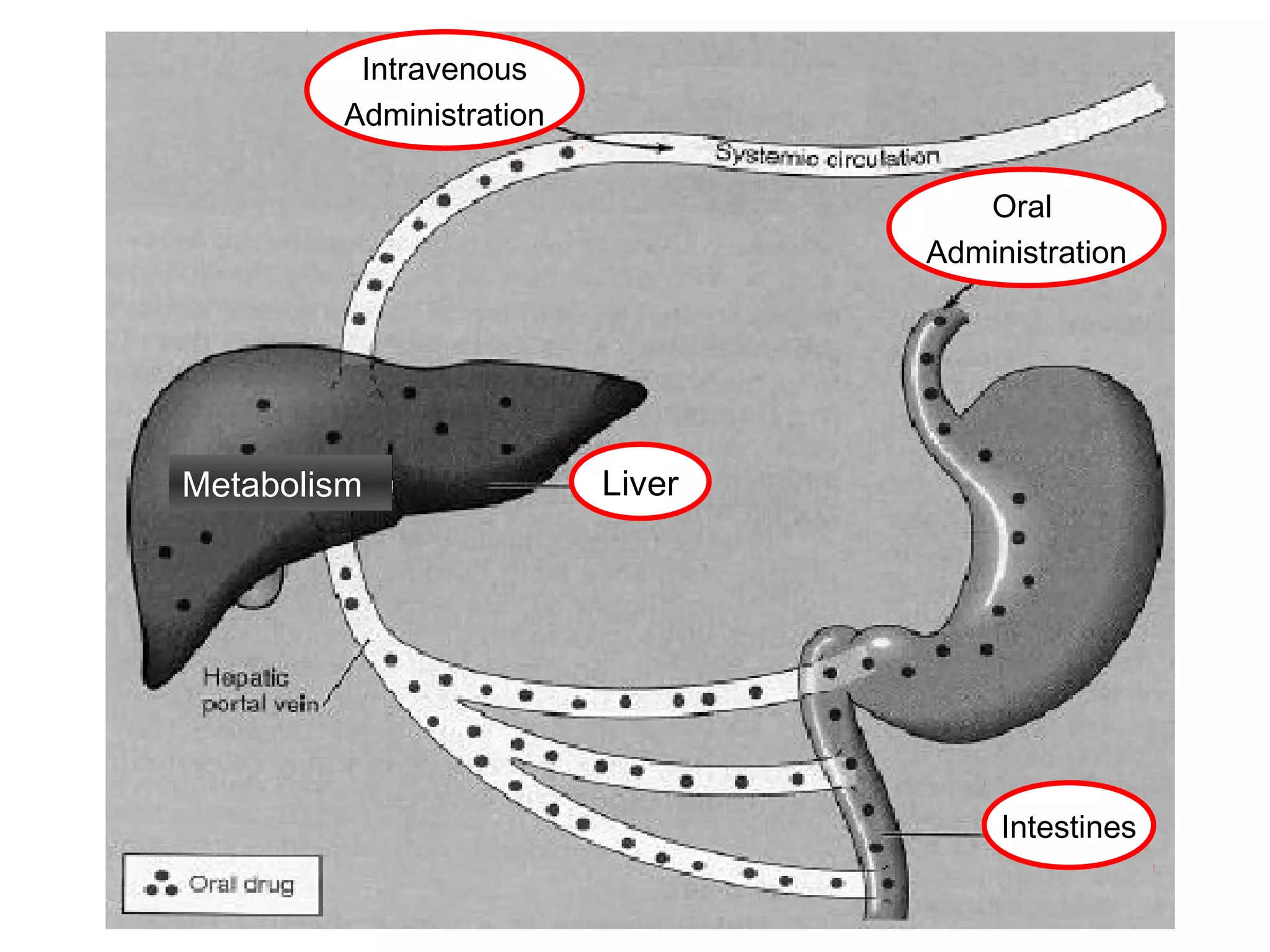
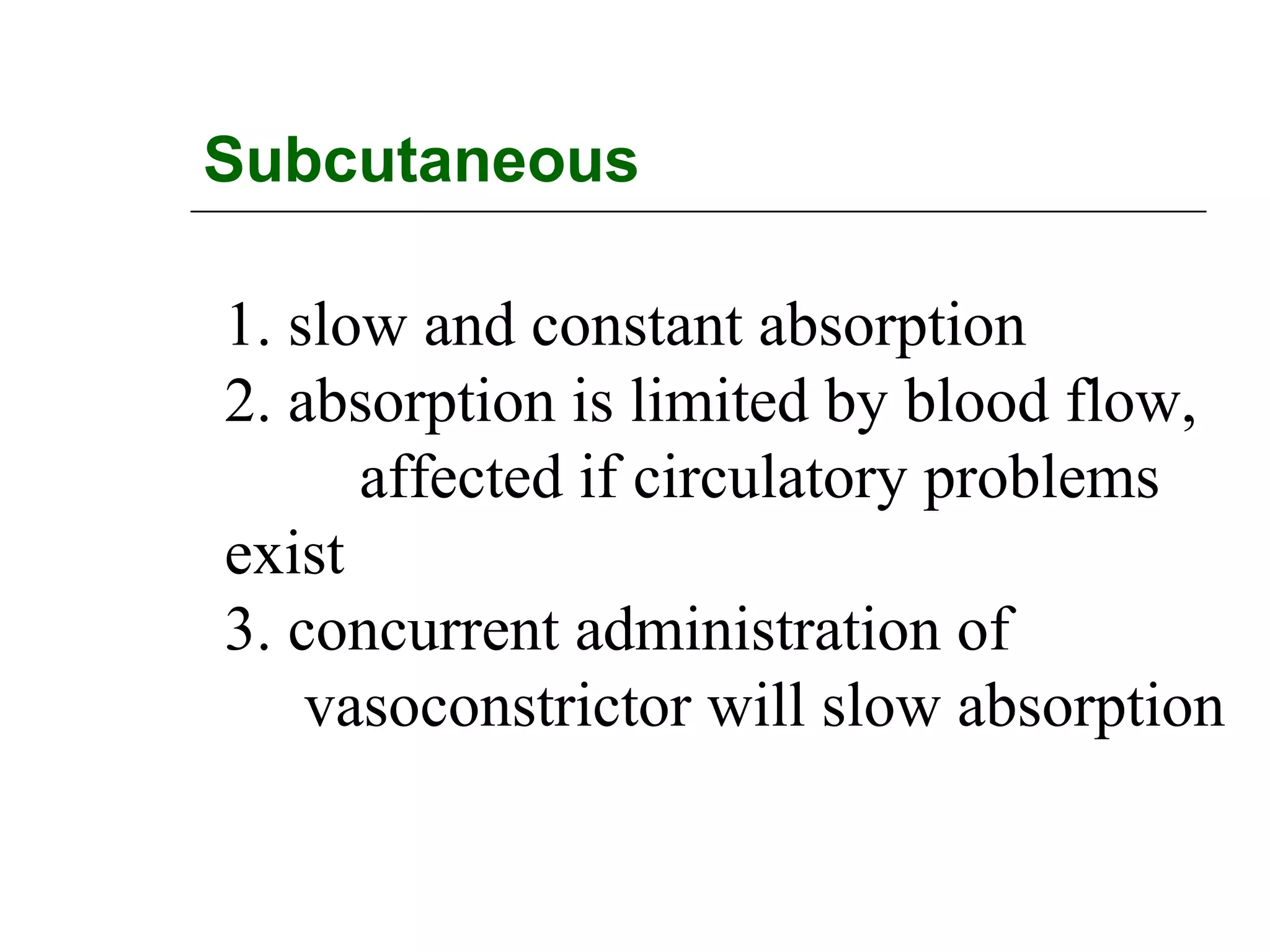
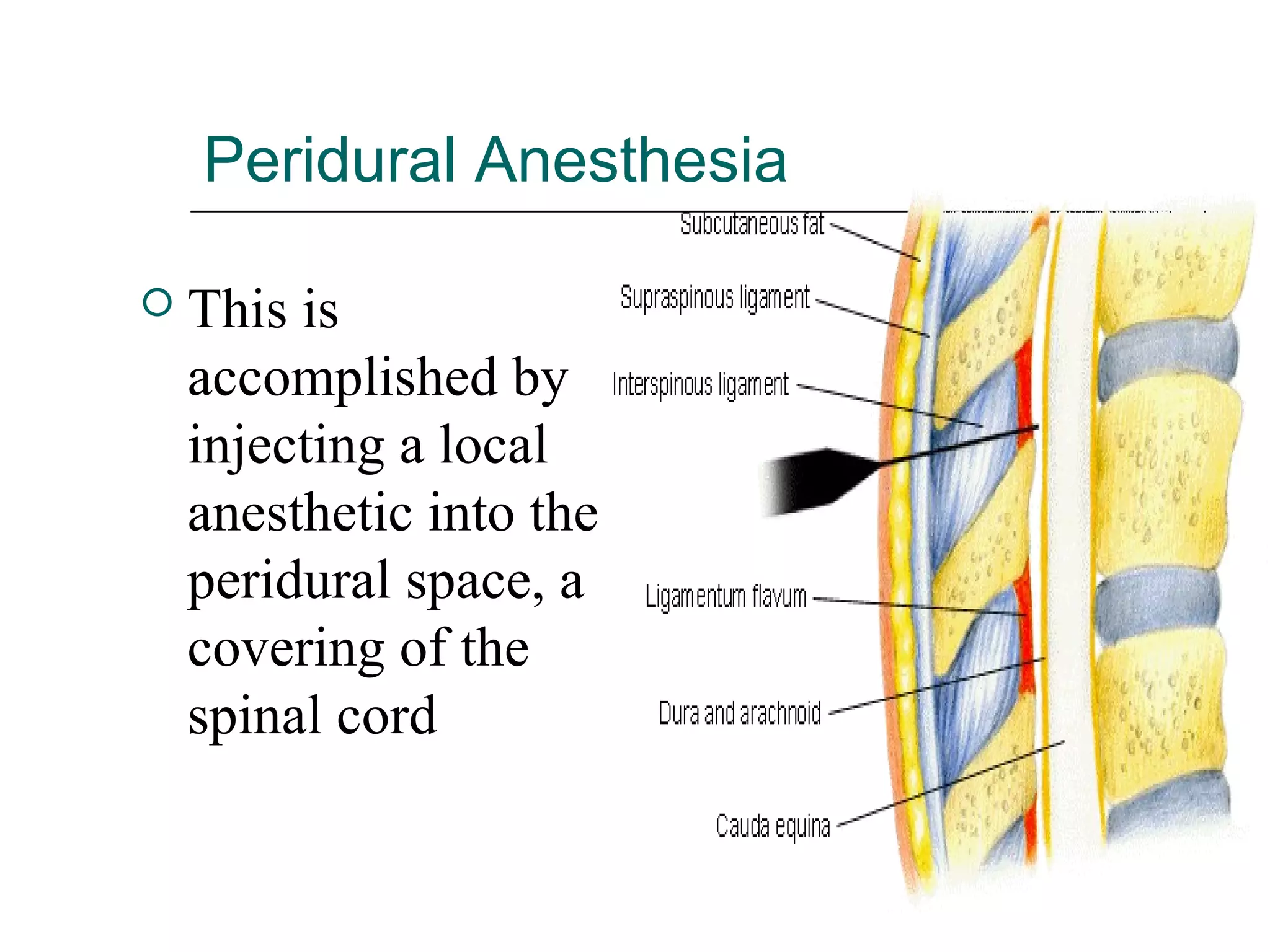
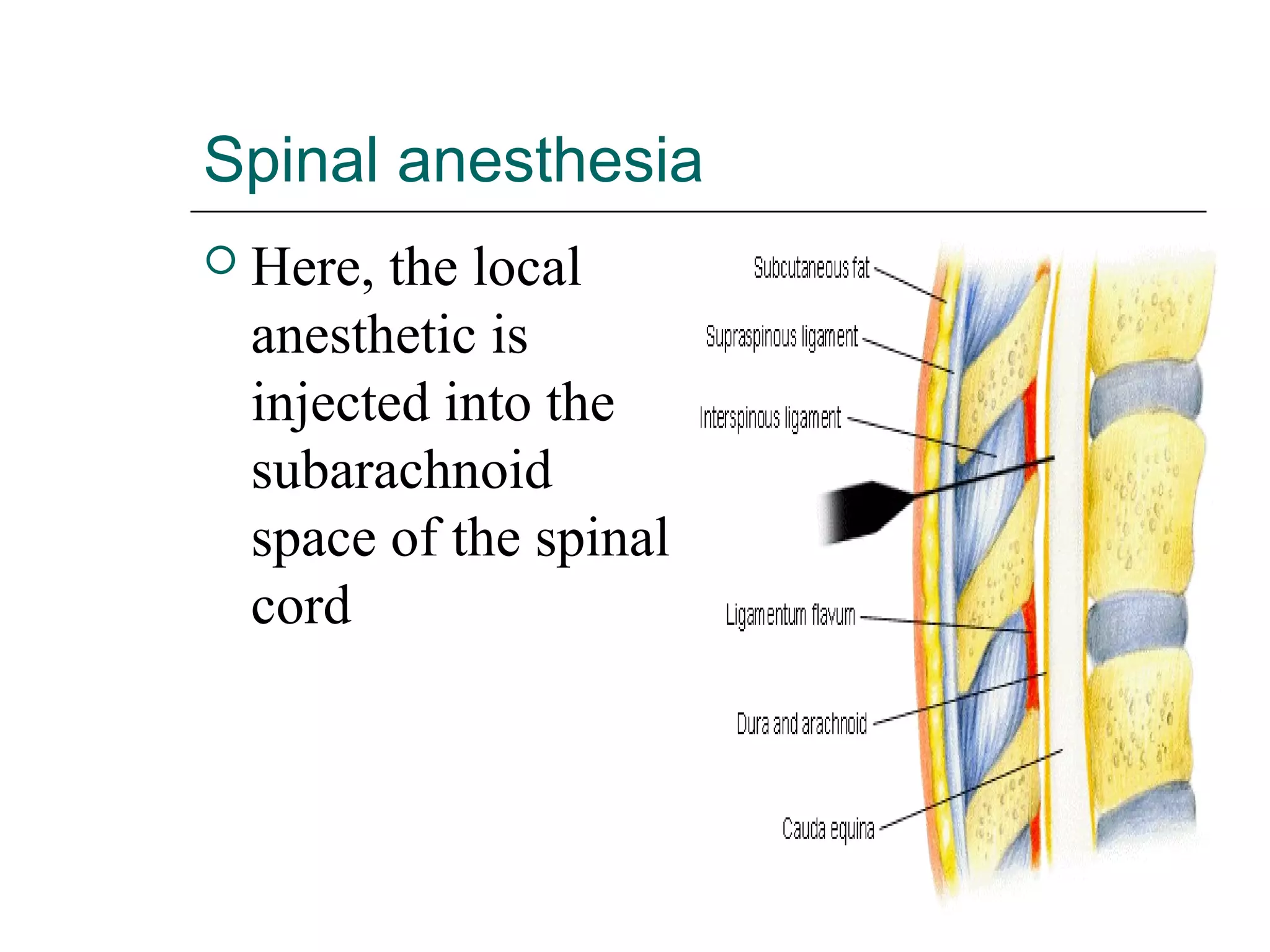
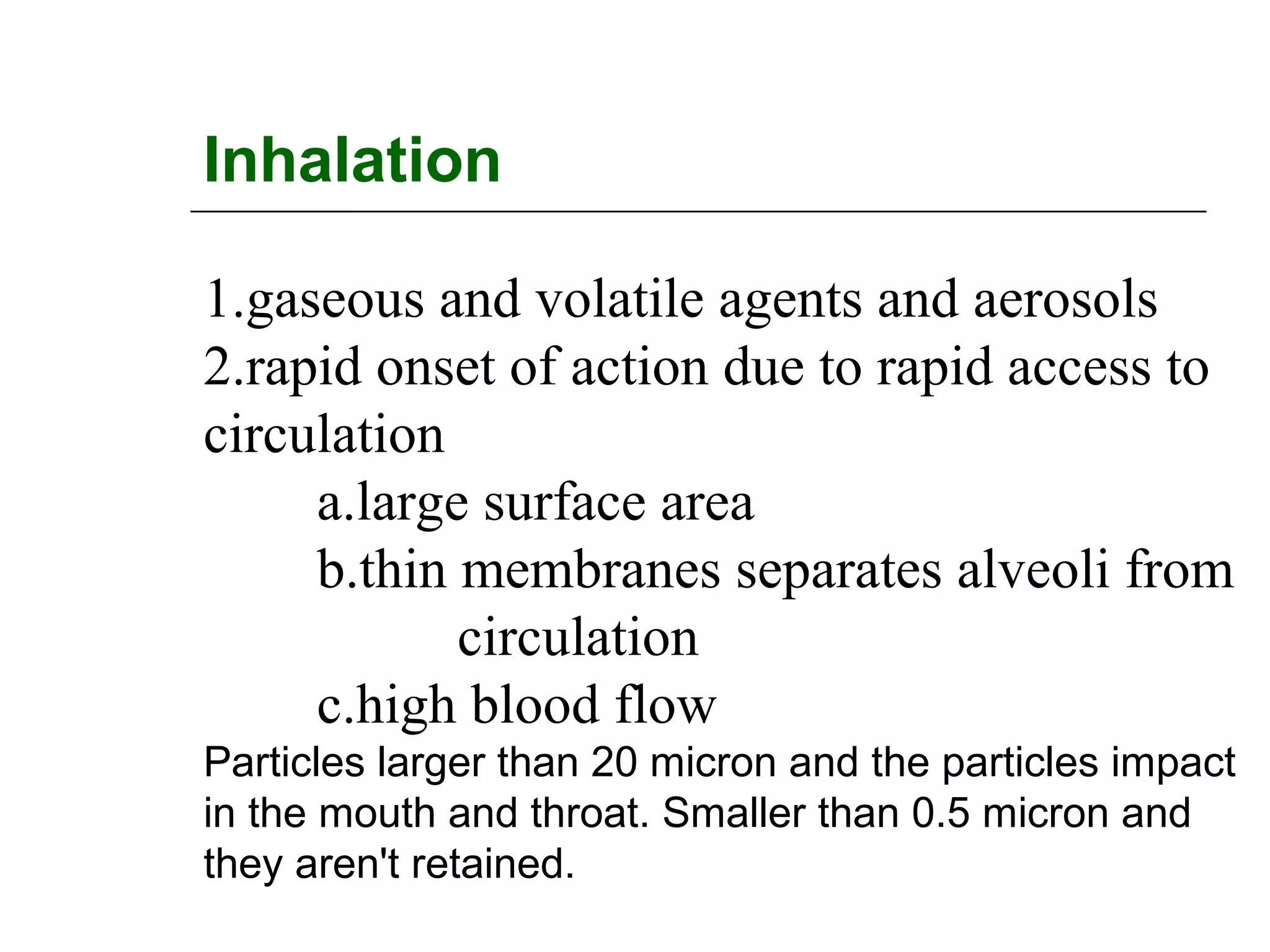
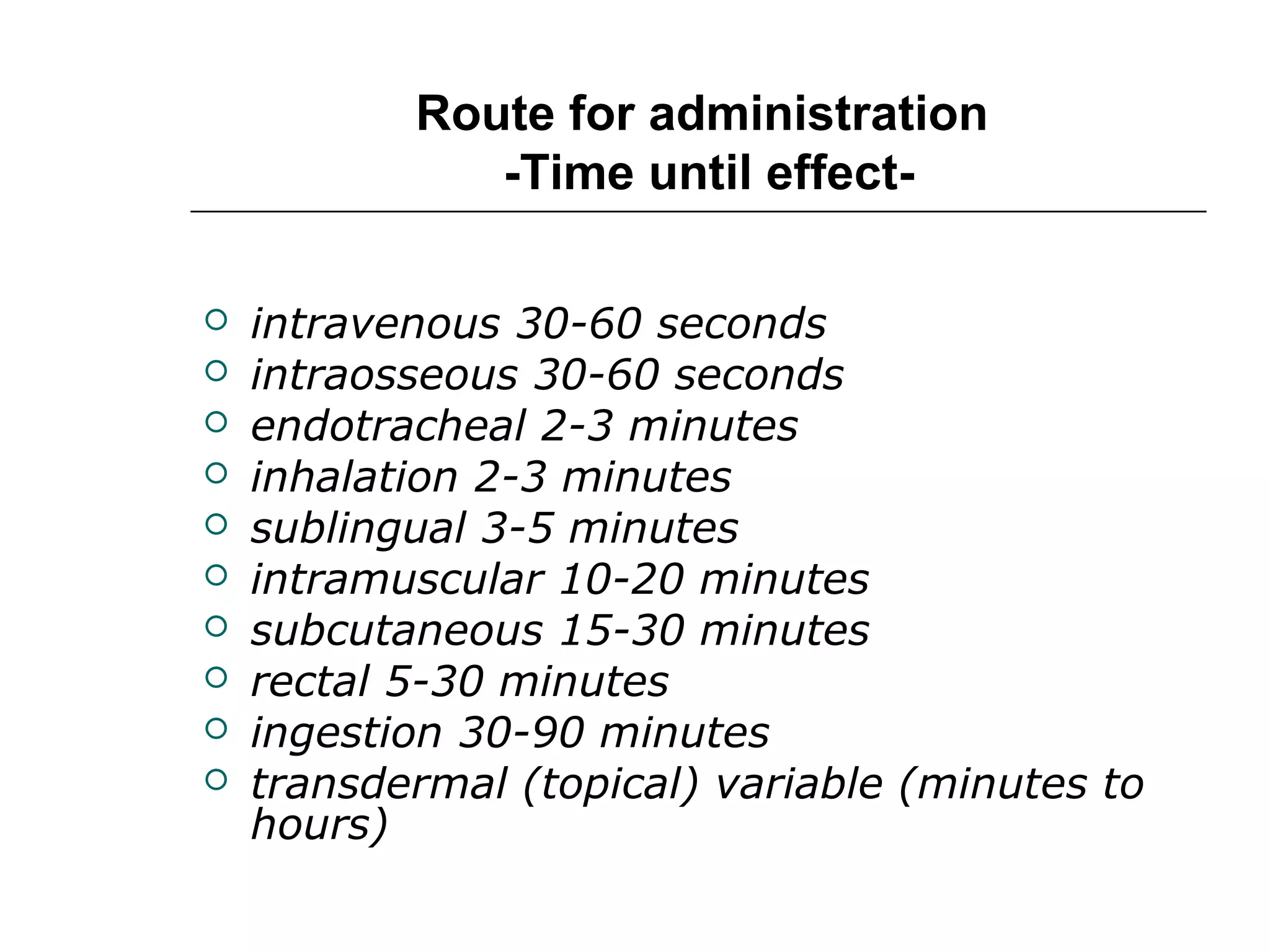
The document discusses the various routes of drug administration which can be divided into enteral and parenteral routes. Enteral routes include oral, sublingual, and rectal while parenteral routes include intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, inhalation, and topical administration. The choice of route depends on factors like the drug's properties, desired effects, rate of absorption, stability, and patient condition. Parenteral routes bypass metabolism while enteral routes are subject to first-pass effect. Different routes provide variable onset of action from seconds to hours.