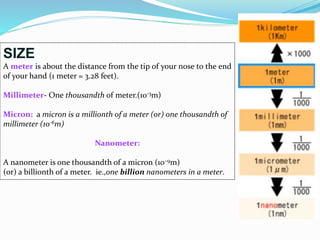
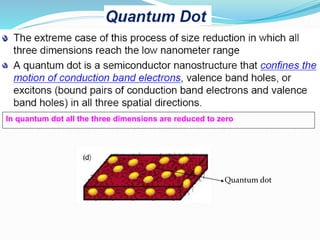
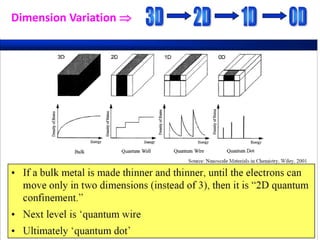
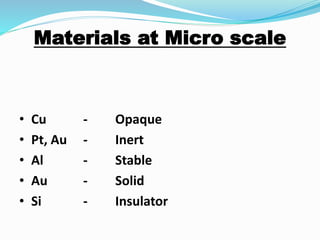
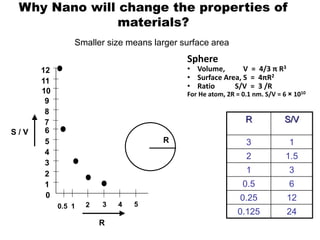
- Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter on the nanometer scale, which is 1 to 100 nanometers.
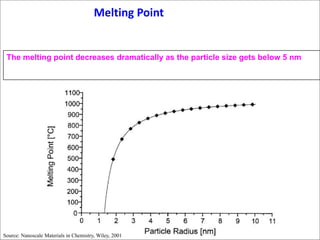
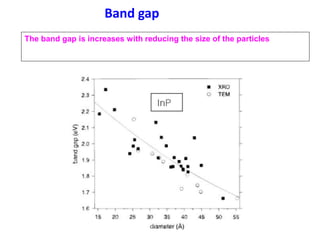
- At the nanoscale, the properties of materials can change dramatically and differ from the properties of macroscale materials. For example, metals can become stronger or change from opaque to transparent.
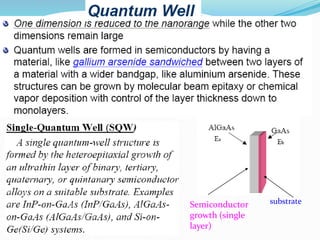
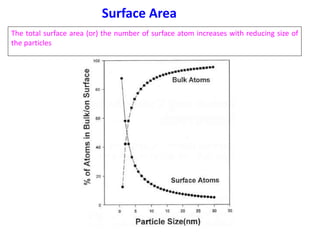
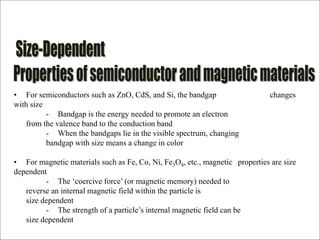
- The properties change due to increased surface area to volume ratio at the nanoscale and quantum effects dominating behavior. The increased surface area affects chemical reactivity, while quantum effects influence bandgap and magnetic properties.
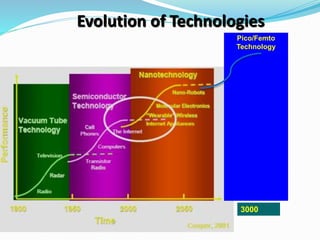
- Controlling materials at the nanoscale allows for designing new materials and systems with applications across many industries like optics, electronics, and biomedicine.