This document discusses motion in one dimension. It provides definitions and equations for position, velocity, and acceleration as functions of time and displacement. Position functions can be expressed as d(t), where d is displacement. Velocity is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time, and acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. The document presents examples of using these definitions and equations to analyze situations with constant displacement, velocity, or acceleration. It also discusses simple harmonic motion and free-fall motion under constant acceleration due to gravity.






![Rates of change
• Note that:
–Displacement’s rate of change is
measured by …
• Velocity (d/t=v) [d’(t)]
–Velocity’s rate of change is measured by
…
• Acceleration (v/t=a) [d’’(t)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2b-170330040308/75/2b-motion-in-one-dimension-7-2048.jpg)
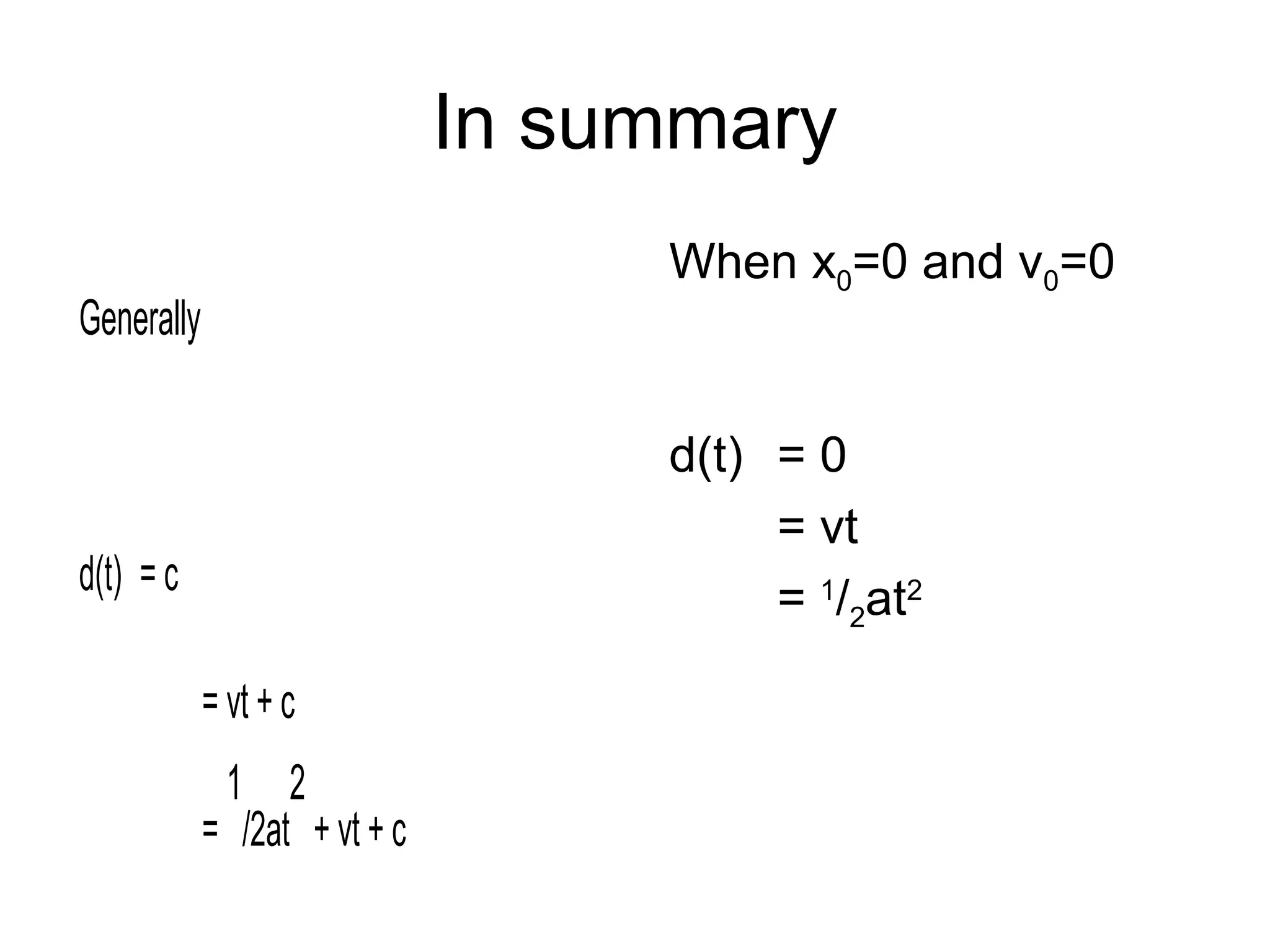
![Back to position functions
d(t) = c
d’(t) = v
d’’(t) = a
d(t) = [d’(t)].dt = v.dt = vt + c
v(t) = [v’(t)].dt = a.dt = at + c
1 2
(what do ‘c’ and ‘d’ represent?)
(‘d’ think of a light rail between stations)
(‘c’ why don’t supersonic jets shoot themselves down?)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2b-170330040308/75/2b-motion-in-one-dimension-8-2048.jpg)