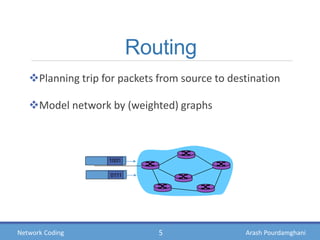
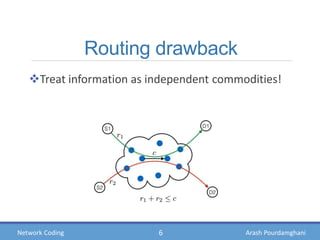
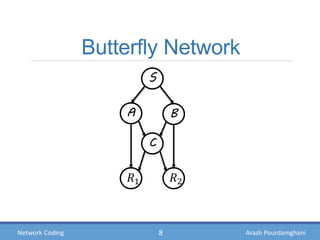
This document provides an introduction to network coding, including:
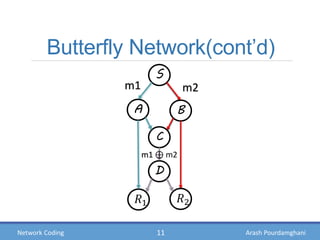
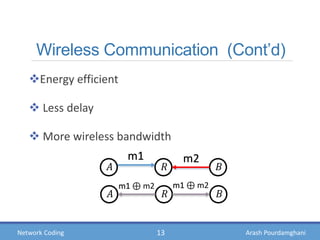
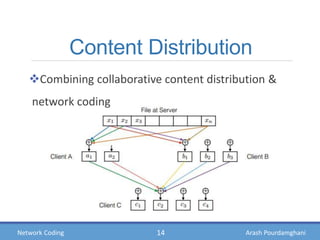
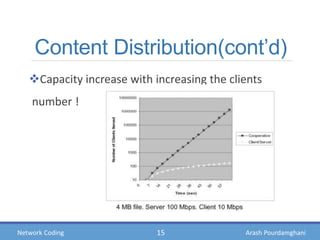
- Examples of how network coding can increase throughput in butterfly networks and wireless communications
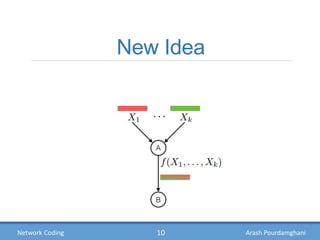
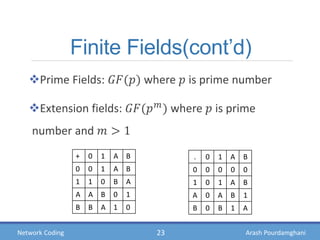
- Theories showing how intermediate nodes can linearly combine information to deliver data at the maximum possible rate
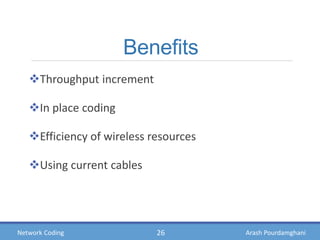
- Benefits of network coding like increased throughput and efficiency, but also challenges like integrating it into existing infrastructure