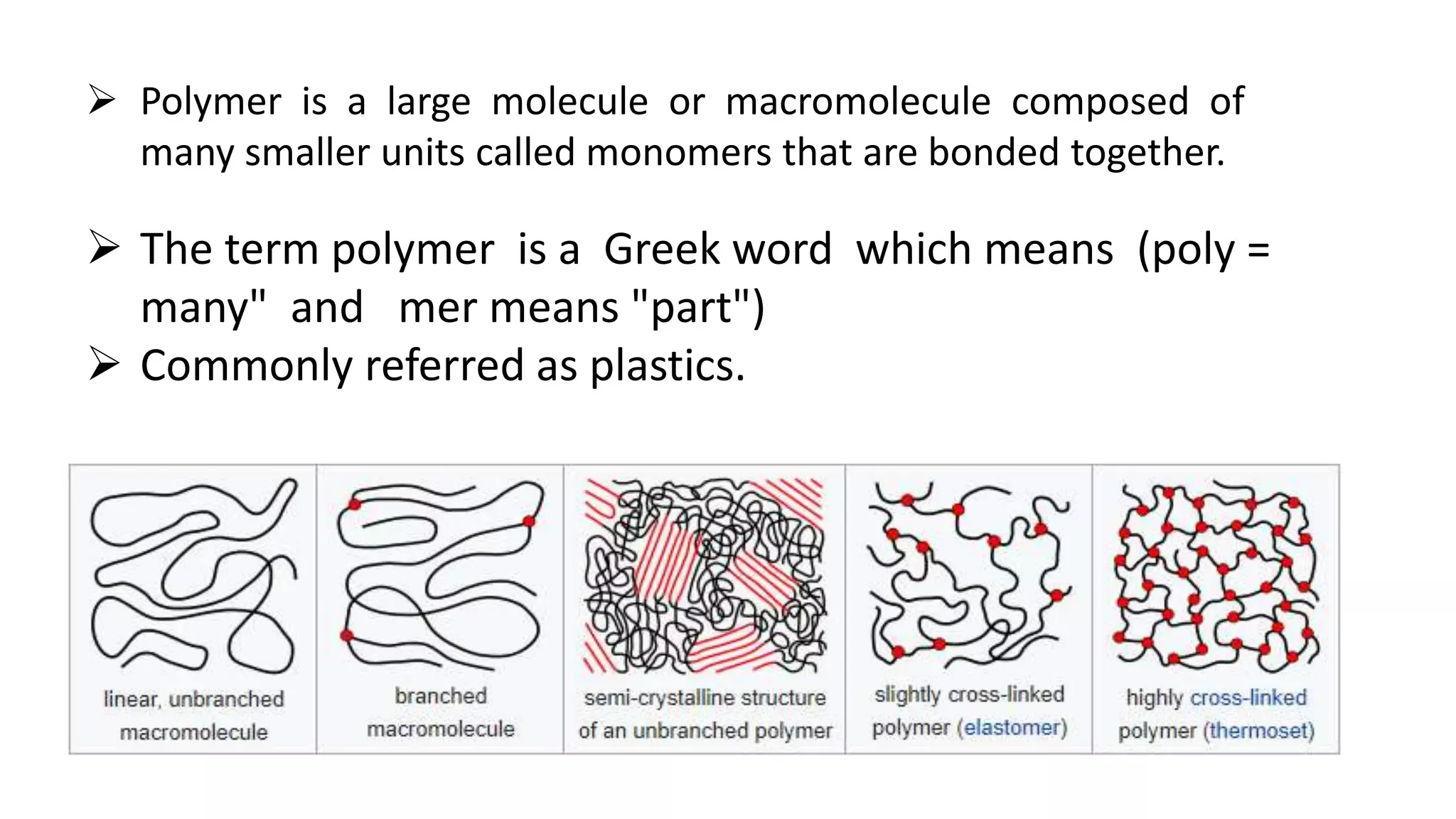
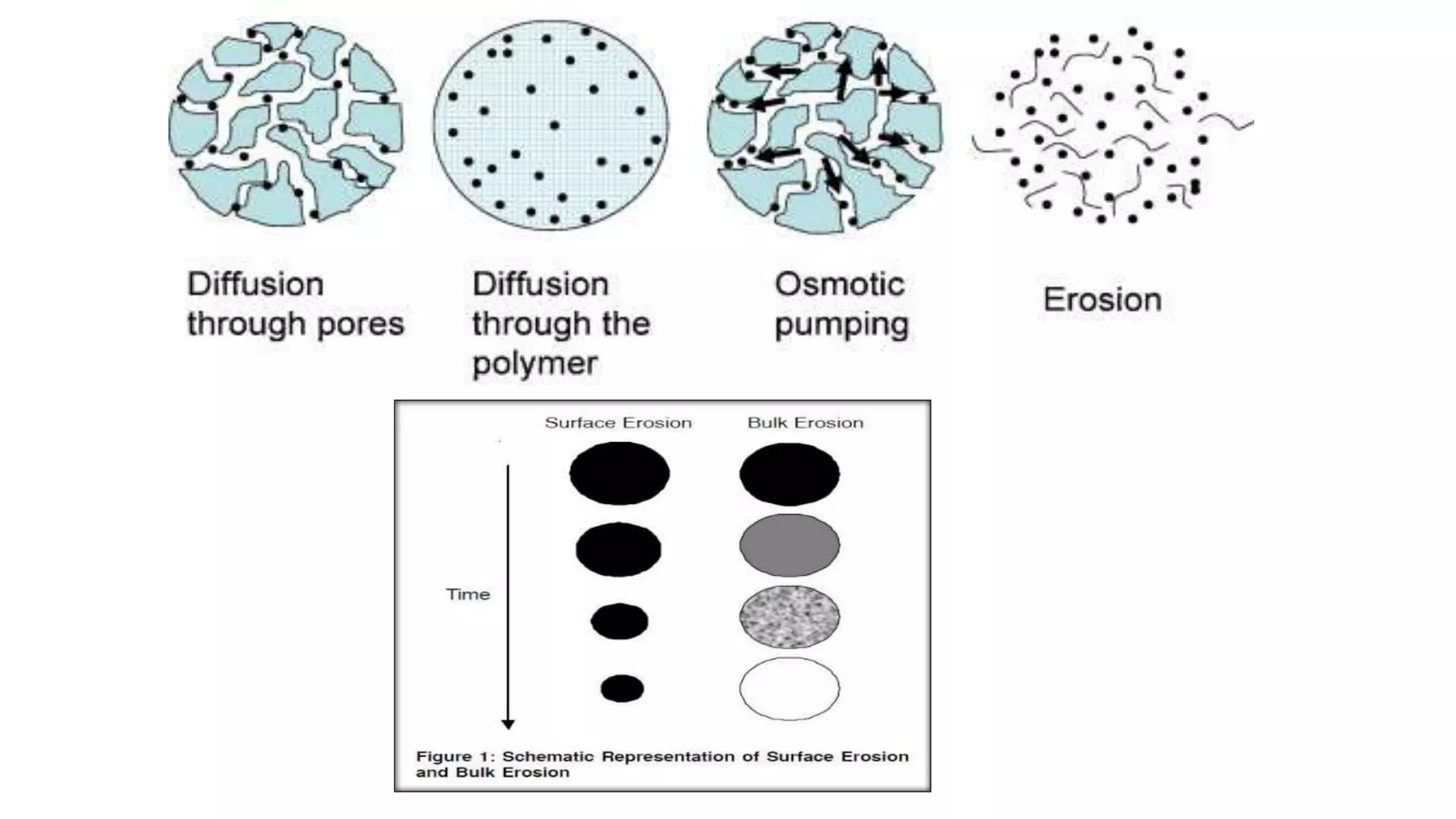
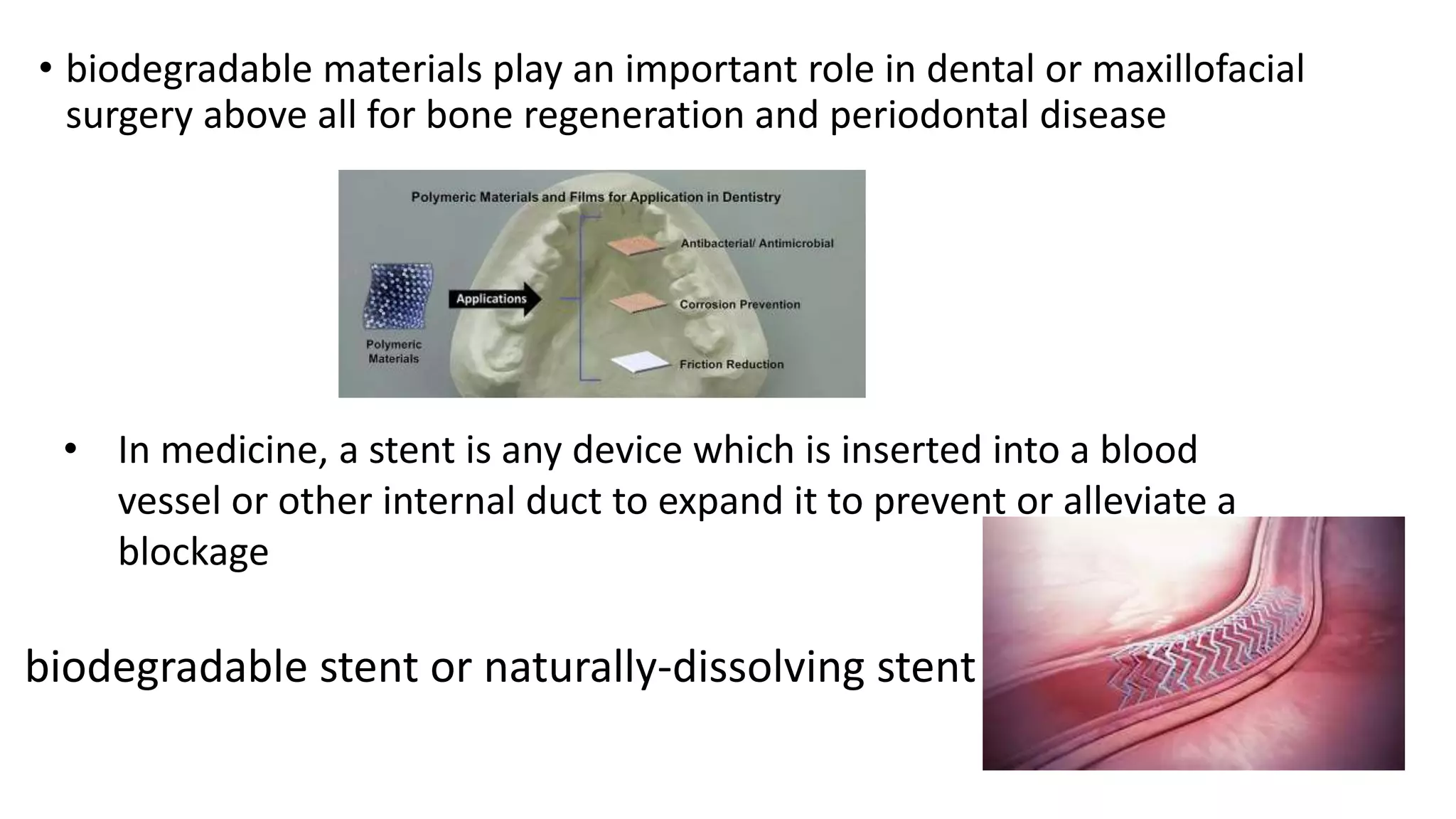
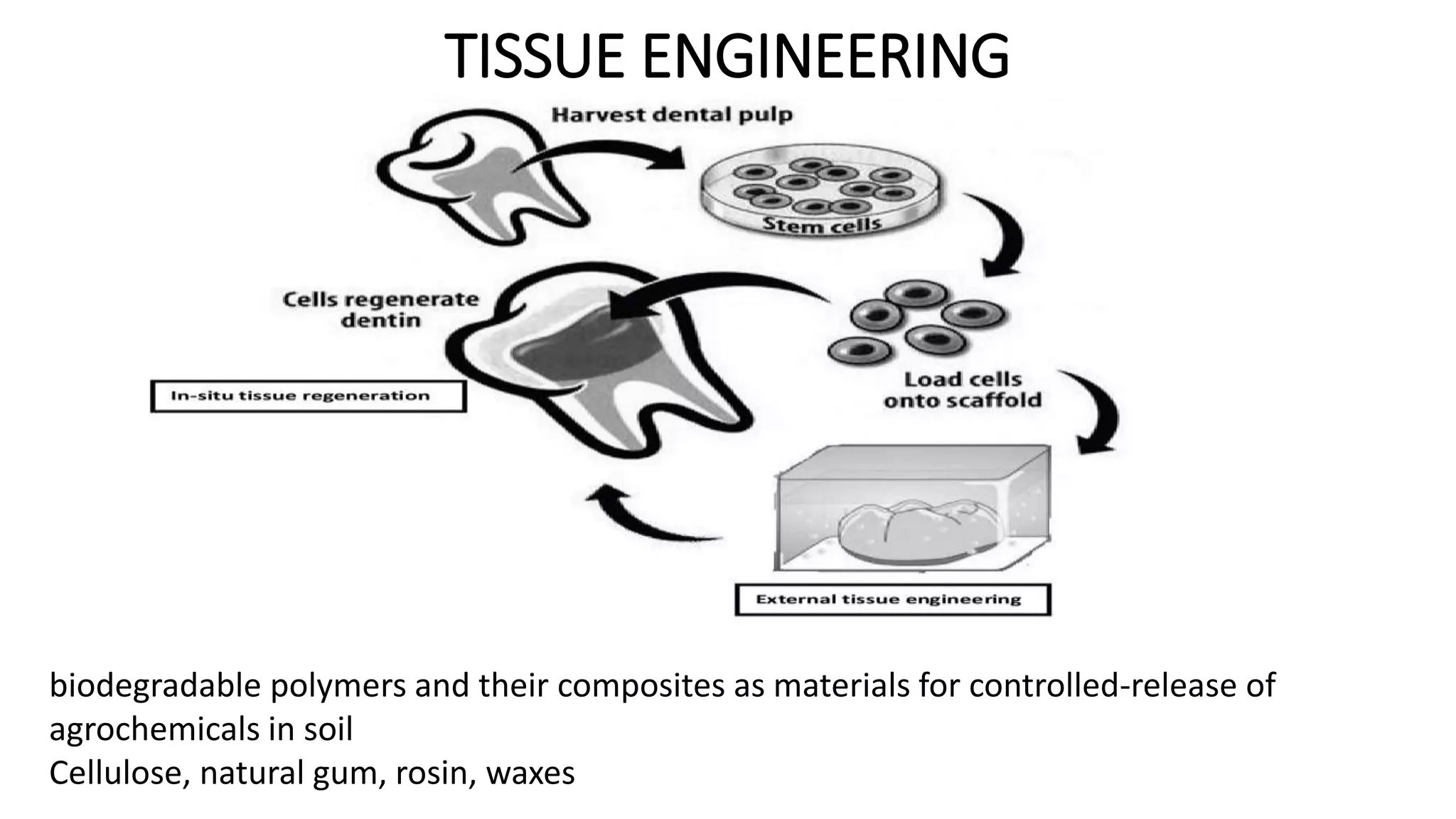
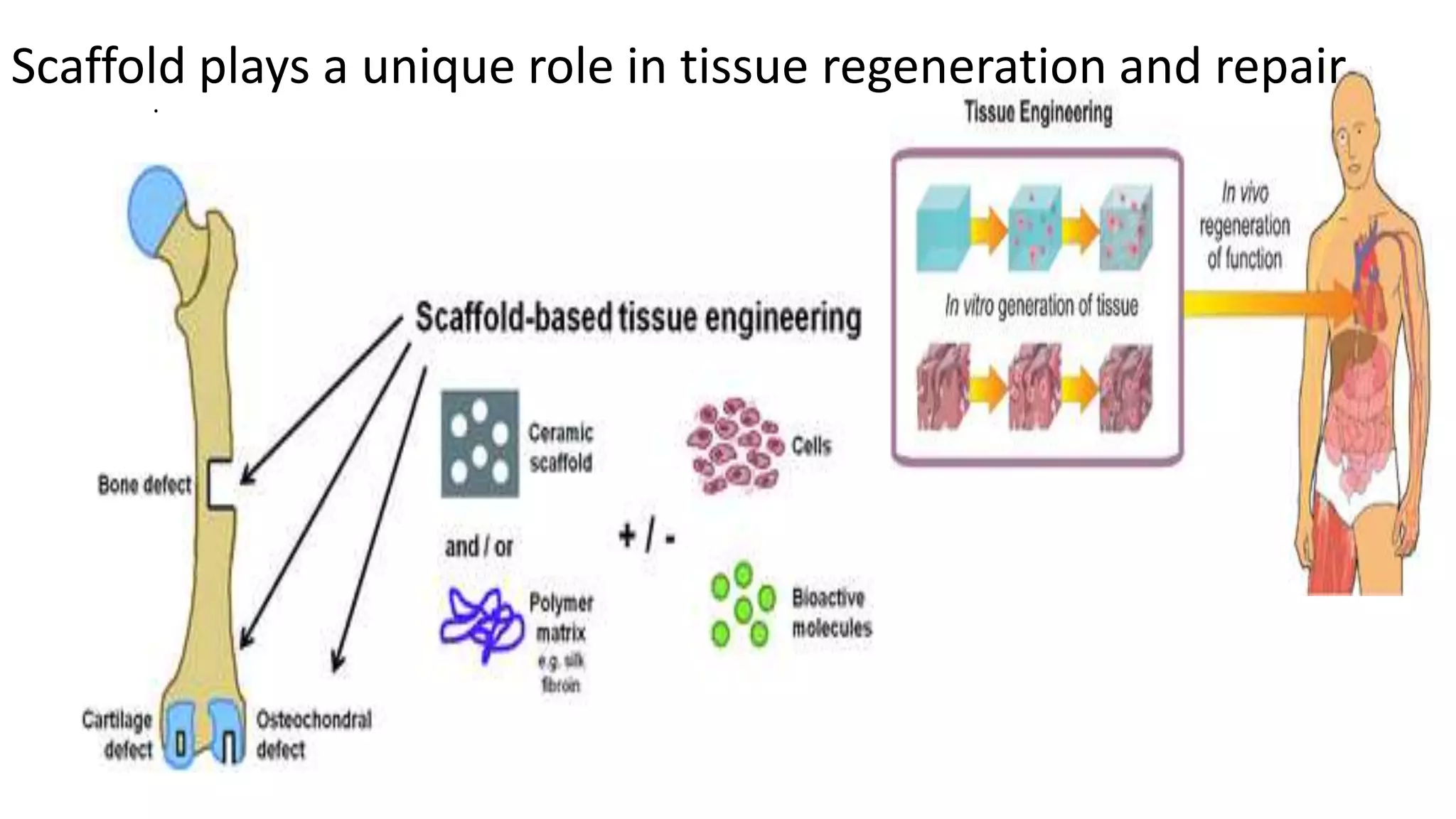
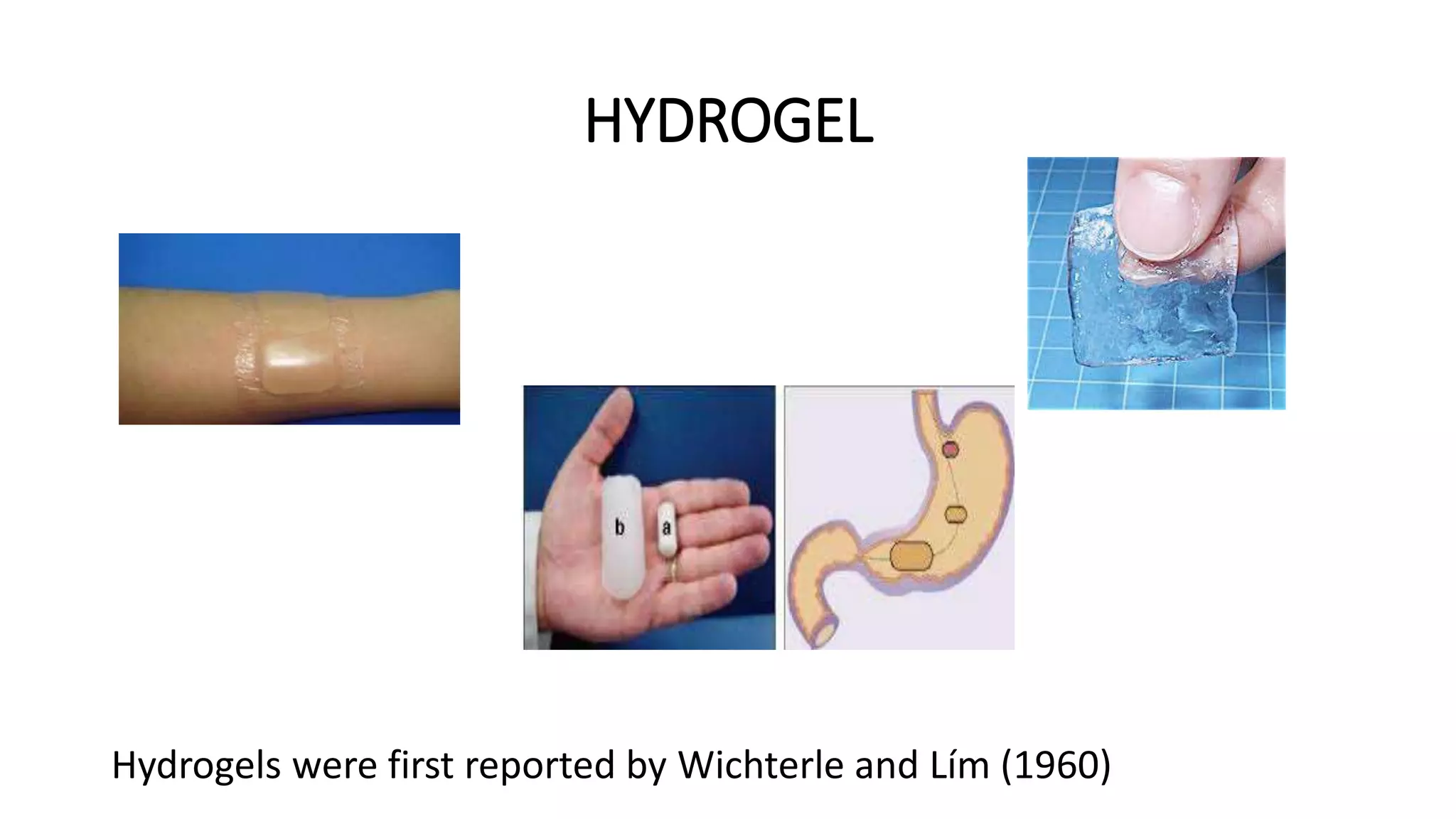
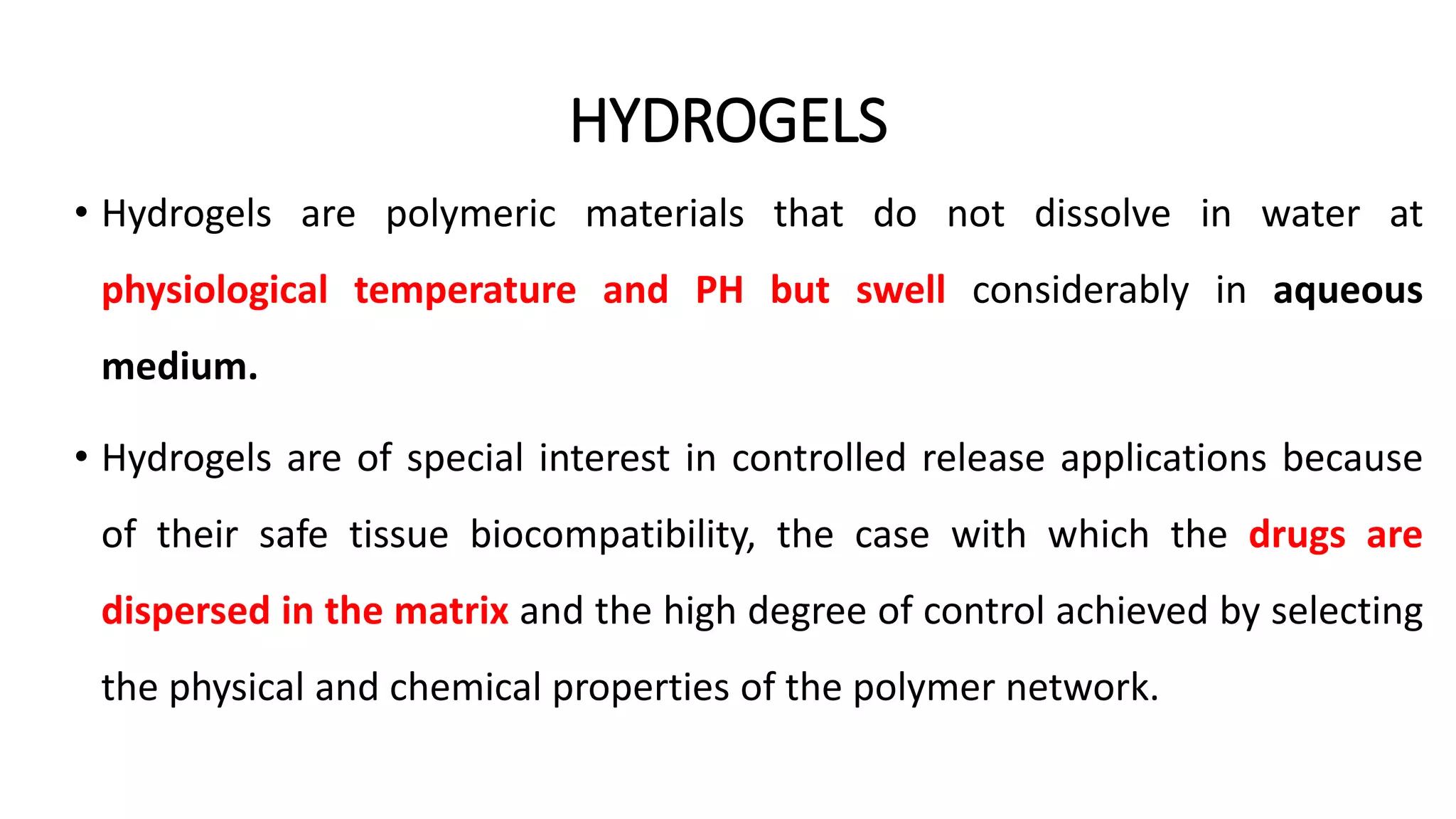
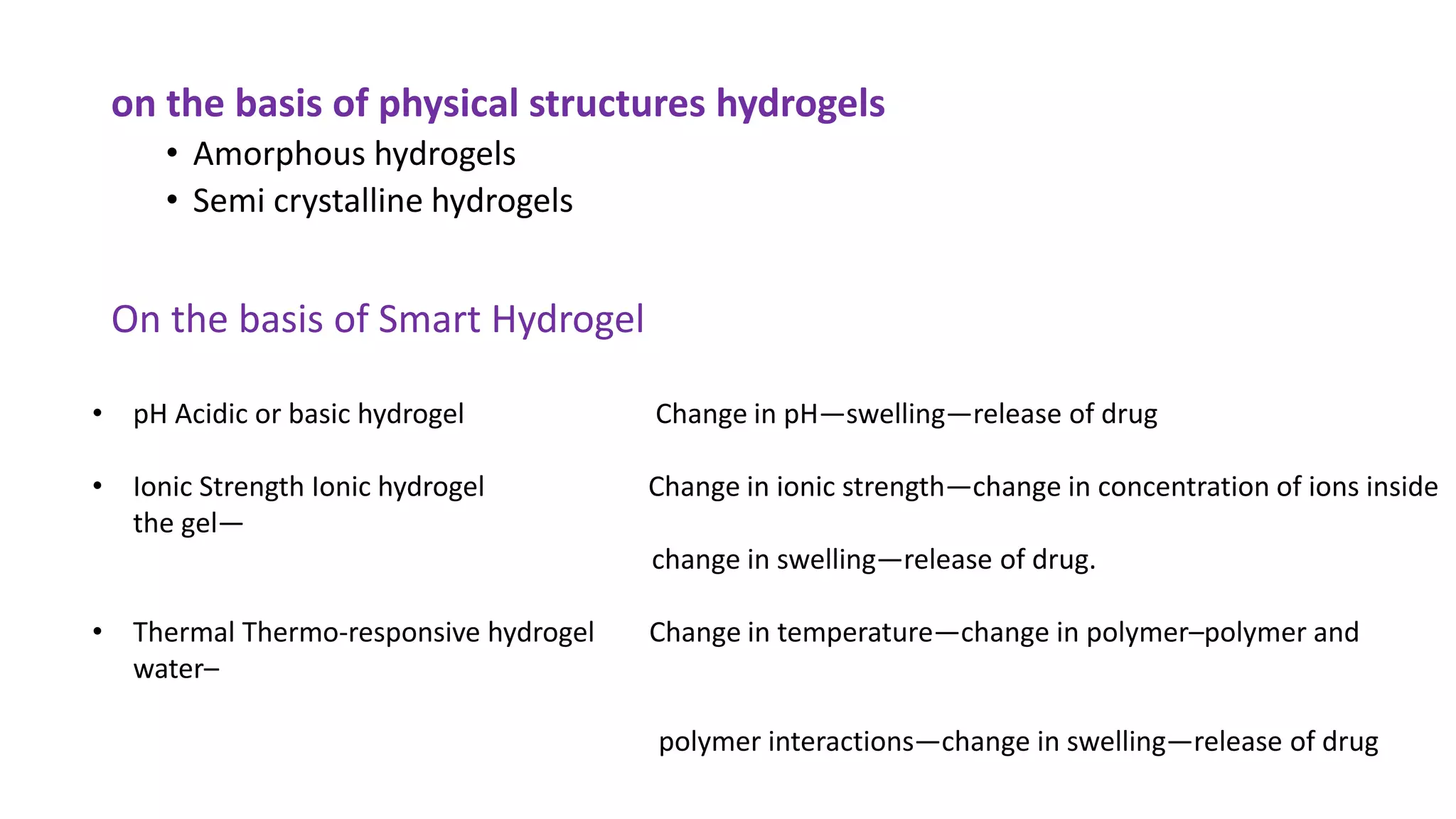
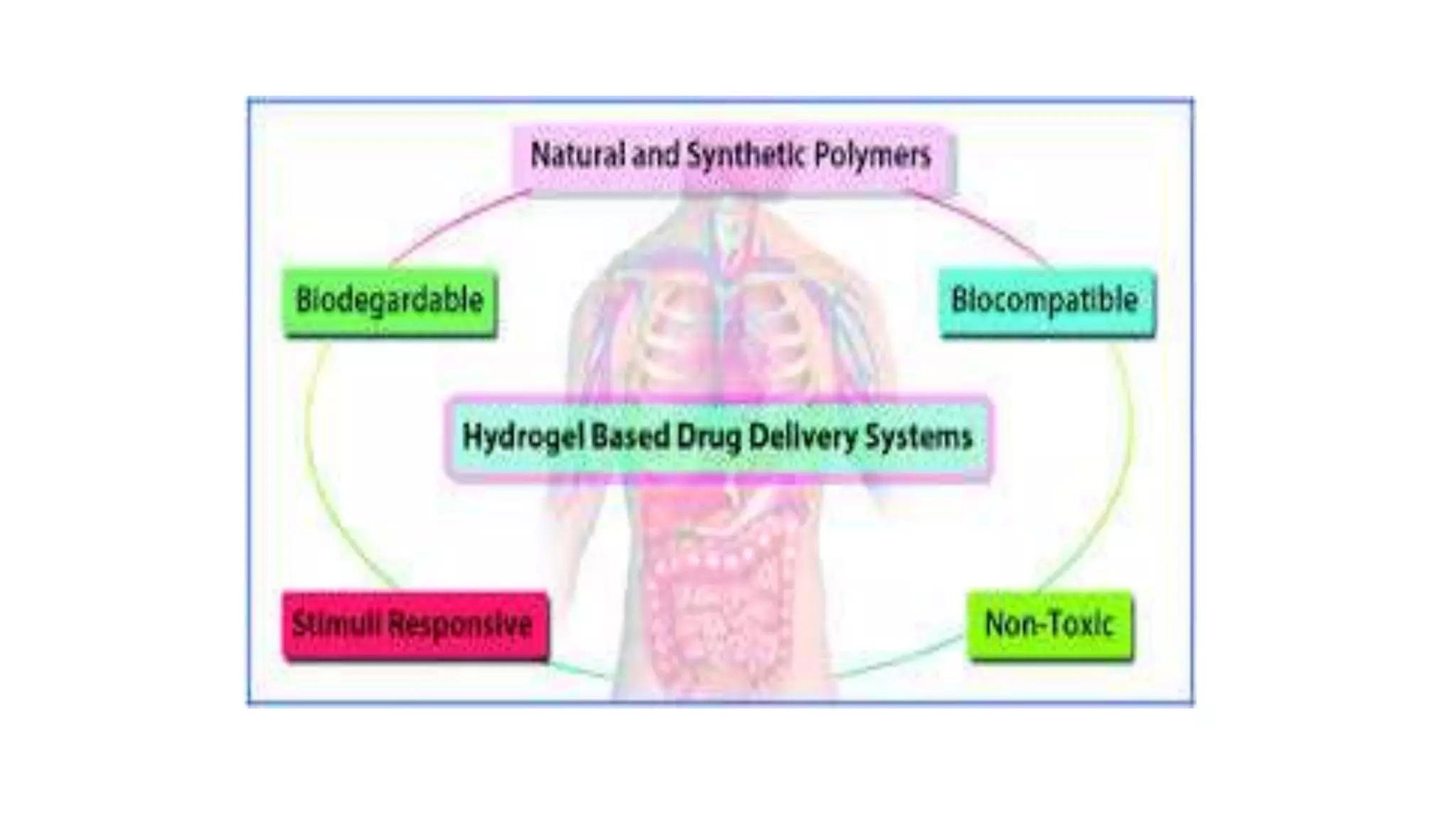
Biodegradable polymers can be used for controlled drug release applications. They degrade in the body through natural processes and produce non-toxic byproducts. Synthetic biodegradable polymers commonly used include PLA, PGA and PLGA. Drug release from polymers occurs through mechanisms like swelling, erosion and degradation. Biodegradable polymers find applications in drug delivery systems like implants, microparticles and hydrogels. Hydrogels are three-dimensional polymer networks that can absorb large amounts of water and are useful for controlled drug delivery.