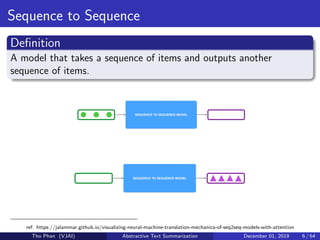
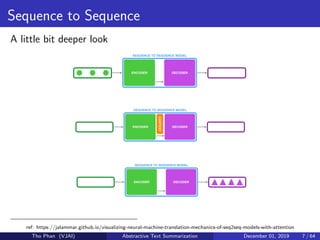
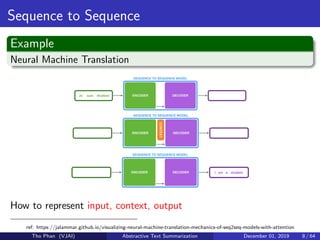
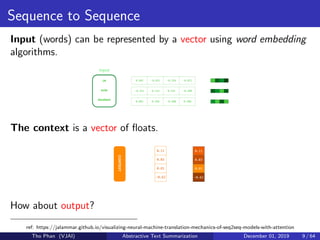
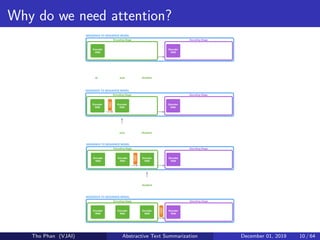
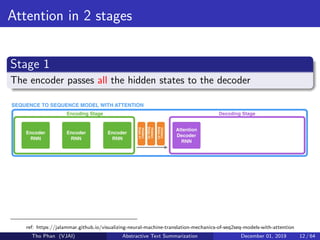
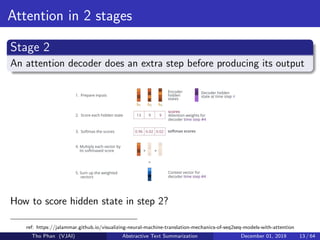
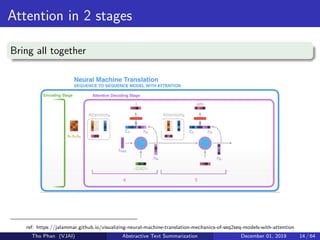
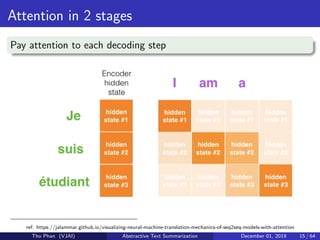
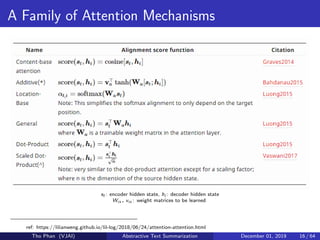
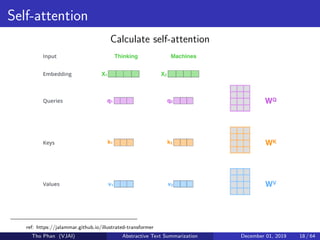
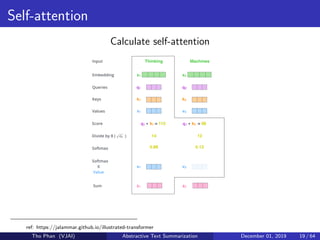
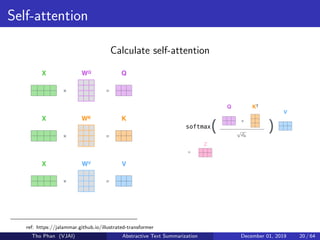
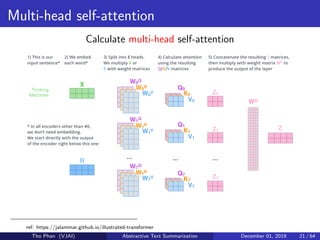
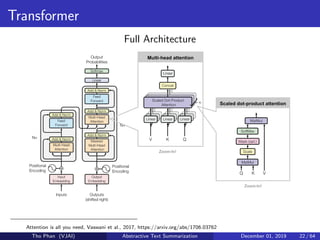
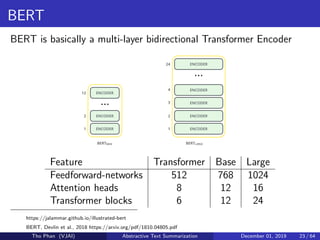
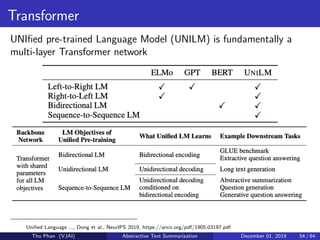
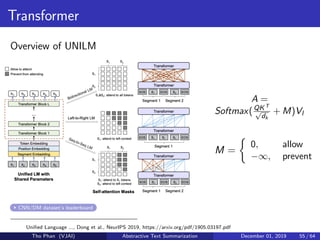
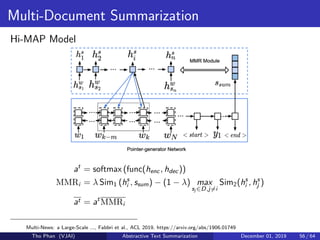
The document discusses the concepts of abstractive text summarization using sequence-to-sequence models with attention mechanisms, highlighting their role in natural language generation. It explains the differences between extractive and abstractive summarization, the importance of attention in improving model performance, and various decoding algorithms. Additionally, it covers evaluation metrics like ROUGE and challenges in measuring the quality of generated summaries.