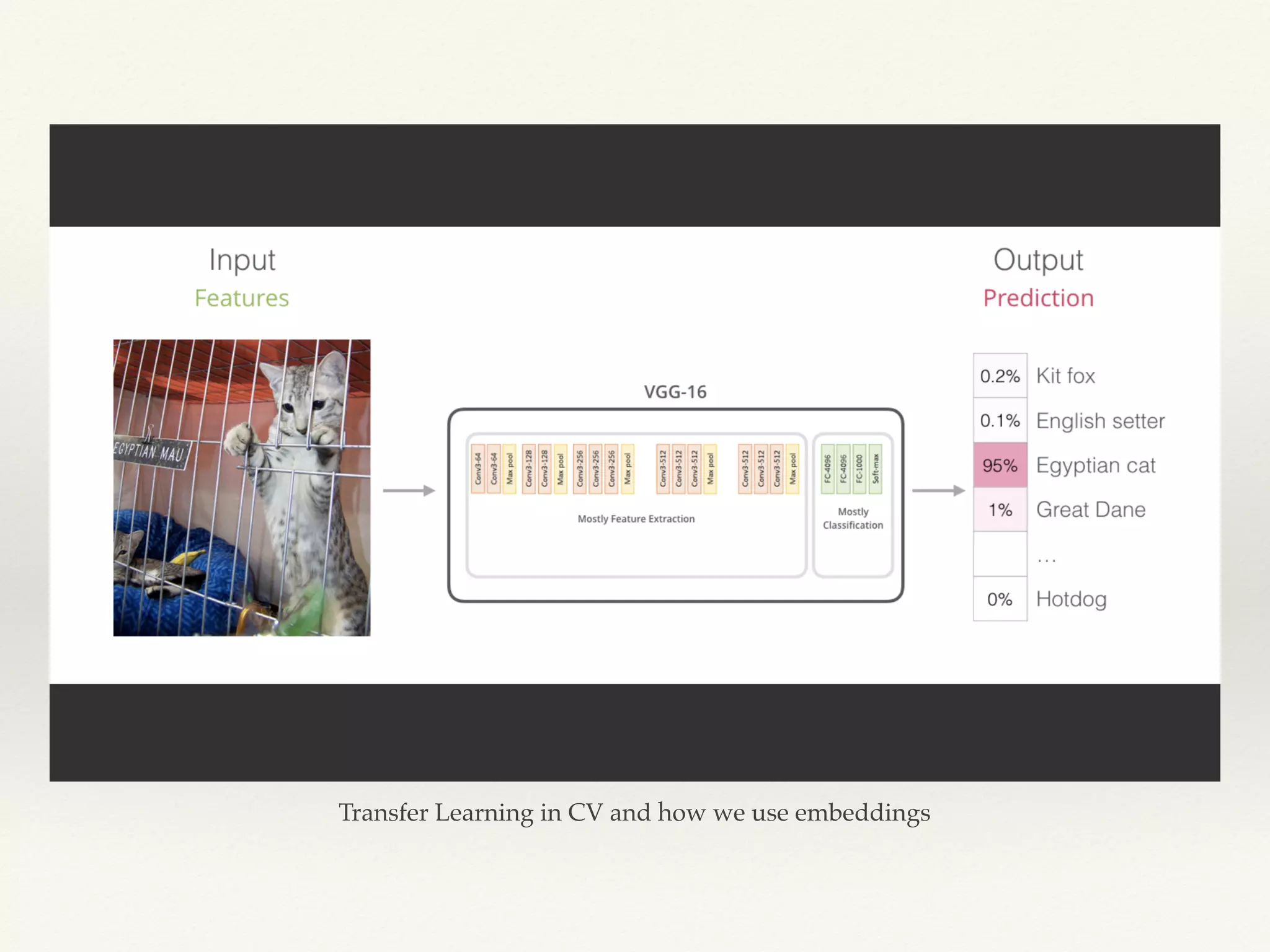
The document discusses transfer learning in natural language processing (NLP), highlighting techniques such as tokenization, stemming, and lemmatization. It explains the importance of word embeddings and the limitations associated with them, including handling out-of-vocabulary words and context diversity. Additionally, it covers the universal language model fine-tuning (ULMFiT) approach and its benefits across various datasets and tasks.