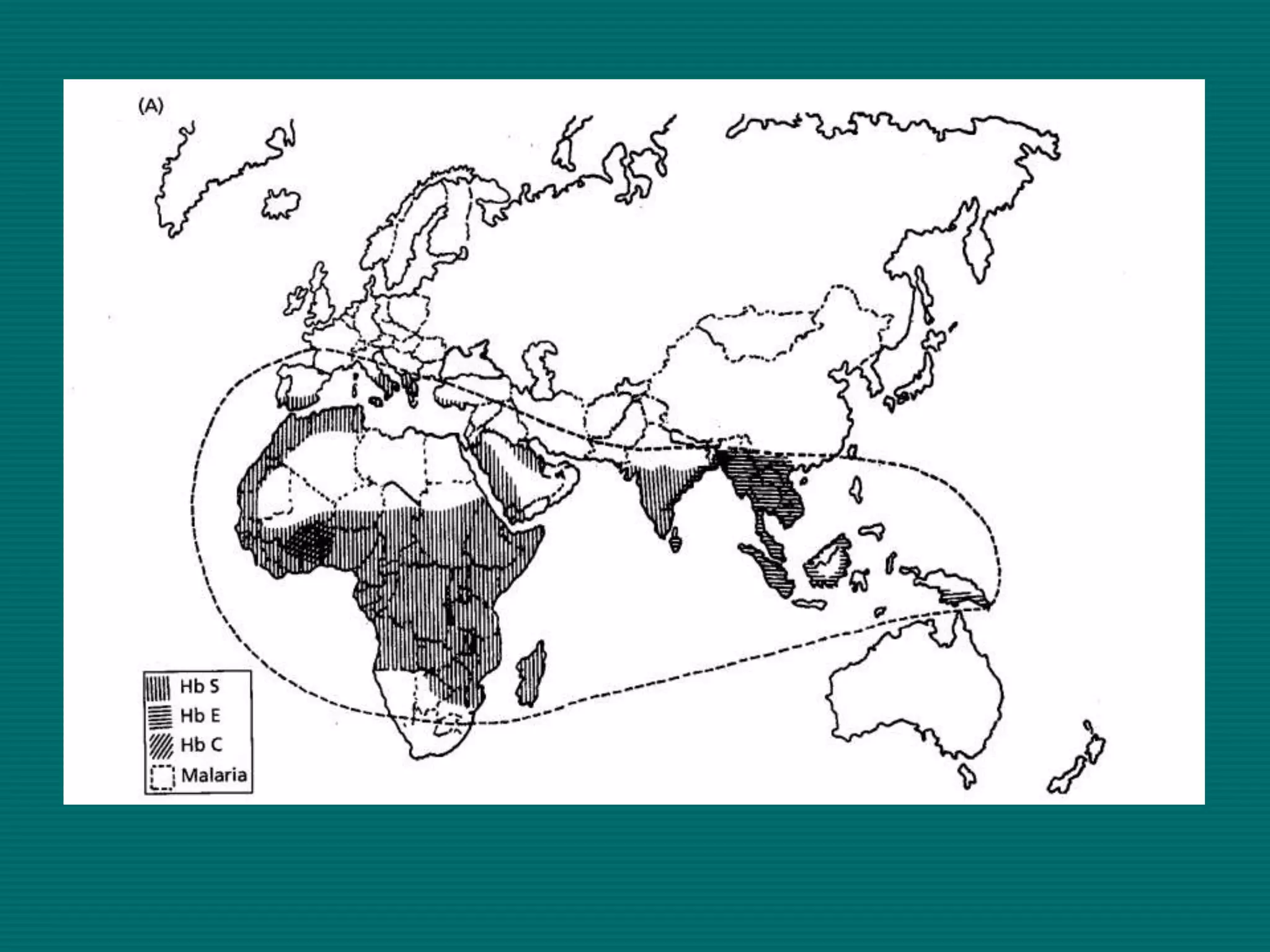
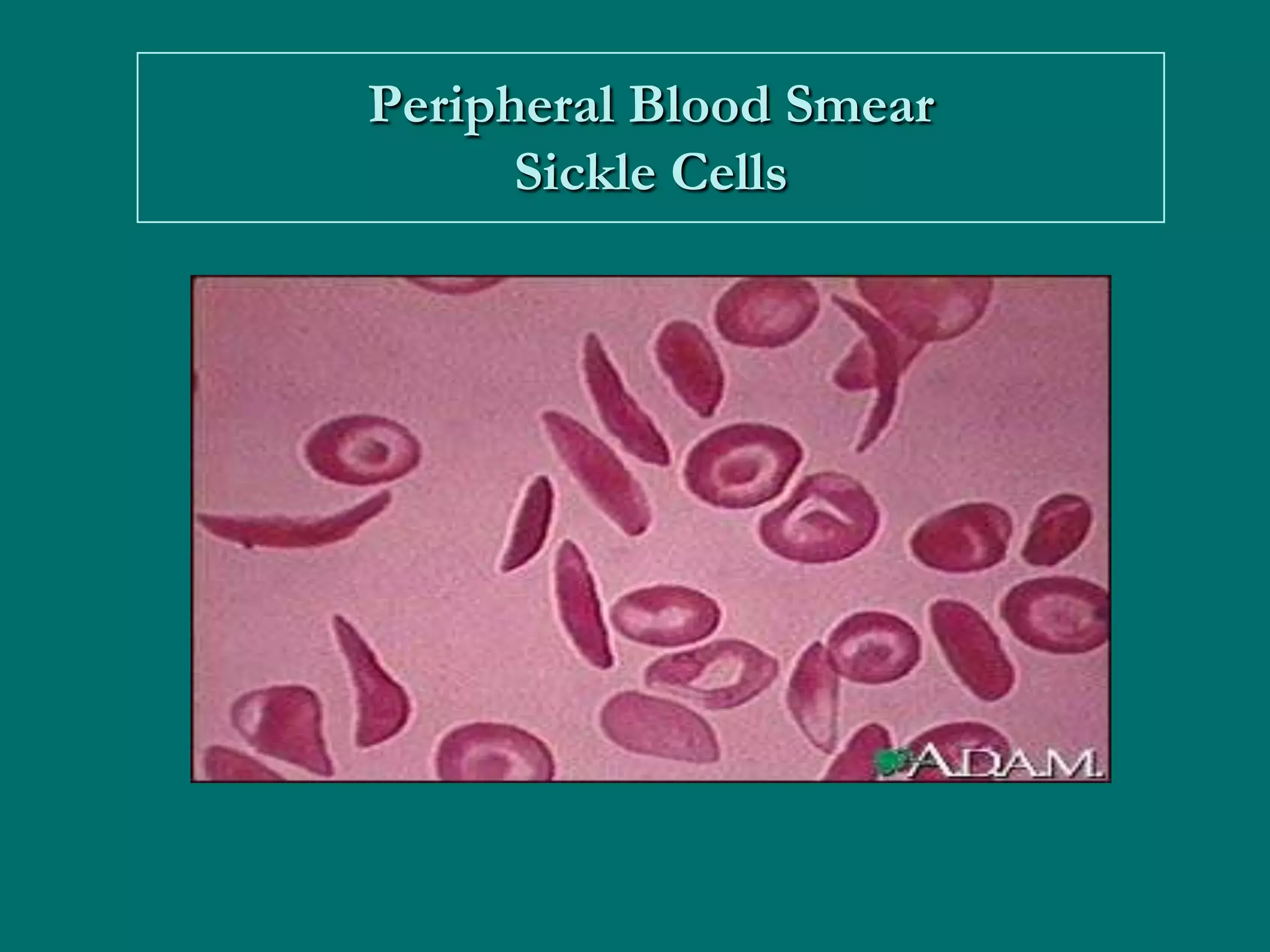
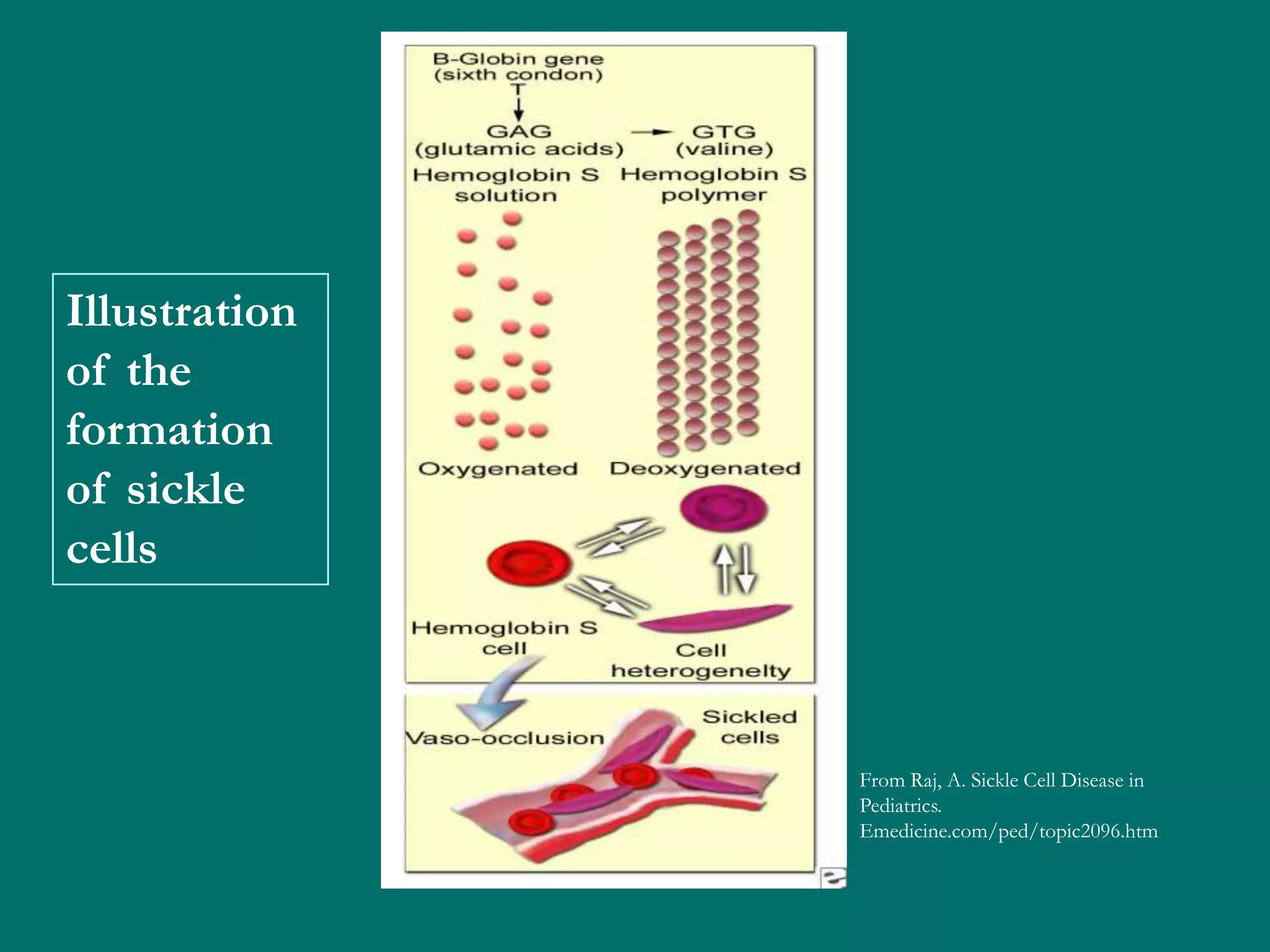
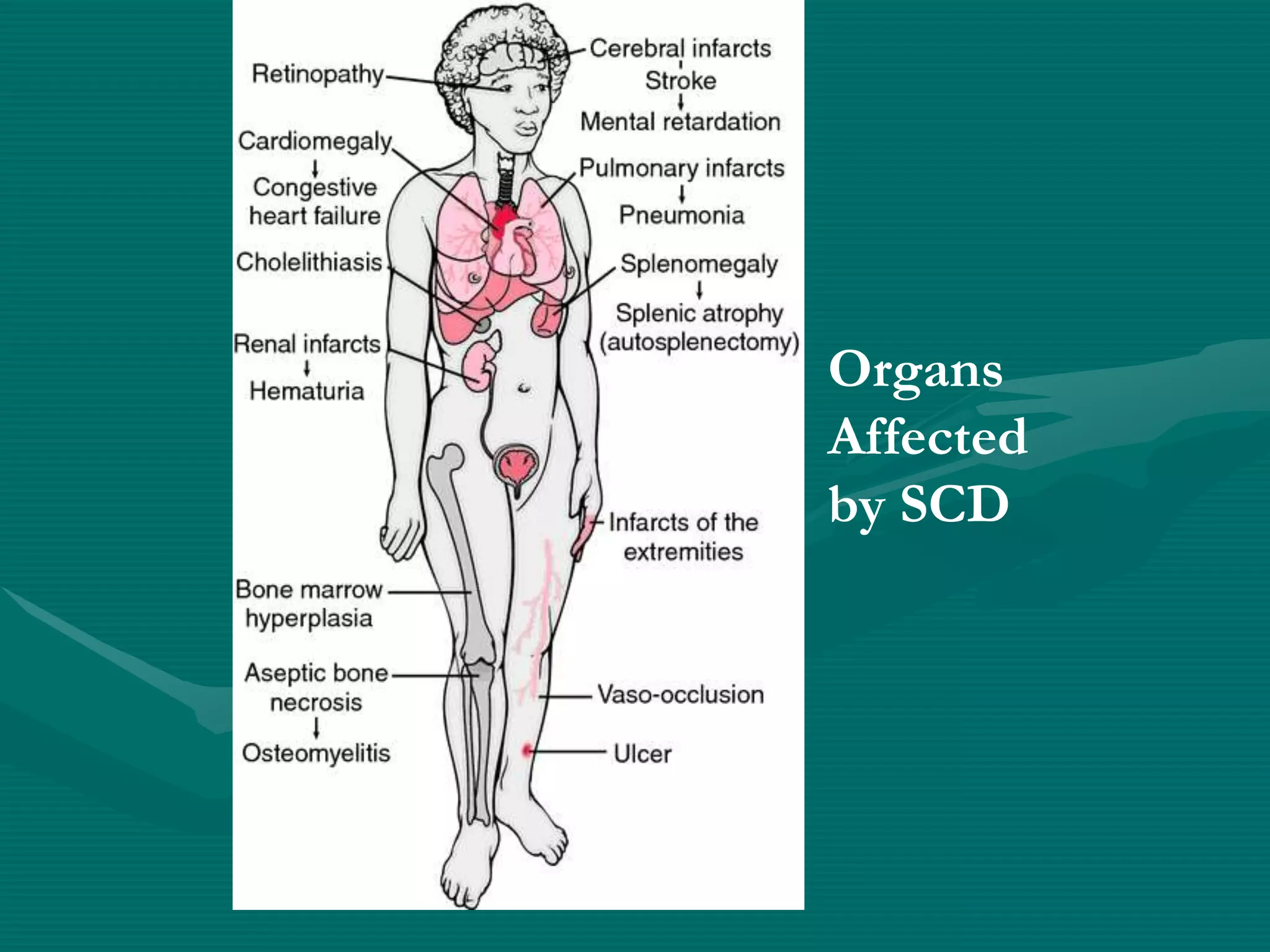
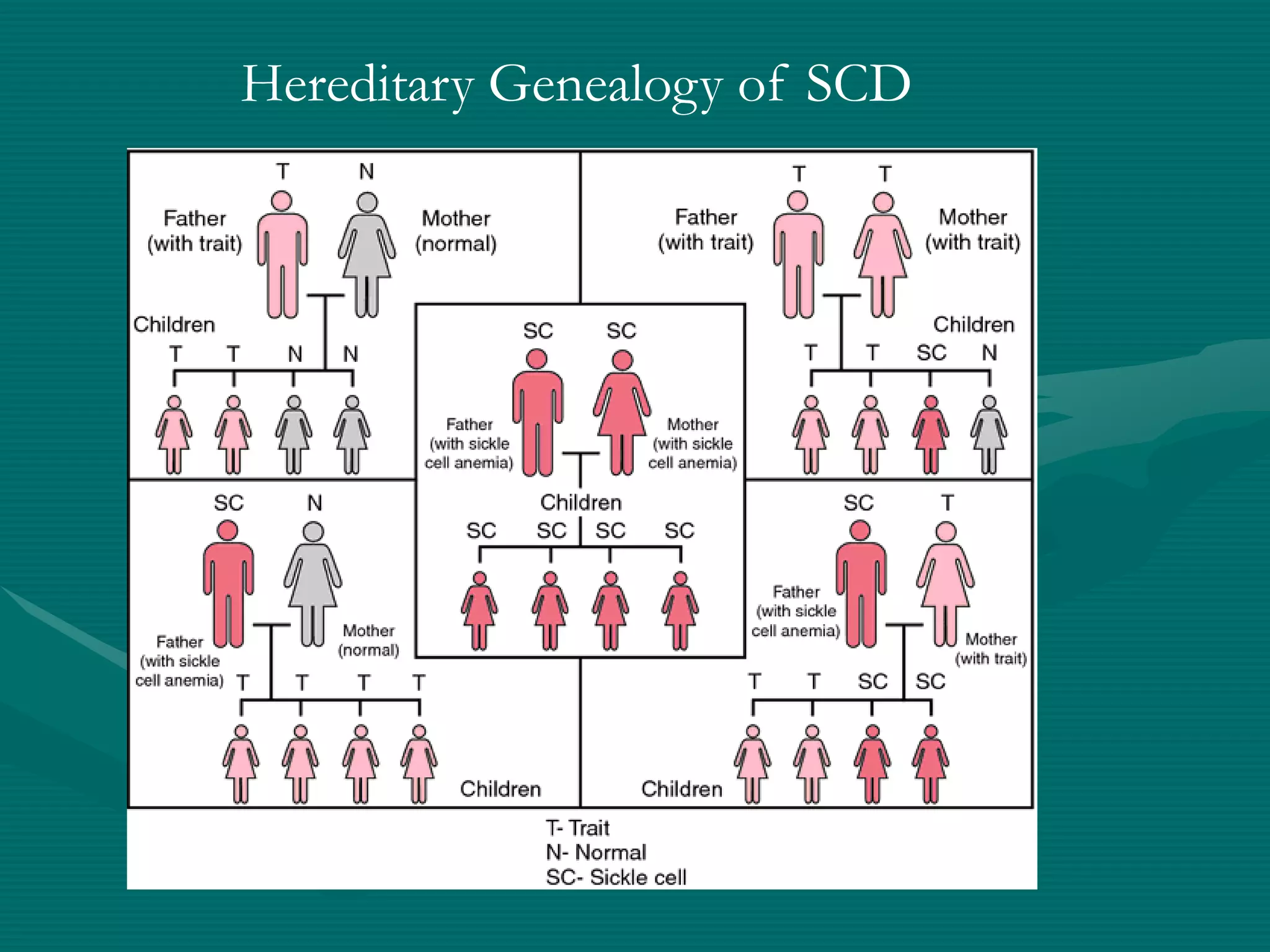
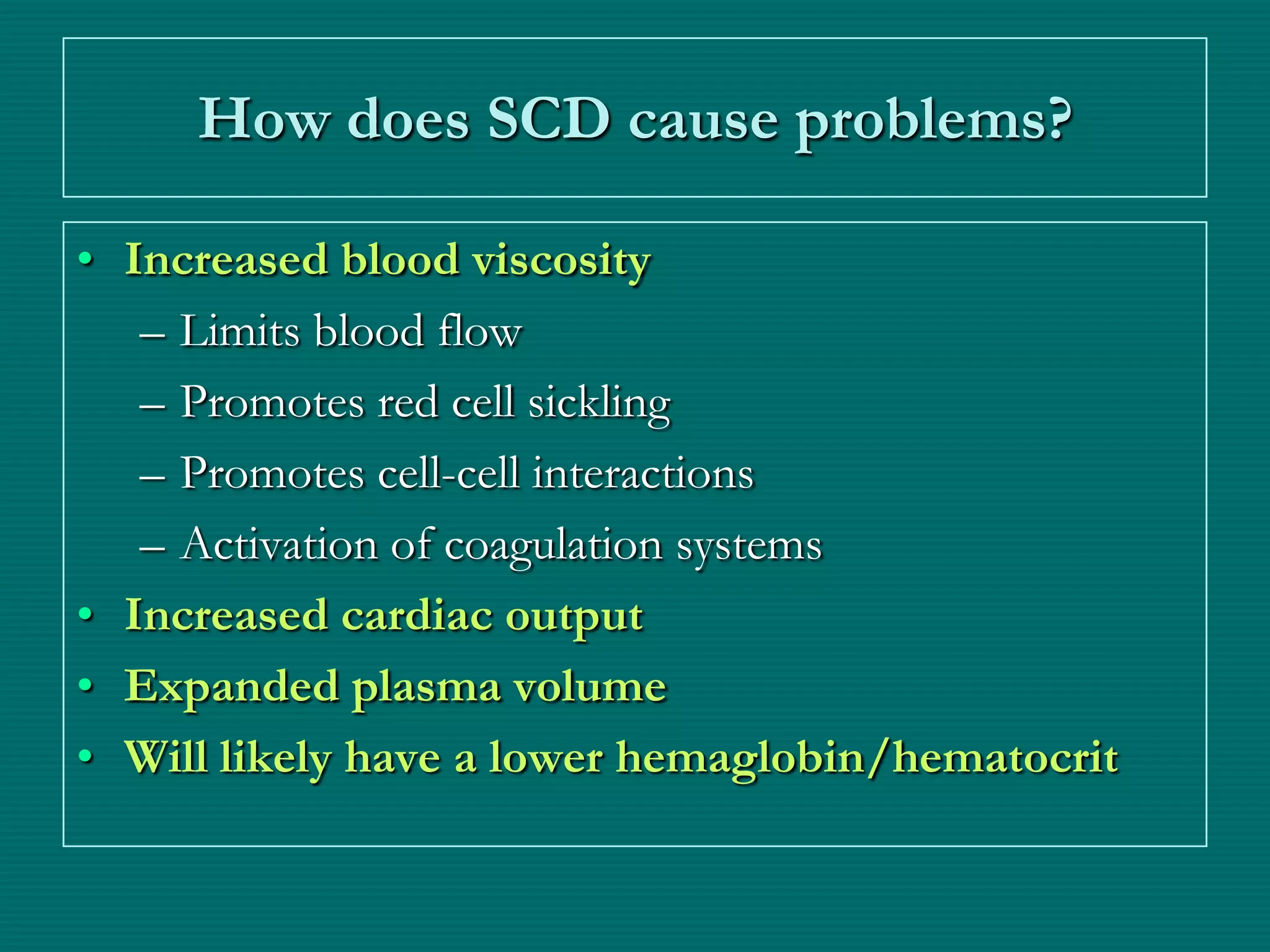
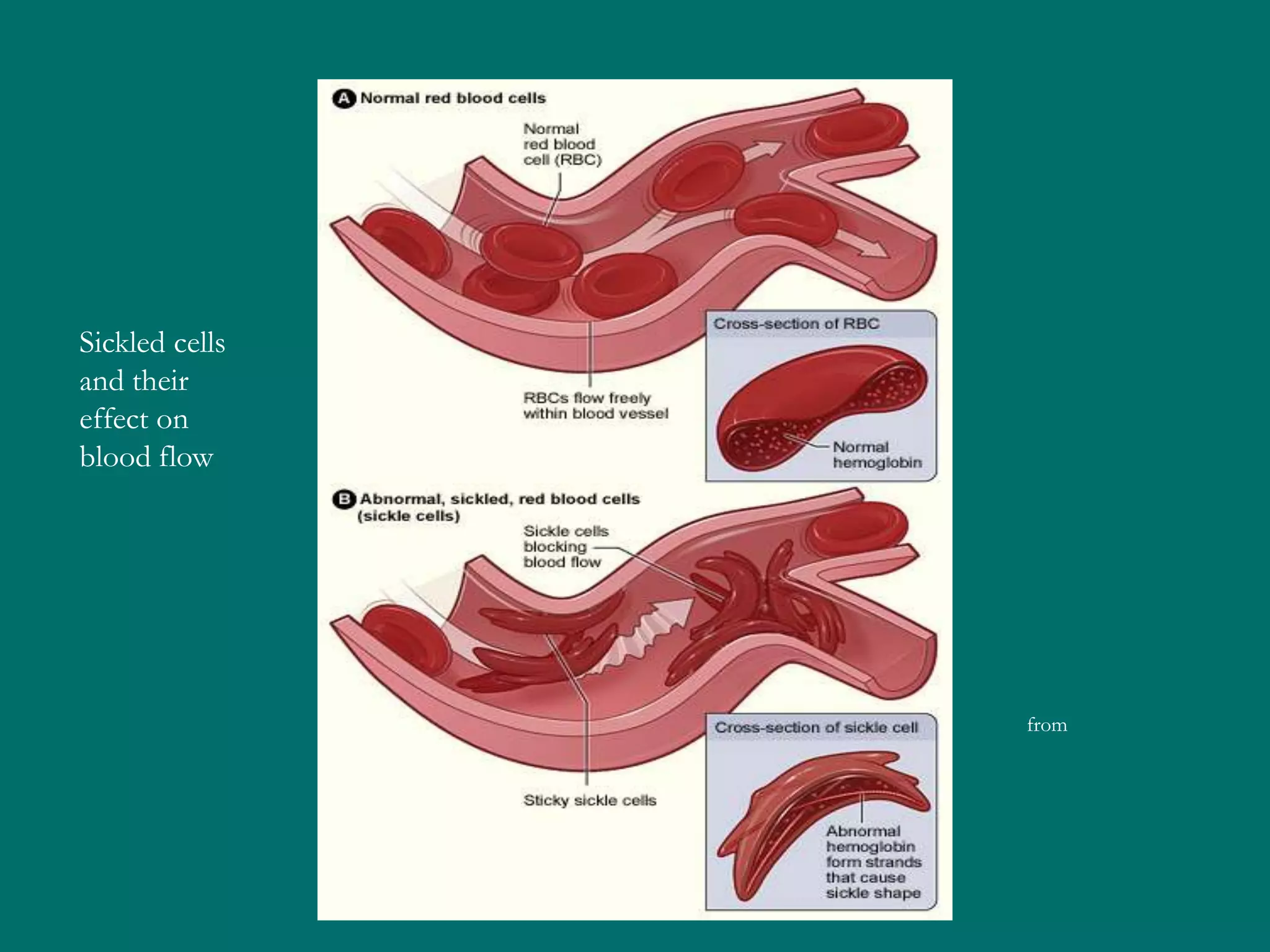
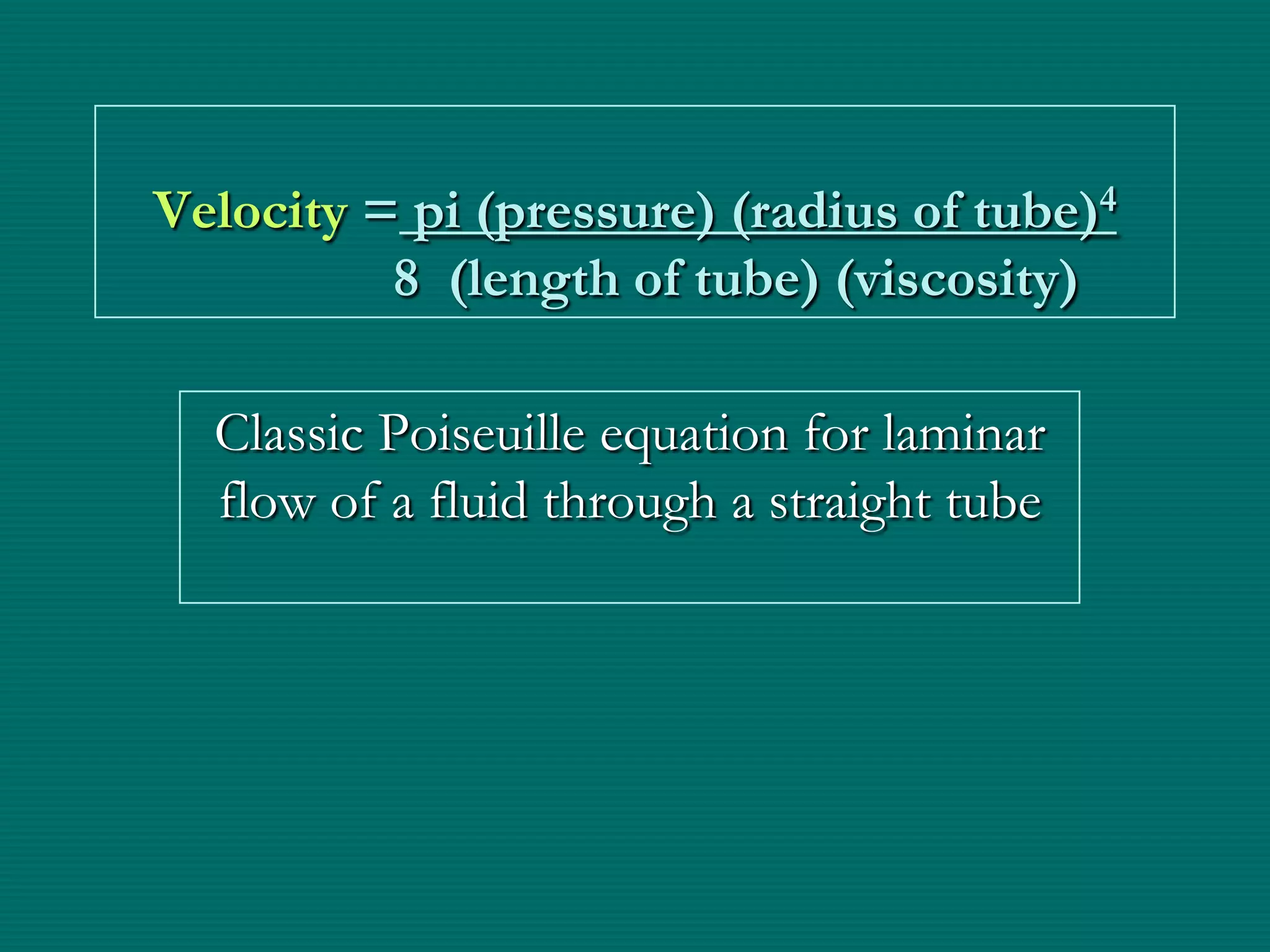
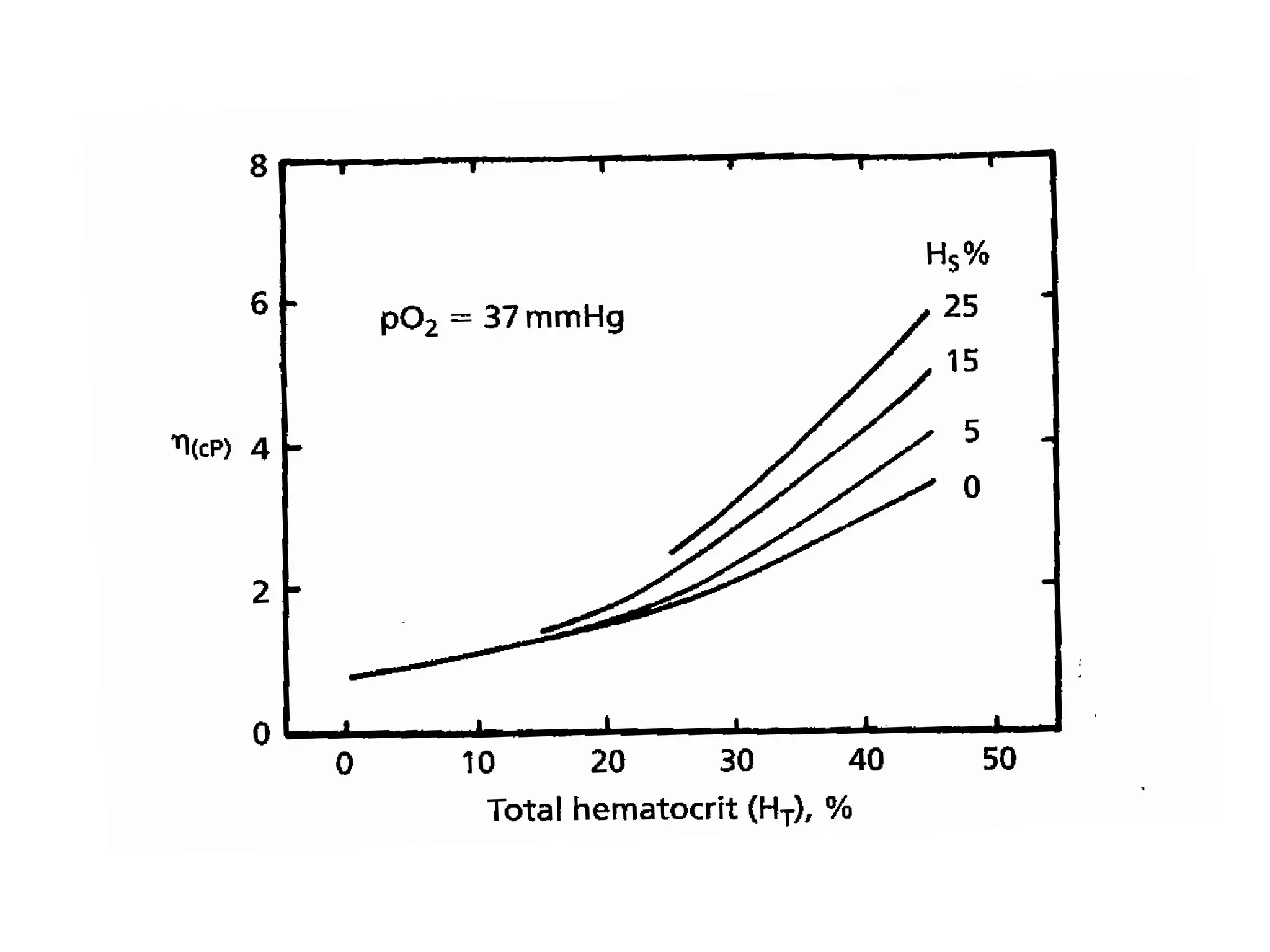
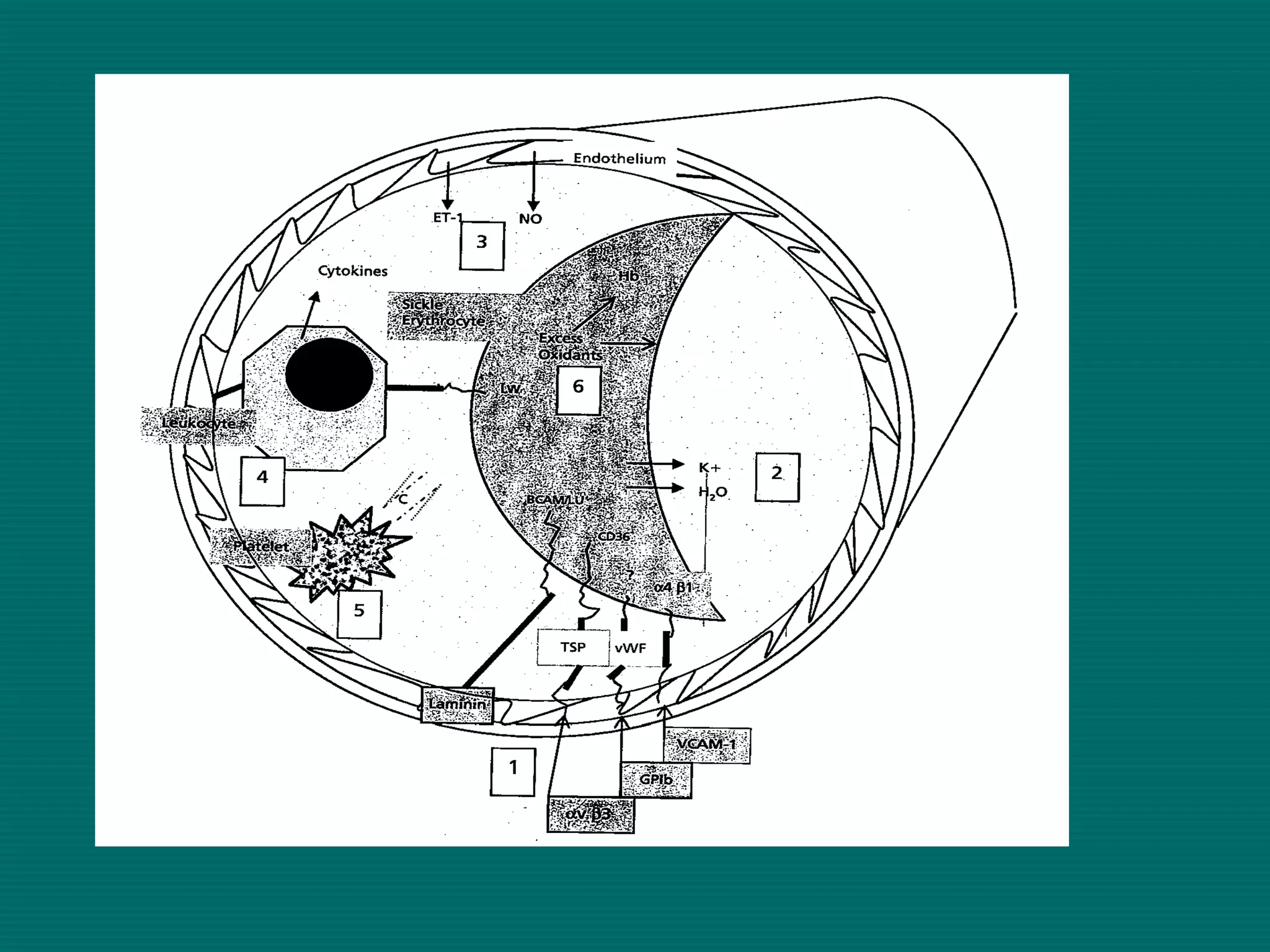
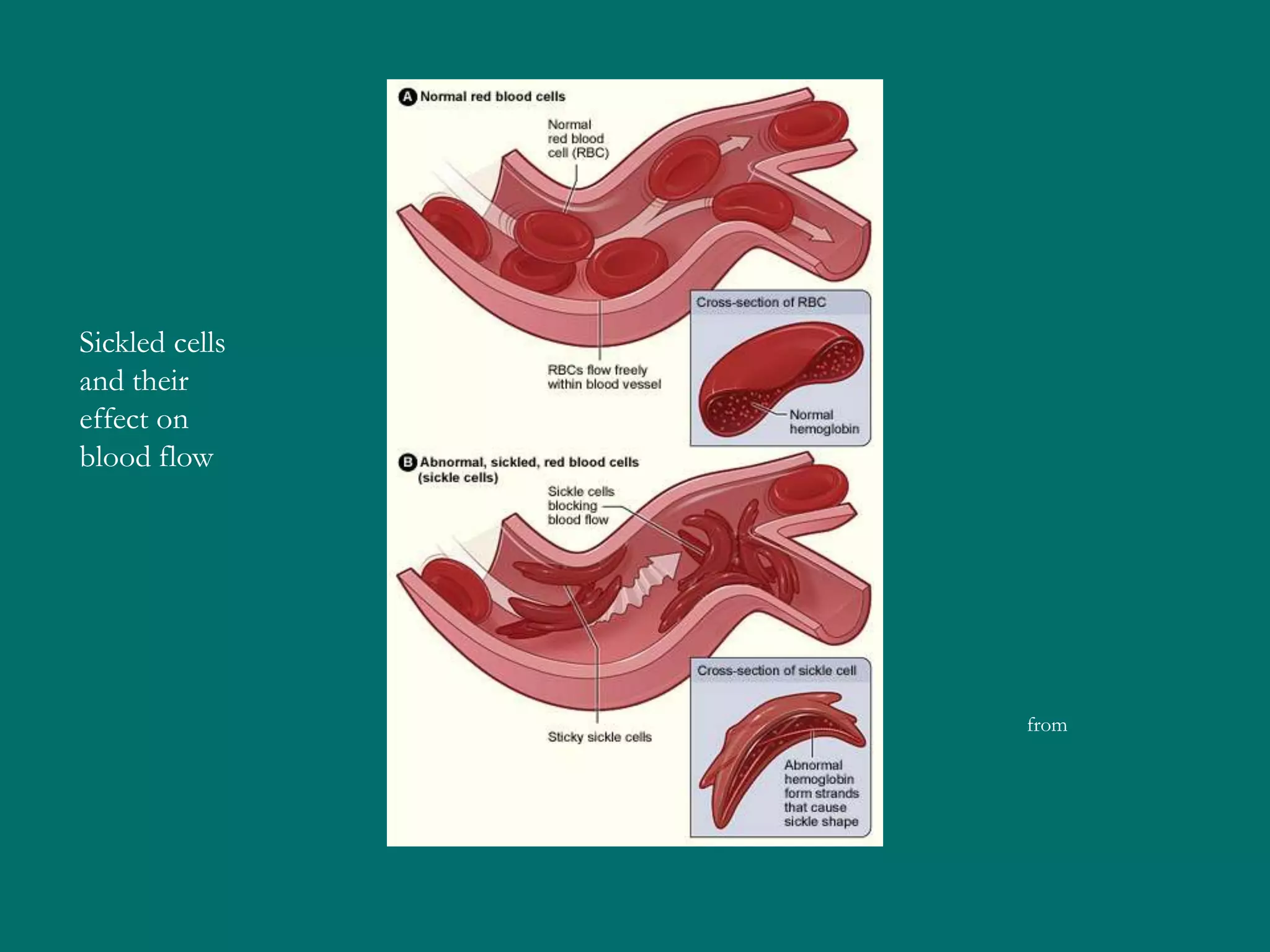
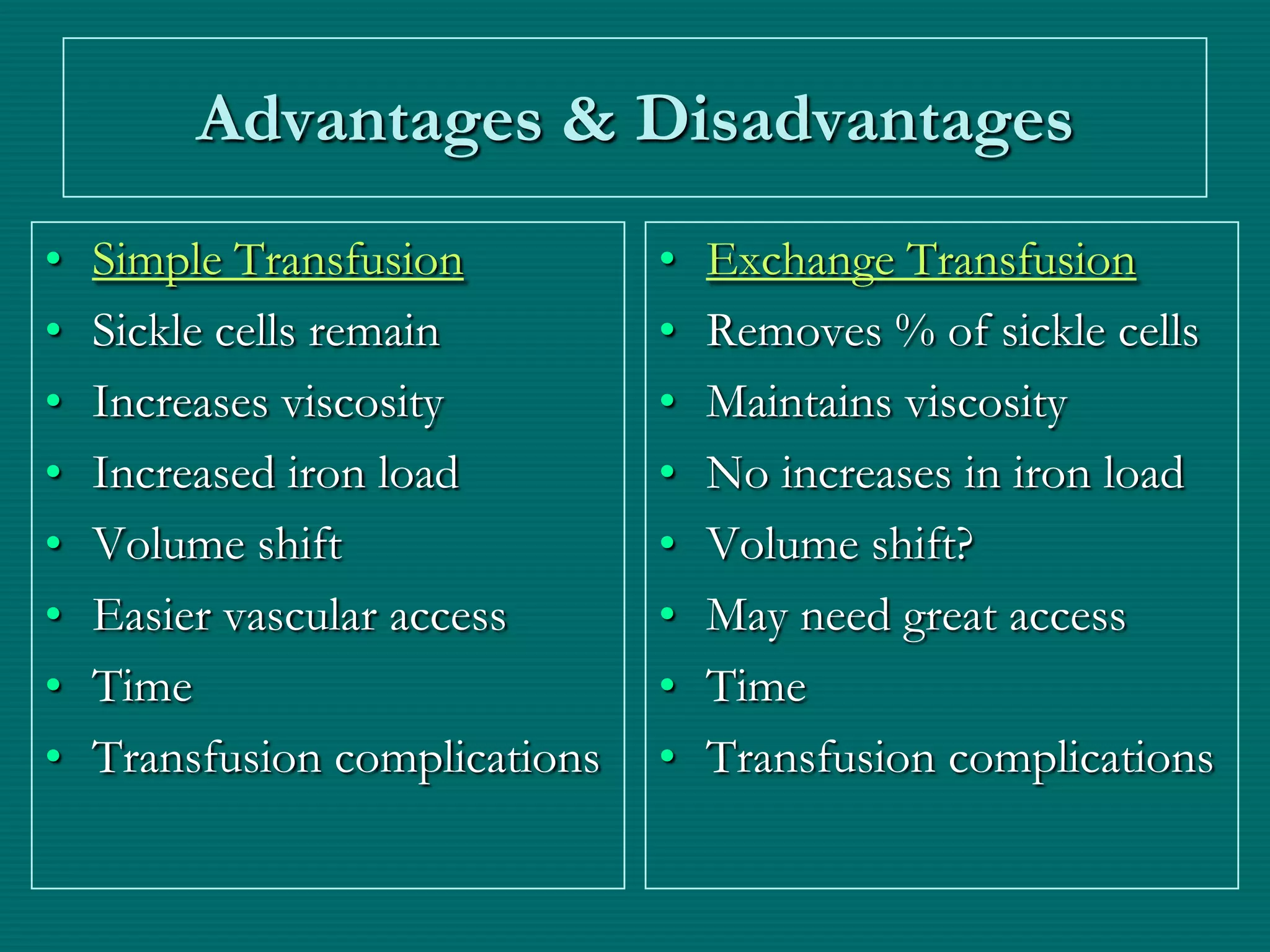
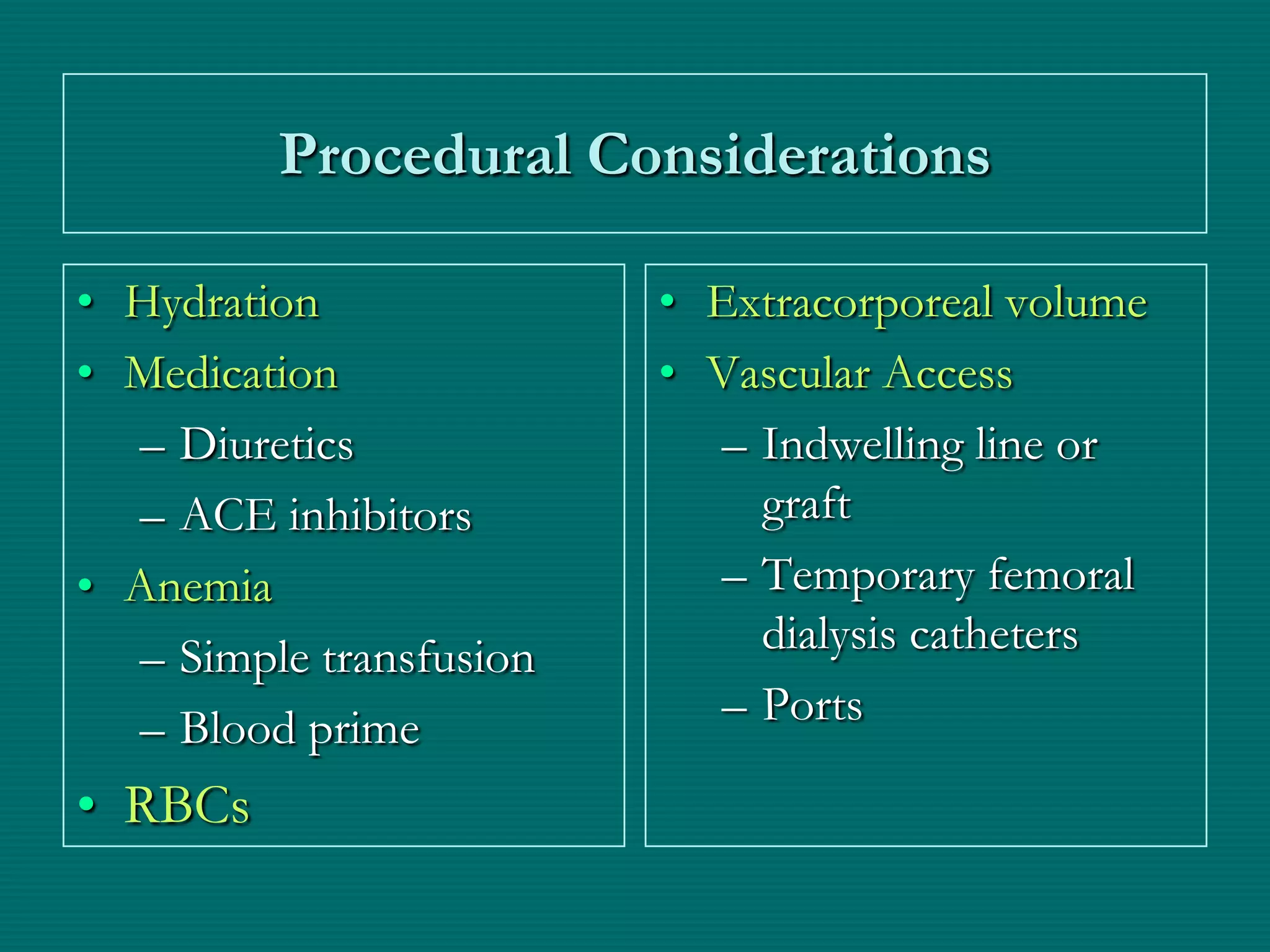
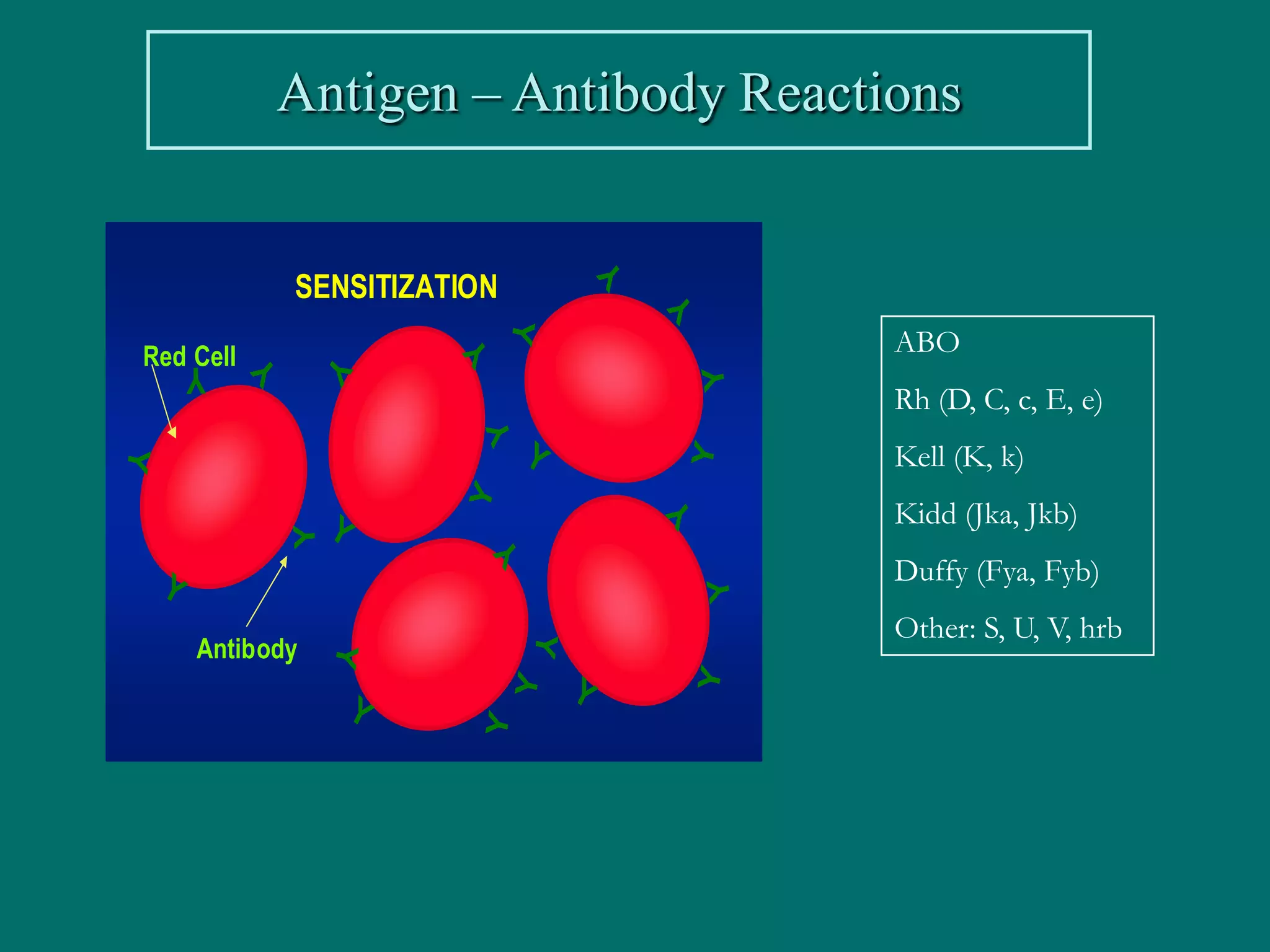
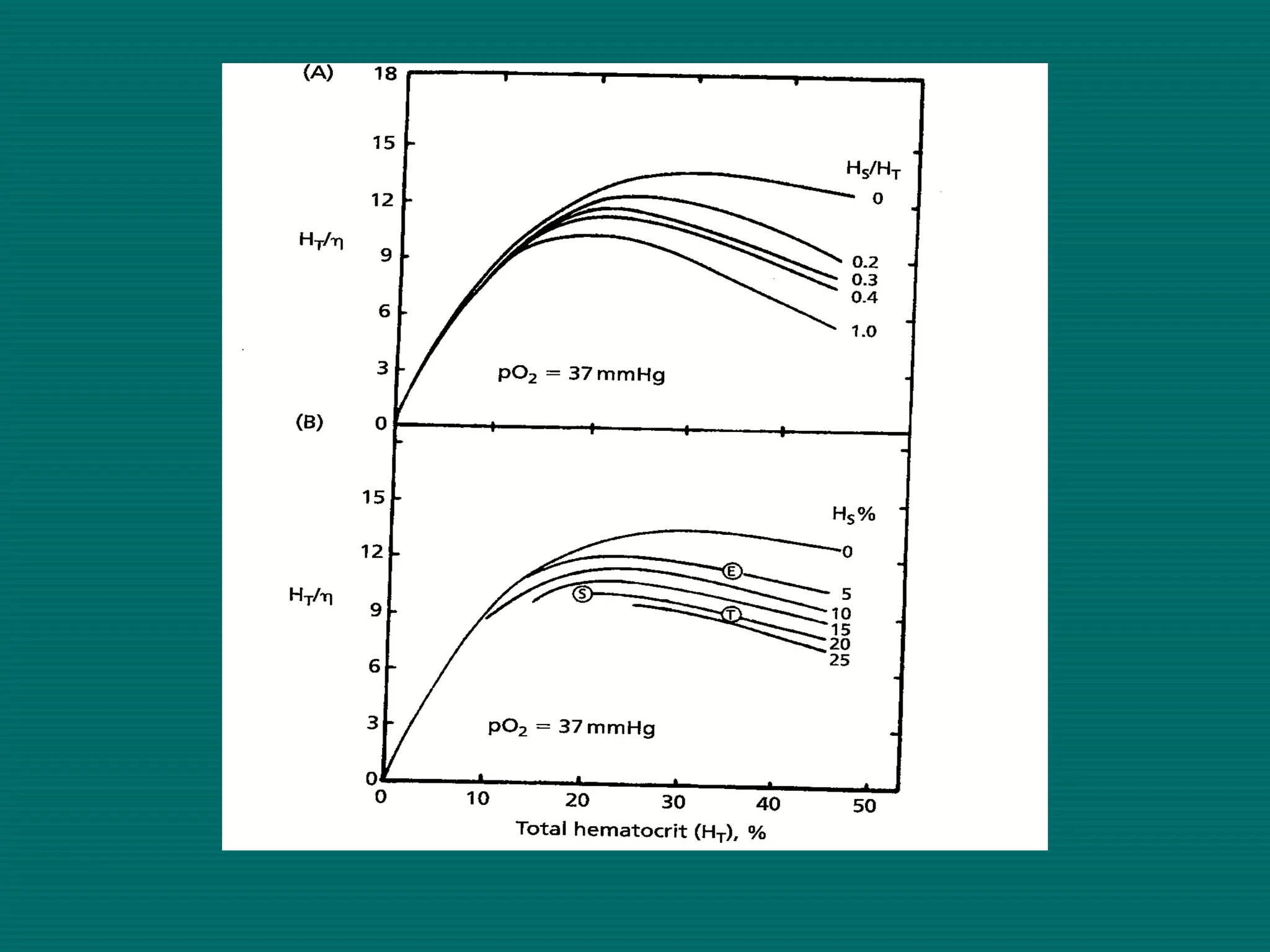
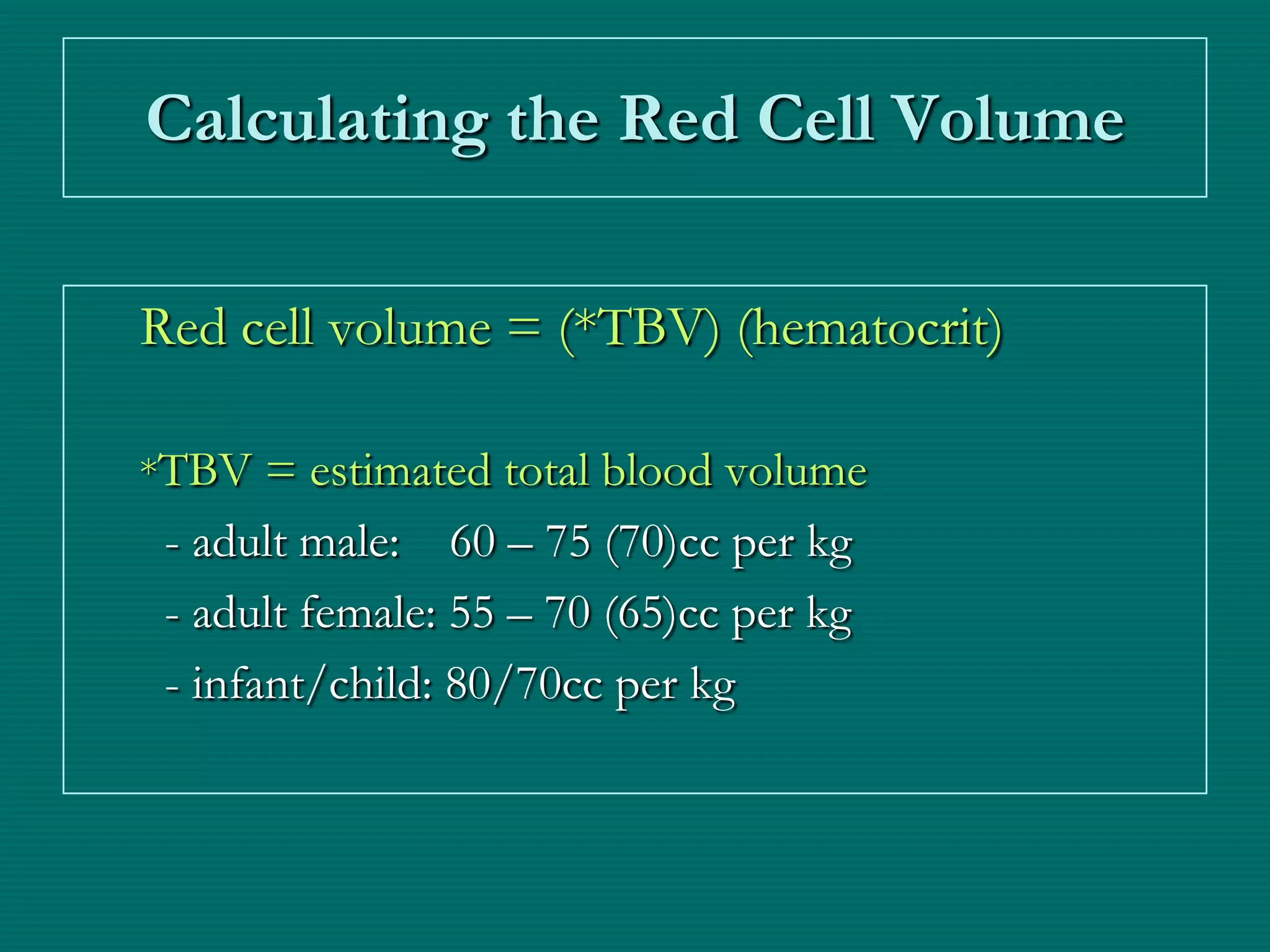
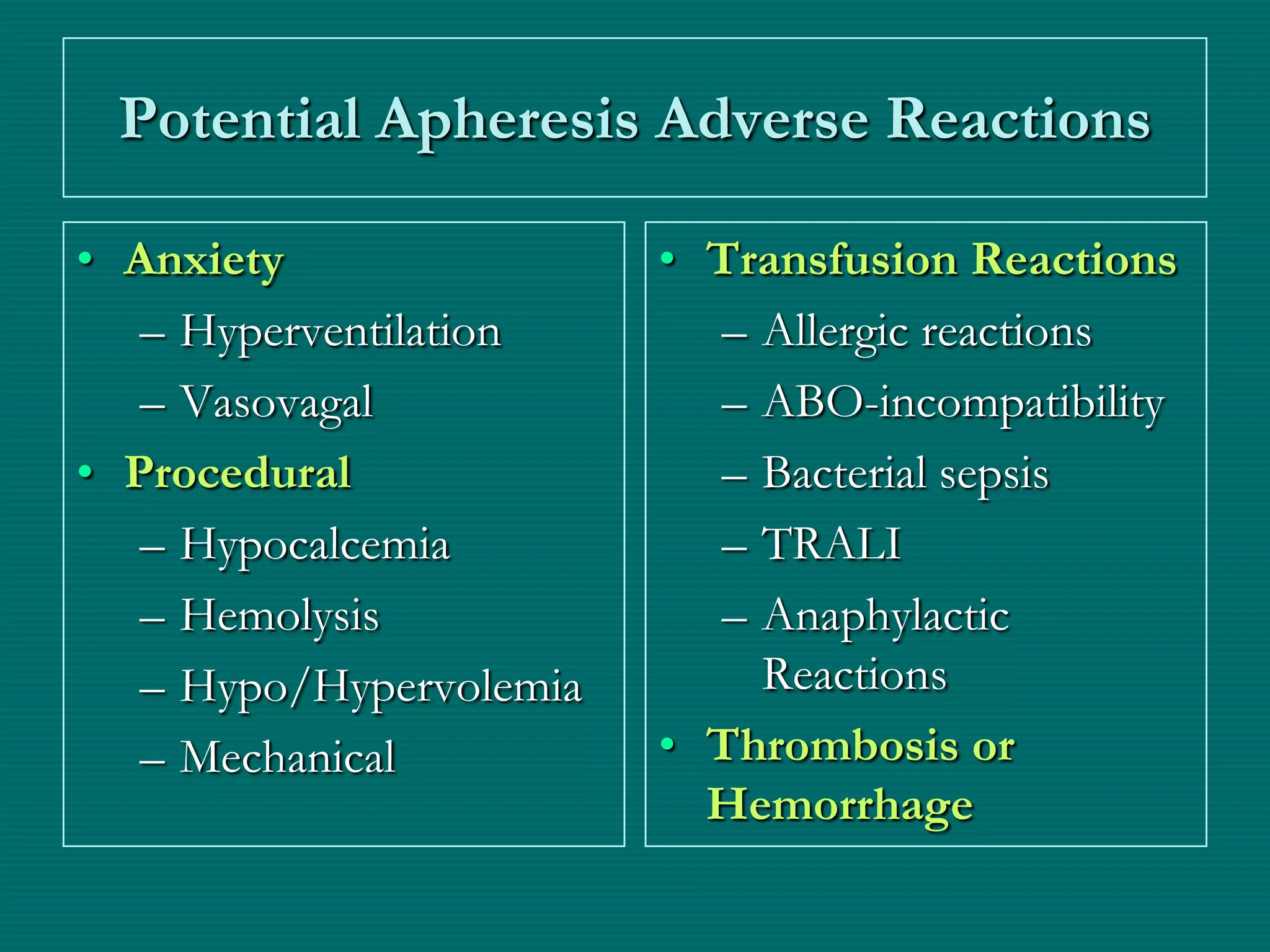
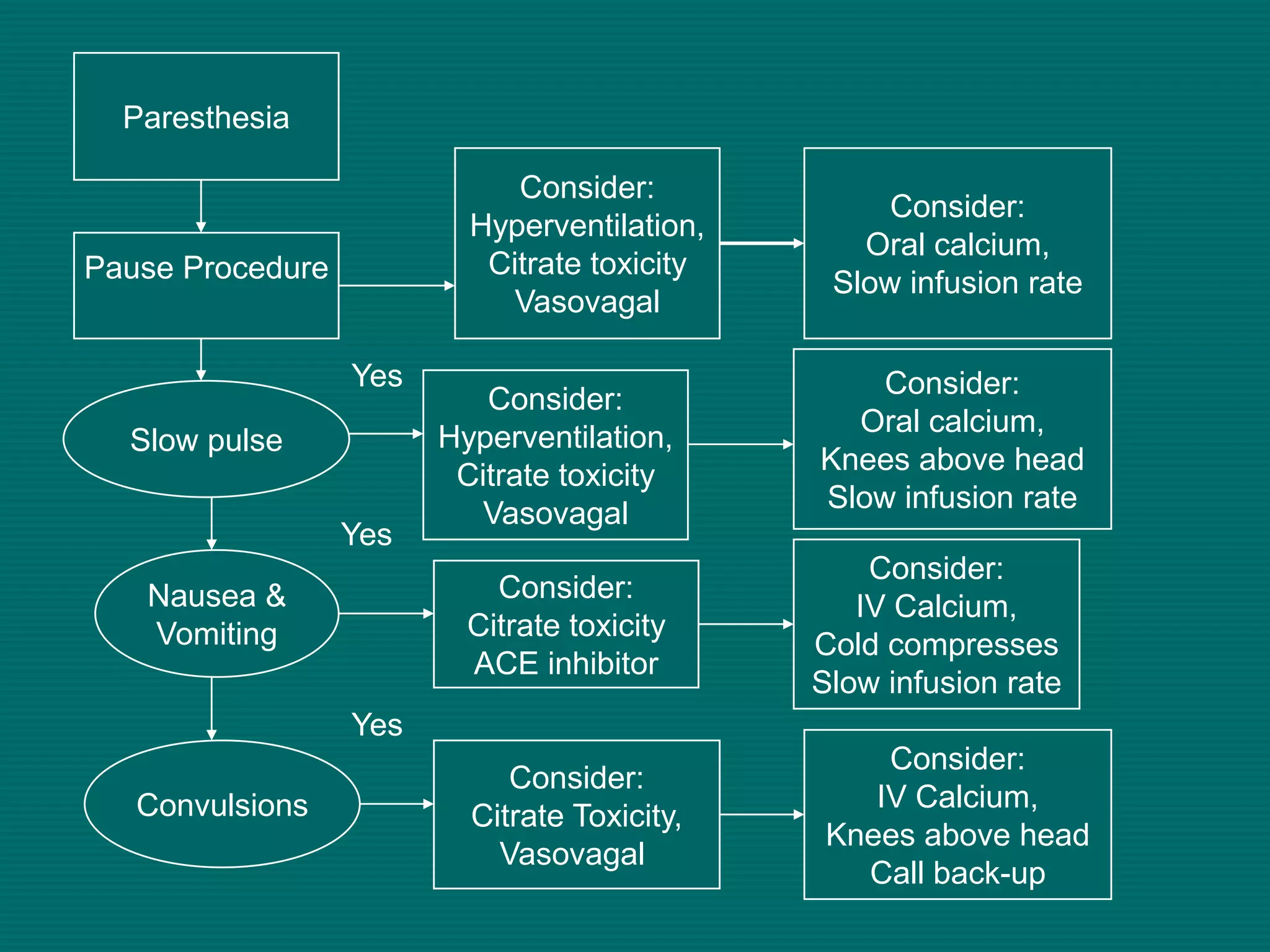
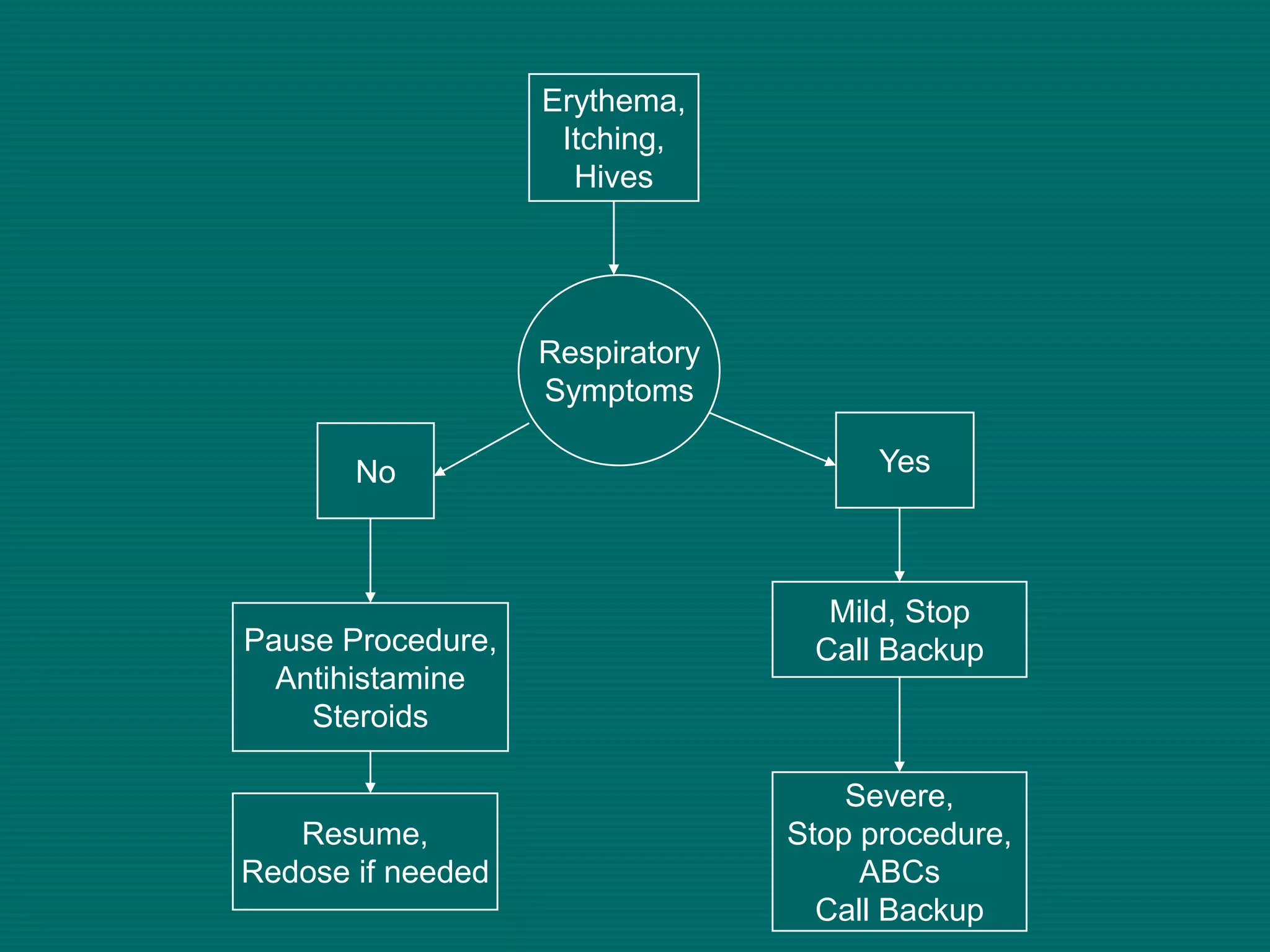
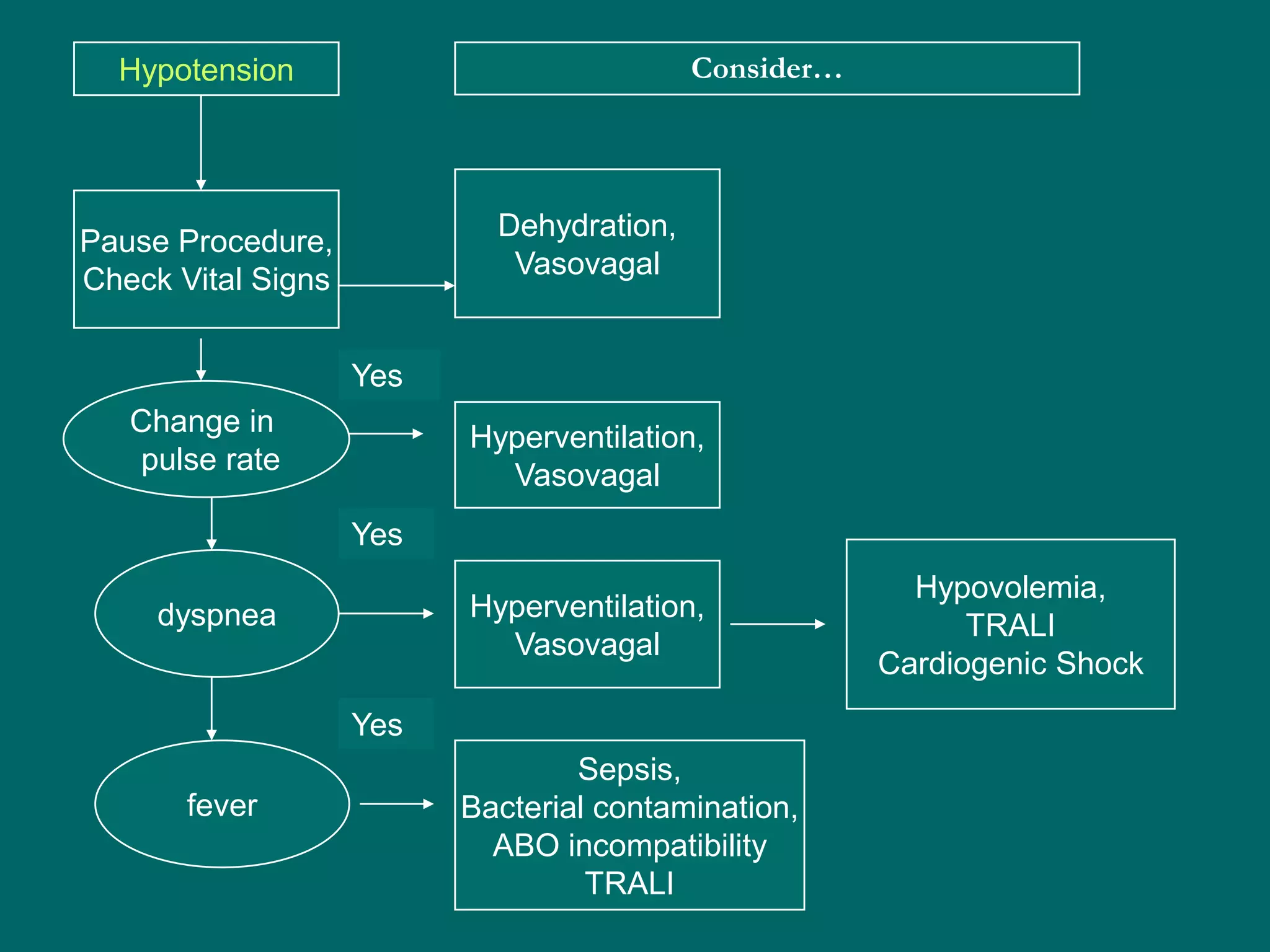
This document provides an overview of sickle cell disease (SCD) and red blood cell exchange transfusions. It discusses the pathophysiology and complications of SCD, including increased blood viscosity and reduced blood flow. Treatment options are presented, with red blood cell exchange transfusions explained as removing sickle cells and replacing them with normal red blood cells to improve oxygen carrying capacity and reduce complications. The document covers procedural considerations for red blood cell exchange transfusions, such as goals, potential complications, and their management. It provides resources for further information.