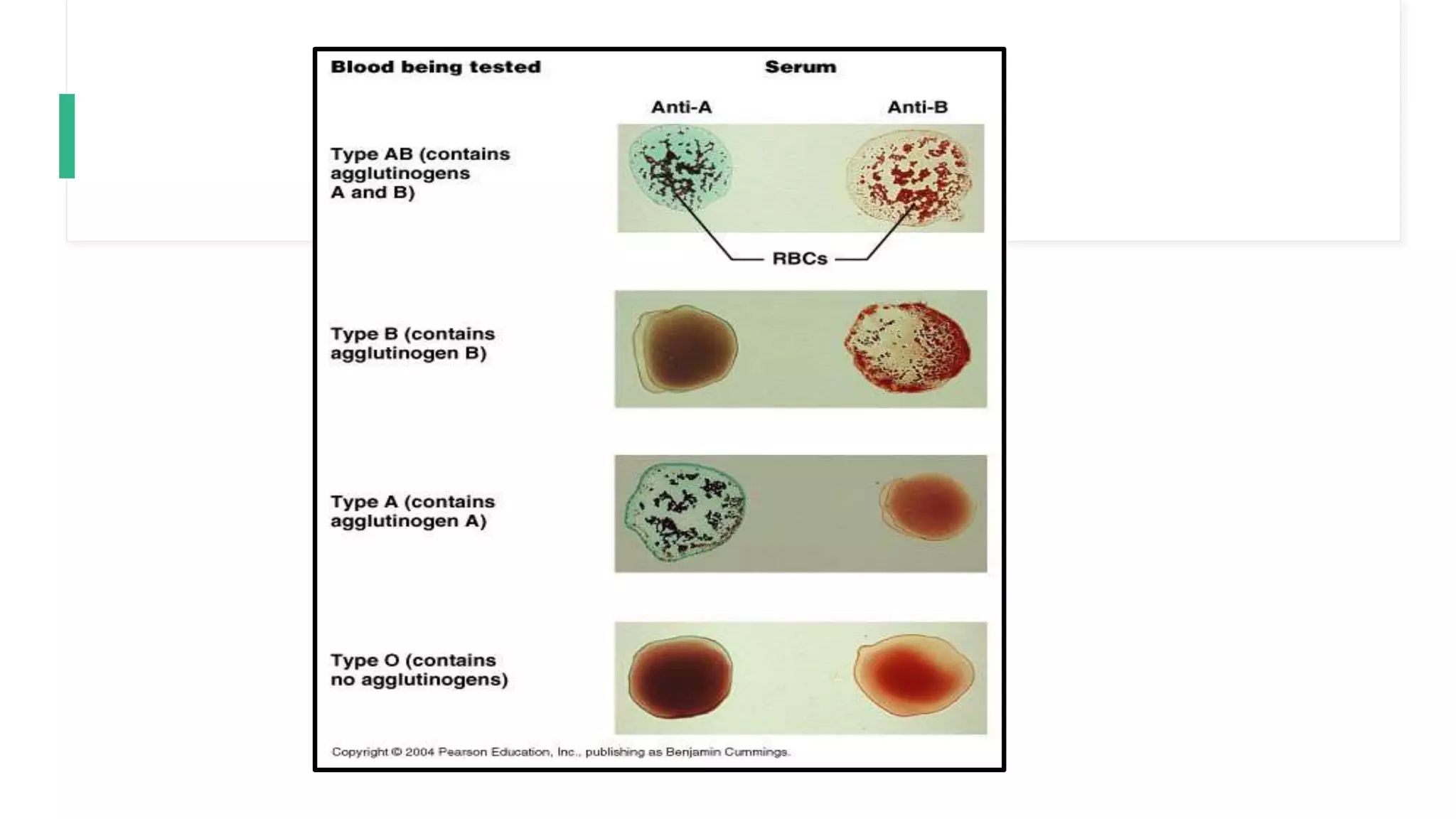
Blood transfusion is done to replace lost blood through bleeding or increase blood counts in anemic patients. It involves collecting blood from healthy donors, testing the donor and recipient blood for compatibility, and transfusing compatible blood or components. Complications can include immunologic reactions like hemolytic transfusion reactions from ABO incompatibility, transfusion-related lung injury, or allergic reactions. Non-immunologic risks are circulatory overload, infections, air embolism, or iron overload. Proper donor selection, compatibility testing, and component preparation can help reduce risks, but complications still occur in some transfusions.