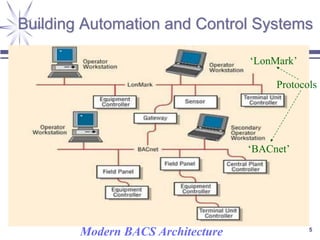
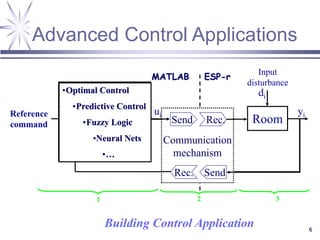
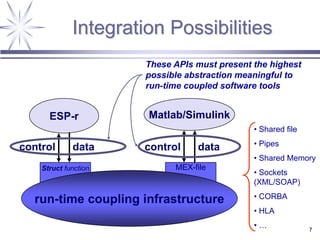
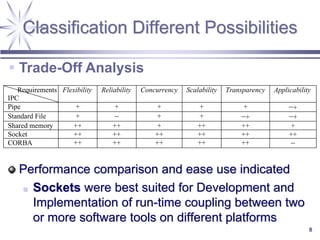
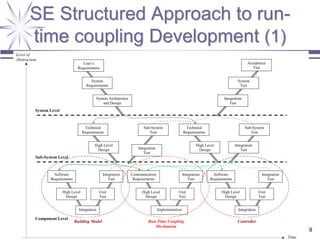
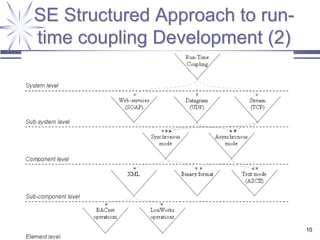
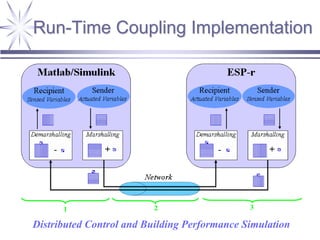
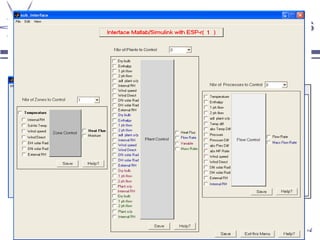
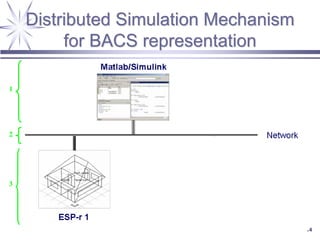
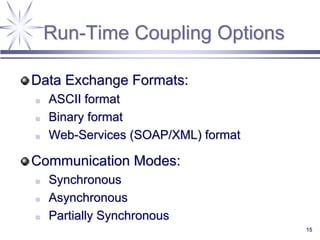
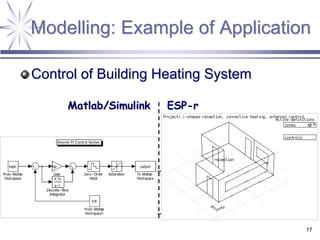
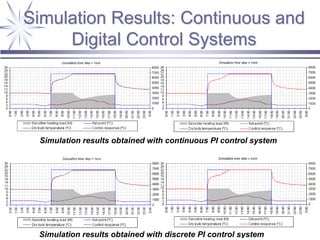
The document discusses a framework for distributed control and performance simulation in building automation systems, specifically integrating MATLAB/Simulink with ESP-R. It outlines the challenges, proposed solutions, and the advantages of a run-time coupling mechanism that facilitates interaction between different simulation platforms. Future work aims to extend this framework for complex, large-scale building control applications.