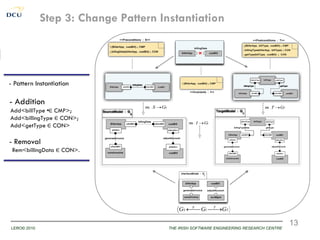
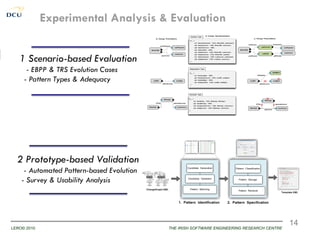
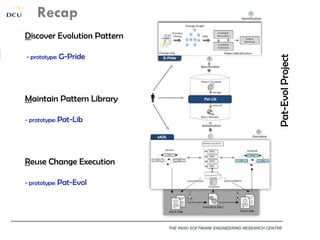
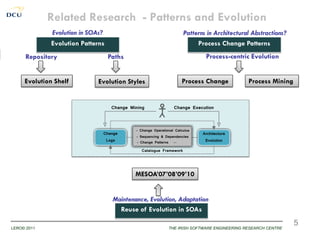
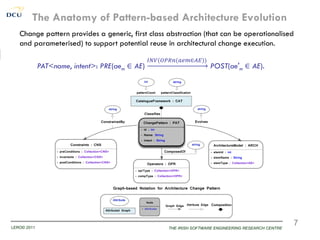
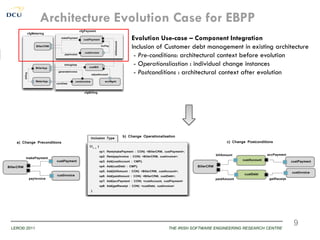
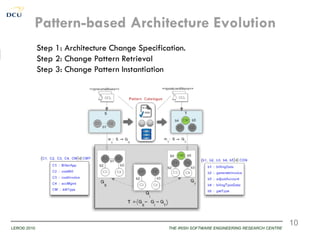
This document discusses using patterns to guide architecture evolution in service-driven systems. It proposes identifying recurring architecture change patterns from logs, formally specifying patterns in a catalogue, and reusing patterns to support evolution. An example evolution case integrating a new component is presented. A pattern-based evolution process involves specifying changes, retrieving relevant patterns, and instantiating patterns to implement the changes. The approach is experimentally analyzed using evaluation scenarios and a prototype for automated pattern-based evolution. Maintaining a pattern library could help discover, specify and reuse patterns to guide architecture-centric software evolution.
![Pattern-driven Reuse in Architecture-centric
Welcome
Evolution for Service Software
Aakash Ahmad, Pooyan Jamshidi and Claus Pahl
Presentation Title
[ahmad.aakash|pooyan.jamshidi|claus.pahl]@computing.dcu.ie
Software and System Engineering group
http://www.computing.dcu.ie/~cpahl/sse-group.htm
School of Computing, Dublin City University, Ireland
THE IRISH SOFTWARE ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTRE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icsoft12pdf-120719113922-phpapp02/85/Pattern-based-Evolution-1-320.jpg)

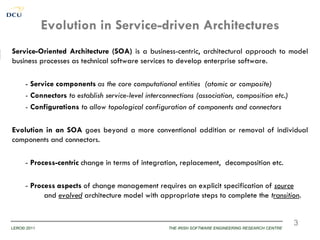
![The needs for Reuse in Service Architecture Evolution
A continuous change in business and technical requirements lead towards frequent
maintenance and evolution cycles in service software.
…community wide efforts are required to develop processes, framework and
patterns etc., to enable systematic maintenance an explicit evolution for SOAs …
[MESOA 07, 08, 09, 10]
4
LERO© 2011 THE IRISH SOFTWARE ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTRE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icsoft12pdf-120719113922-phpapp02/85/Pattern-based-Evolution-4-320.jpg)
![Change Patterns to guide Architecture Evolution
Central Hypothesis: The application of change patterns to architectural transformation supports potential
reuse in architecture-centric software evolution.
Pattern Identification – recurring sequences from Architecture Change Logs [IWSSA’12]
Pattern Specification – once-off formal specification in Pattern Catalogue [SHARK’12]
Pattern Instantiation – multiple instantiations to support pattern-based reuse in evolution.
Pattern-based Evolution Benefits for Pattern-based Reuse
6
LERO© 2011 THE IRISH SOFTWARE ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTRE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icsoft12pdf-120719113922-phpapp02/85/Pattern-based-Evolution-6-320.jpg)
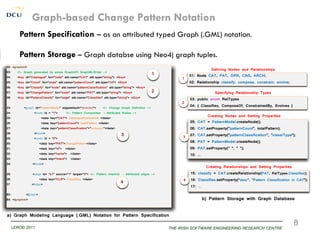
![Step 1: Change Specification
A declarative specification allows syntactical context of architectural change:
i) Source Architecture Model (GS)
ii) Architectural Constraints as pre- and post-conditions (PRE, POST ∈ [CNS])
iii) Architecture Elements (AE) that need to evolved such that AE ∈ GS.
Context Constraints: Gs inv, pre, post -- Constraints specification on architecture model
-- Invarinats for structural integrity of component and connector
inv: Constraints.INV -> forAll(Component.hasPORT >= 1)
-- Preconditions to specify existence of architecture elements before evolution
pre: Constraints.PRE -> exists(Component = ‘BillerApp’)
pre: Constraints.PRE -> exists(Connector(BillerApp, custBill) | Connector = ‘billingData’)
-- Post to specify existence of architecture elements after evolution
post: Constraints.POST-> exists(Component = ‘BillerApp’)
post: Constraints.POST -> exists(Component = ‘custBill’)
post: Constraints.POST -> exists(Connector(billType, custBill) | Connector = ‘getType’)
OCL-based Constraints Specification on Architecture Models
11
LERO© 2010 THE IRISH SOFTWARE ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTRE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icsoft12pdf-120719113922-phpapp02/85/Pattern-based-Evolution-11-320.jpg)
![Step 2: Change Pattern Retrieval
(Root) <relatesTo> [Nodes] :
(ChangePattern) <isComposedOf, ConstrainedBy, Evolves> [Operators | Constraints | ArchitectureModel]
Query - Which change pattern(s) allow integration of a mediator component among two directly connected
components?
01: START pattern = node(ChangePattern)
02: MATCH (pattern) – [:ConstrainedBy] - > (Constraints)
03: – [:Composedof] - > (Operators)
04: WHERE Operators IS NOT Null
05: RETURN ChangPattern.name, ChangePattern.intent, Operators.operatorType
Listing: Cypher Query to Retrieve Pattern Name, Intent and Operationalisation
START - command to set the primary node(s),
MATCH - based on user-specified change constraints respectively.
WHERE - allows for additional conditional checking, while
RETURN - provides the gathered results.
12
LERO© 2010 THE IRISH SOFTWARE ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTRE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icsoft12pdf-120719113922-phpapp02/85/Pattern-based-Evolution-12-320.jpg)