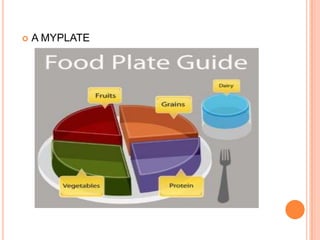
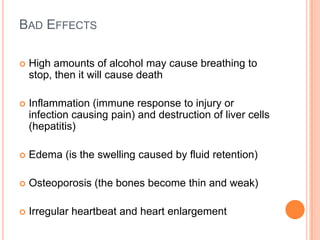
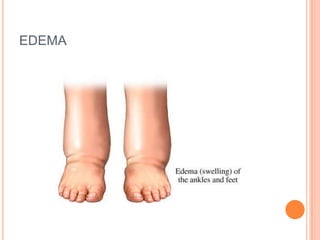
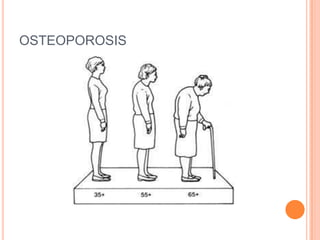
A balanced diet consists of foods from all food groups eaten in moderation, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and fiber. It helps ensure intake of necessary nutrients. Alcohol is absorbed in the stomach and intestines and affects the mind and body. High amounts can cause breathing to stop and death, while regular consumption is linked to inflammation and destruction of the liver, edema, osteoporosis, and irregular heartbeats. Fatty foods provide energy but saturated and trans fats are linked to high cholesterol, heart disease, and diabetes if consumed in excess.