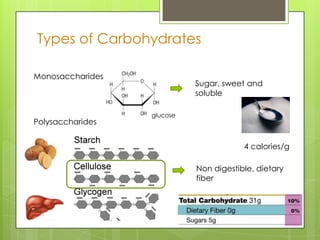
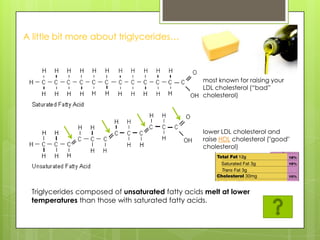
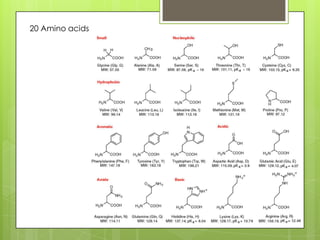
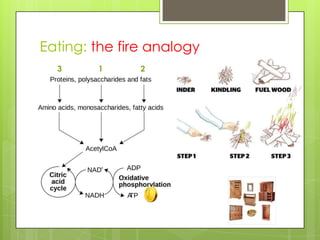
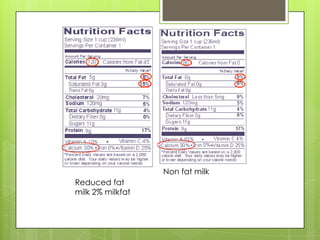
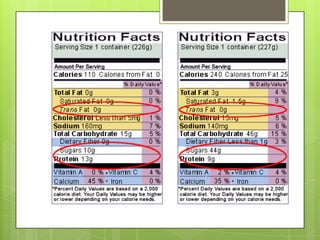
This document discusses the biochemistry of the molecules that make up living things. It focuses on carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Carbohydrates like glucose are a source of energy, while lipids store energy and make up cell membranes. Proteins have many roles including structure, transport, and catalyzing reactions as enzymes. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, while the building blocks of carbohydrates and lipids are carbon-containing molecules. Overall, the document examines the essential macronutrients that power our bodies and allow for life.