The document discusses arrays in Java programming. It covers topics like declaring and initializing one-dimensional arrays, accessing array elements, passing arrays as method parameters, common array operations like finding the largest/smallest element, and arrays of objects. Multidimensional arrays and methods for processing arrays are also introduced.




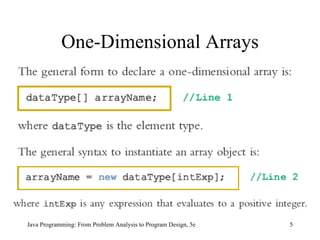
![Array num: int [] num = new int [5]; Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e Arrays](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-8-320.jpg)
![Array num: int [] num = new int [5]; Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e Arrays (continued)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-9-320.jpg)
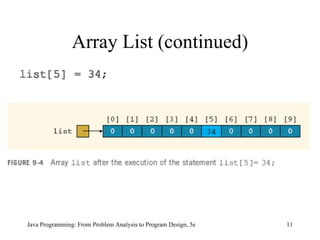
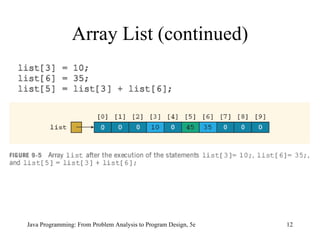


![The initializer list contains values, called initial values , that are placed between braces and separated by commas sales[0]= 12.25 , sales[1]= 32.50 , sales[2]= 16.90 , sales[3]= 23.00 , and sales[4]= 45.68 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e Array Initialization during Declaration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-15-320.jpg)

![Associated with each array that has been instantiated, there is a public ( final ) instance variable length The variable length contains the size of the array The variable length can be directly accessed in a program using the array name and the dot operator int [] list = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60}; Arrays and the Instance Variable length Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-17-320.jpg)
![Arrays and the Instance Variable length (continued) This statement creates the array list of six components and initializes the components using the values given Here list.length is 6 int [] numList = new int[10]; This statement creates the array numList of 10 components and initializes each component to 0 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-18-320.jpg)
![The value of numList.length is 10 numList[0] = 5; numList[1] = 10; numList[2] = 15; numList[3] = 20; These statements store 5 , 10 , 15 , and 20 , respectively, in the first four components of numList You can store the number of filled elements, that is, the actual number of elements, in the array in a variable, say numOfElement It is a common practice for a program to keep track of the number of filled elements in an array Arrays and the Instance Variable length (continued) Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-19-320.jpg)
![Loops used to step through elements in array and perform operations int [] list = new int[100]; int i; for (i = 0; i < list.length; i++) //process list[i], the (i + 1)th //element of list for (i = 0; i < list.length; i++) list[i] = console.nextInt(); for (i = 0; i < list.length; i++) System.out.print(list[i] + " "); Processing One-Dimensional Arrays Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-20-320.jpg)
![Arrays (continued) Some operations on arrays Initialize Input data Output stored data Find largest/smallest/sum/average of elements Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e double [] sales = new double [10]; int index; double largestSale, sum, average;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-21-320.jpg)
![Code to Initialize Array to Specific Value (10.00) Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e for ( int index = 0; index < sales.length; index++) sales[index] = 10.00;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-22-320.jpg)
![Code to Read Data into Array Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e for ( int index = 0; index < sales.length; index++) sales[index] = console.nextDouble();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-23-320.jpg)
![Code to Print Array Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e for ( int index = 0; index < sales.length; index++) System.out.print(sales[index] + " ");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-24-320.jpg)
![Code to Find Sum and Average of Array Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e sum = 0; for ( int index = 0; index < sales.length; index++) sum = sum + sales[index]; if (sales.length != 0) average = sum / sales.length; else average = 0.0;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-25-320.jpg)
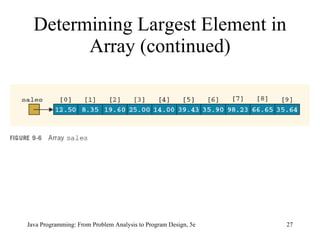
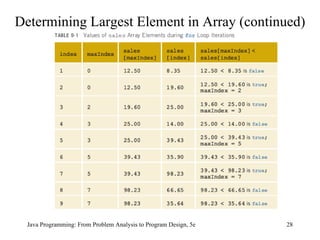
![Determining Largest Element in Array Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e maxIndex = 0; for ( int index = 1; index < sales.length; index++) if (sales[maxIndex] < sales[index]) maxIndex = index; largestSale = sales[maxIndex];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-26-320.jpg)

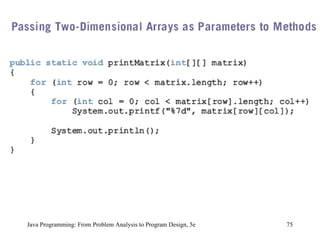
![Declaring Arrays as Formal Parameters to Methods A general syntax to declare an array as a formal parameter dataType[] arrayName public static void arraysAsFormalParameter( int [] listA, double [] listB, int num) { //... } int [] intList = new int [10]; double [] doubleNumList = new double [15]; int number; arraysAsFormalParameter(intList, doubleNumList, number); Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-30-320.jpg)
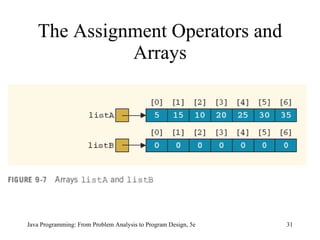
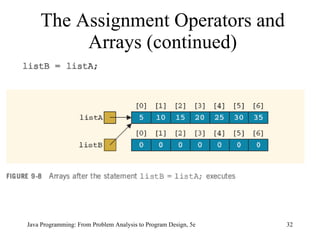


![Relational Operators and Arrays (continued) Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e boolean areEqualArrays ( int [] firstArray, int [] secondArray) { if (firstArray.length != secondArray.length) return false ; for ( int index = 0; index < firstArray.length; index++) if (firstArray[index] != secondArray[index]) return false ; return true ; } if (areEqualArrays(listA, listB)) ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-35-320.jpg)




![Suppose that you want to determine whether 27 is in the list First you compare 27 with list[0] Because list[0] ≠ 27 , you then compare 27 with list[1] Because list[1] ≠ 27 , you compare 27 with list[2] ; because list[2] = 27 , the search stops This search is successful Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-41-320.jpg)
![Search for 10 Search starts at the first element in the list, that is, at list[0] This time, the search item, which is 10 , is compared with every item in the list; eventually, no more data is left in the list to compare with the search item; this is an unsuccessful search Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-42-320.jpg)
![public static int seqSearch( int [] list, int listLength, int searchItem) { int loc; boolean found = false ; loc = 0; while (loc < listLength && !found) if (list[loc] == searchItem) found = true ; else loc++; if (found) return loc; else return -1; } Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-43-320.jpg)
![Arrays of Objects Can use arrays to manipulate objects Example: create array named array1 with N objects of type T T[] array1 = new T[N] Can instantiate array1 as follows: for ( int j = 0; j <array1.length; j++) array1[j] = new T(); Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-44-320.jpg)
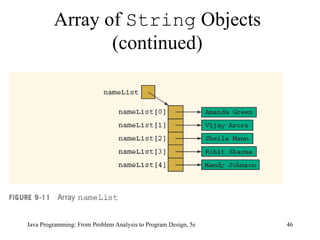
![Array of String Objects String[] nameList = new String[5]; nameList[0] = "Amanda Green"; nameList[1] = "Vijay Arora"; nameList[2] = "Sheila Mann"; nameList[3] = "Rohit Sharma"; nameList[4] = "Mandy Johnson"; Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-45-320.jpg)
![Clock[] arrivalTimeEmp = new Clock[100]; Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e Arrays of Objects (continued)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-47-320.jpg)
![Instantiating Array Objects Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e for ( int j = 0; j < arrivalTimeEmp.length; j++) arrivalTimeEmp[j] = new Clock();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-48-320.jpg)
![Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e arrivalTimeEmp[49].setTime(8, 5, 10); Instantiating Array Objects (continued)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-49-320.jpg)

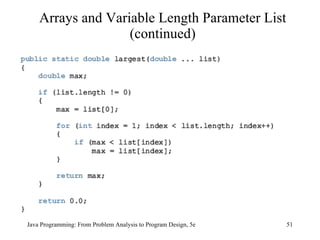


![foreach loop (continued) sum = 0; for ( double num : list) sum = sum + num; The for statement in Line 2 is read: for each num in list The identifier num is initialized to list[0] In the next iteration, the value of num is list[1] , and so on for ( double num : numList) { if (max < num) max = num; } Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-56-320.jpg)
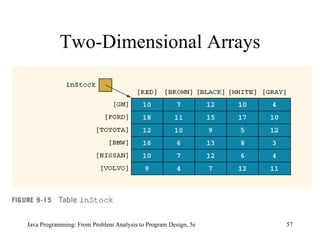

![double [][] sales = new double [10][5]; Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e Two-Dimensional Arrays (continued)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-59-320.jpg)

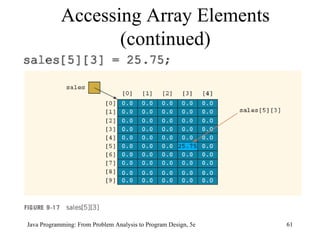

![Two-Dimensional Arrays and the Instance Variable length (continued) Each row of matrix is a one-dimensional array; matrix[0] , in fact, refers to the first row The value of the expression: matrix[0].length is 15, the number of columns in the first row matrix[1].length gives the number of columns in the second row, which in this case is 15, and so on Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-63-320.jpg)
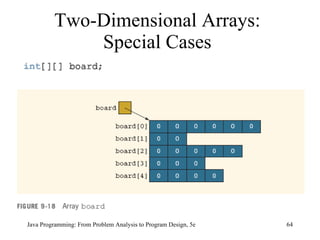

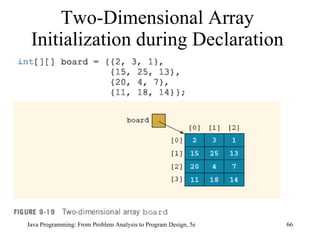

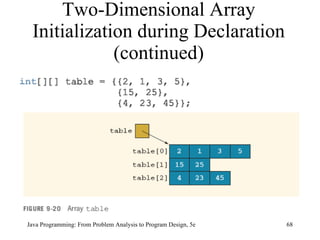
![Two-Dimensional Arrays: Processing Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e Initialization for ( int row = 0; row < matrix.length; row++) for ( int col = 0; col < matrix[row].length; col++) matrix[row][col] = 10; Print for ( int row = 0; row < matrix.length; row++) { for ( int col = 0; col < matrix[row].length; col++) System.out.printf("%7d", matrix[row][col]); System.out.println(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-70-320.jpg)
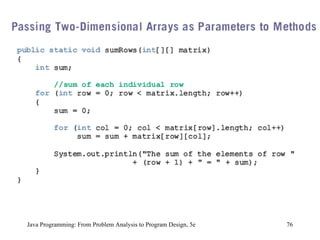
![Two-Dimensional Arrays: Processing (continued) Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e Input for ( int row = 0; row < matrix.length; row++) for ( int col = 0; col < matrix[row].length; col++) matrix[row][col] = console.nextInt(); Sum by Row for ( int row = 0; row < matrix.length; row++) { sum = 0; for ( int col = 0; col < matrix[row].length; col++) sum = sum + matrix[row][col]; System.out.println("Sum of row " + (row + 1) + " = "+ sum); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-71-320.jpg)
![Two-Dimensional Arrays: Processing (continued) Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e Sum by Column for ( int col = 0; col < matrix[0].length; col++) { sum = 0; for ( int row = 0; row < matrix.length; row++) sum = sum + matrix[row][col]; System.out.println("Sum of column " + (col + 1) + " = " + sum); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-72-320.jpg)
![Two-Dimensional Arrays: Processing (continued) Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e Largest Element in Each Row for ( int row = 0; row < matrix.length; row++) { largest = matrix[row][0]; for ( int col = 1; col < matrix[row].length; col++) if (largest < matrix[row][col]) largest = matrix[row][col]; System.out.println("The largest element of row " + (row + 1) + " = " + largest); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-73-320.jpg)
![Two-Dimensional Arrays: Processing (continued) Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e Largest Element in Each Column for ( int col = 0; col < matrix[0].length; col++) { largest = matrix[0][col]; for ( int row = 1; row < matrix.length; row++) if (largest < matrix[row][col]) largest = matrix[row][col]; System.out.println("The largest element of col " + (col + 1) + " = " + largest); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-74-320.jpg)

![Multidimensional Arrays Can define three-dimensional arrays or n-dimensional array (n can be any number) Syntax to declare and instantiate array d ataType[][]…[] arrayName = new dataType[intExp1][intExp2]…[intExpn]; Syntax to access component arrayName[indexExp1][indexExp2]…[indexExpn] intExp1 , intExp2 , ..., intExpn = positive integers indexExp1,indexExp2 , ..., indexExpn = non-negative integers Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-78-320.jpg)
![Loops to Process Multidimensional Arrays Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 5e double [][][] carDealers = new double [10][5][7]; for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i++) for ( int j = 0; j < 5; j++) for ( int k = 0; k < 7; k++) carDealers[i][j][k] = 10.00;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9781111530532pptch09-111003182050-phpapp01/85/9781111530532-ppt-ch09-79-320.jpg)



