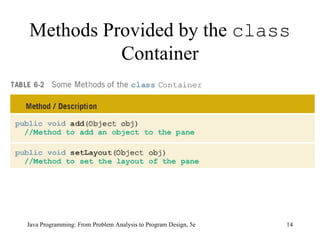
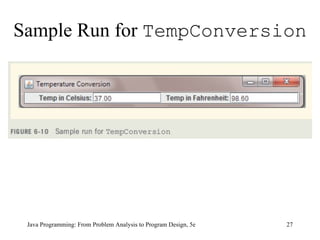
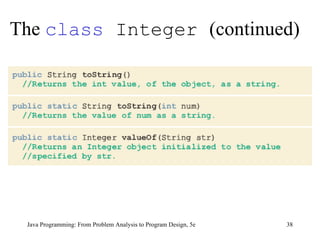
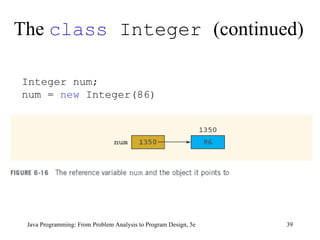
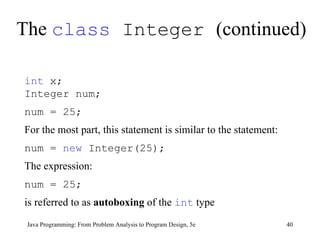
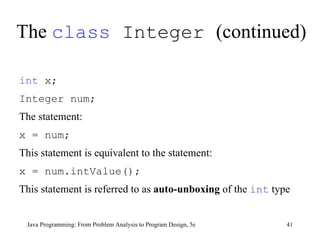
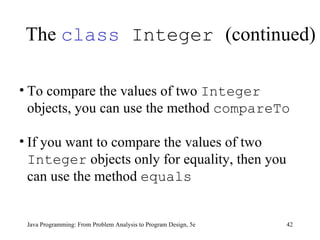
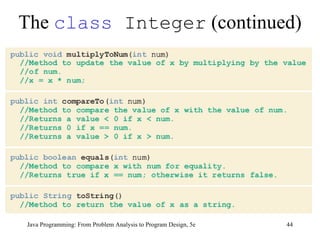
This chapter discusses graphical user interfaces (GUIs) and object-oriented design in Java programming. It covers basic GUI components like JFrame, JLabel, JTextField and JButton. It explains how events and listeners work in GUI applications and provides examples of designing classes and methods for a temperature converter program and a candy machine program. The chapter summary emphasizes the key concepts like creating windows with JFrame, using labels, text fields and buttons to build the GUI, handling events with listeners, and applying object-oriented principles to problem solving.