1) Arrays allow storing and accessing multiple values of the same data type. They are declared with the data type, followed by square brackets and the array name.
2) Array components are accessed using their index number within square brackets after the array name. Index numbers start at 0.
3) The length property returns the number of components in the array, which must be considered to avoid accessing components outside the bounds of the array.


![import java.util.*;
public class ReverseOrder
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
int item0, item1, item2, item3, item4;
int sum;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter five integers one number per line");
item0 = input.nextInt();
item1 = input.nextInt();
item2 = input.nextInt();
item3 = input.nextInt();
item4 = input.nextInt();
sum = item0 + item1 + item2 + item3 + item4;
System.out.println("The sum of the numbers = " + sum);
System.out.println("The numbers in reverse order are: ");
System.out.println(item4 + " " + item3 + " " + item2 + " " + item1 +
" " + item0);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-3-2048.jpg)


![One-Dimensional Arrays
Syntax to declare an array:
Syntax to access an array component:
arrayName[indexExp]
<dataType>[] <arrayName> = new <dataType>[intExp];
Or
<dataType> <arrayName>[]= new <dataType>[intExp];
1. dataType : a type of data will be store in
array or component type
2. arrayName : a reference variable for array
3. intExp : size of an array (> 0)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-6-2048.jpg)
![Example
This statement declare and
creates the array num of 5
components.
Each component is int data type
The components are num[0],
num[1], num[2], num[3], num[4]
The value in square bracket [ ] is
call index and it start at 0
int[] num = new int[5]; or
int num[] = new int[5];
num](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-7-2048.jpg)
![Continue
In java, [ ] is call as array subscripting operator
Items in an array is called elements
element
index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-8-2048.jpg)
![Continue
Array of five
integers called test
Array of five
characters
called grade
test[0] = 85;
test[1] = 98;
test[2] = 75;
test[3] = 87;
test[4] = 68;
grade[0] = ‘B’;
grade[1] = ‘C’;
grade[2] = ‘B’;
grade[3] = ‘A’;
grade[4] = ‘C’;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-9-2048.jpg)
![Assign a value into array
Assume the declaration as above.
Statement;
list[3] = 10;
list[6] = 35;
list[5] = list[3] + list[6];
will store 10, 45 and 35 into the array in list[3],
list[5] and list[6] respectively. (see next figure)
int[] list = new int[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-10-2048.jpg)

![Specifying Array Size During
Program
Execution (dynamic array)
Array that are created during program execution is
called dynamic array
Enables user to specify the size of the array
The system use the value of arraysize to
instantiate the object list
int arraySize;
System.out.print("Enter the size of the array: ");
arraySize = input.nextInt();
int[] list = new int[arraySize];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-12-2048.jpg)
![Array Initialization During
Declaration
We also can assign a value into the array during
declaration
The values, called initial values, are placed
between braces and separated by commas
When declaring and initializing arrays, the size
of the array is determined by the number of
initial values within the braces.
If an array is declared and initialized
simultaneously, we do not use the operator new
to instantiate the array object.
double[]sales = {12.25, 32.50, 16.90, 23.00,
45.68};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-13-2048.jpg)
![Arrays and the Instance Variable
length
A public instance variable length is associated with
each array that has been instantiated.
The variable length contains the size of the array.
The variable length can be directly accessed in a
program using the array name and the dot operator.
int[] list = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60};
This statement creates the array list of six components
and initializes the components using the values given.
Here list.length is 6.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-14-2048.jpg)

![1. Initializing an array to a specific
value
Eg.
to initialize every component of the array
sale with a value of 10.00
double[] sales = new double[10];
int index;
for (index = 0; index < sales.length;index++)
sales[index] = 10.00;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-16-2048.jpg)
![2. Input data into an array
double[] sales = new double[10];
int index;
for (index = 0; index < sales.length;index++)
sales[index] = input.nextDouble();
double[] sales = new double[10];
int index;
for(index = 0; index < sales.length;index++)
System.out.print(sales[index] + " ");
3. Printing an array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-17-2048.jpg)
![4. Find the sum and average of an
array
double[] sales = new double[10];
int index, sum;
double average;
sum = 0;
for(index = 0; index < sales.length;index++)
sum = sum + sales[index];
if (sales.length != 0)
average = sum / sales.length;
else
average = 0.0;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-18-2048.jpg)
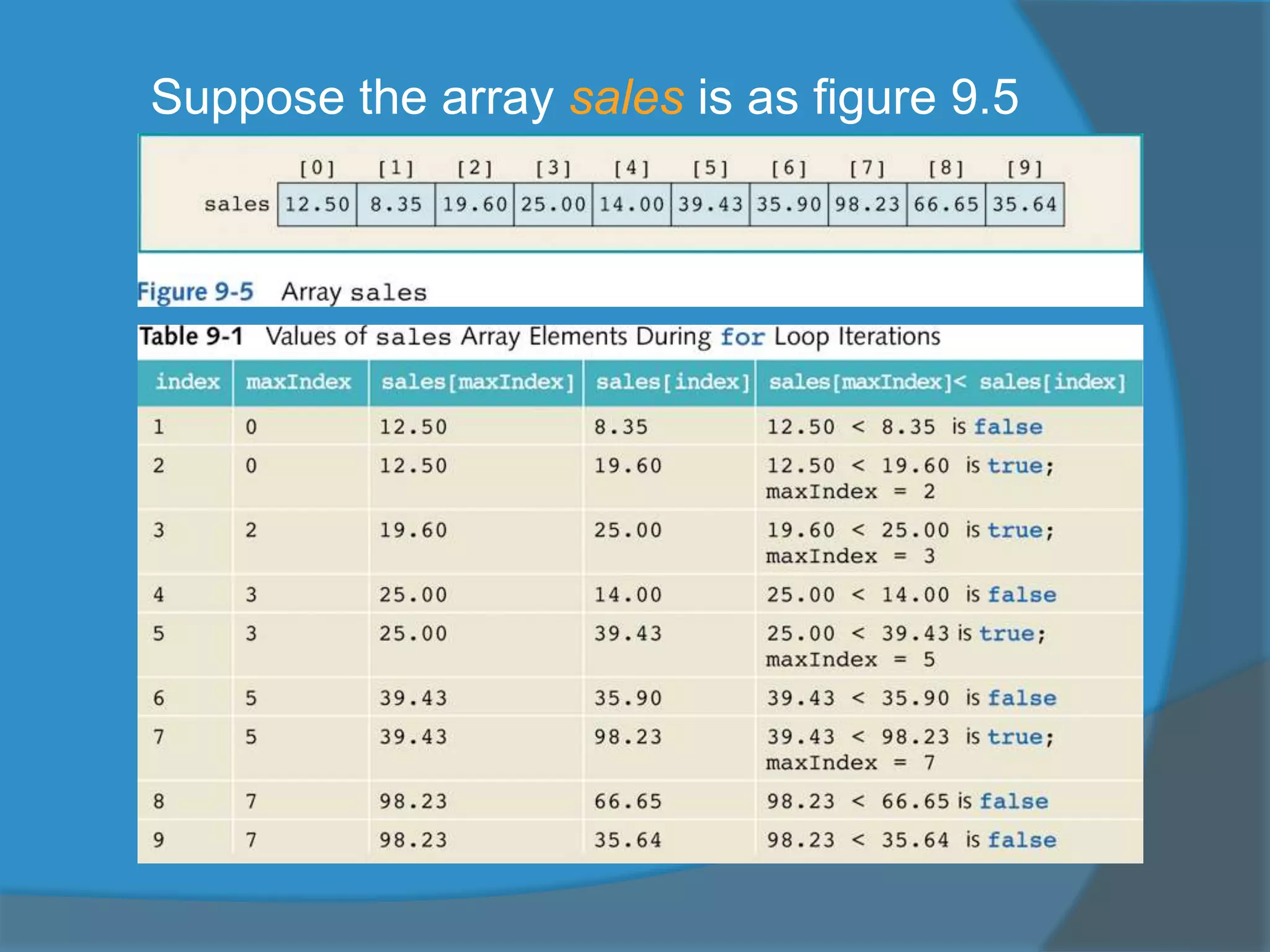
![5. Determining the largest element
in the array
double[] sales = new double[10];
int index, maxIndex;
double largestSale;
maxIndex = 0;
for(index = 1; index<sales.length;index++)
if (sales[maxIndex] < sales[index])
maxIndex = index;
largestSale = sales[maxIndex];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-19-2048.jpg)

![example
Consider the following declaration:
The component num[i] is valid if i = 0, 1,
2….9
When i < 0 or i >= 10, the component
num[i] is invalid (the index is out of bounds)
double[] num = double[10];
int i;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-22-2048.jpg)
![Consider the following loops
for (i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
list[i] = 5;
When i = 10; list[i] =
list[10] = 5;
The program tries to access
list[10] but does not exist
We say the index is out of
bound
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
list[0]
list[1]
list[2]
list[3]
list[4]
list[5]
list[6]
list[7]
list[8]
list[9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swcrcdxlqg2nwc2xofr0-140524210931-phpapp02/75/Chapter-7-1-23-2048.jpg)