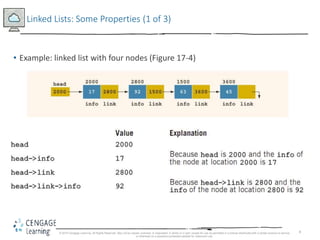
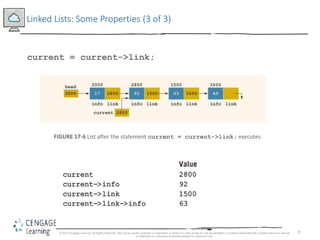
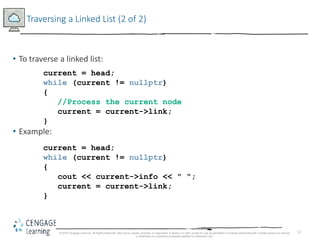
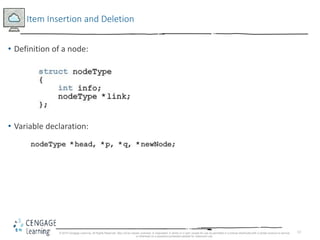
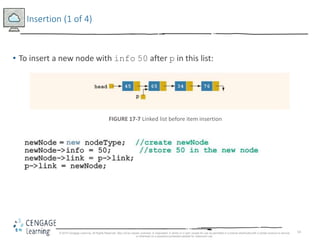
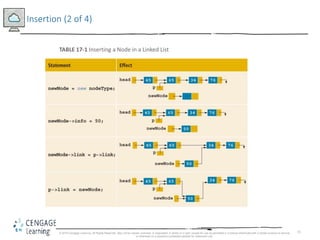
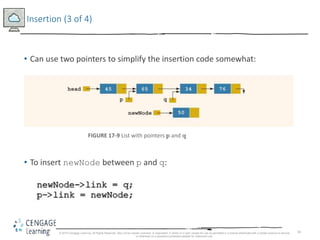
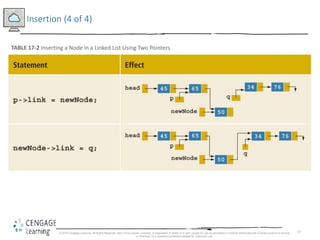
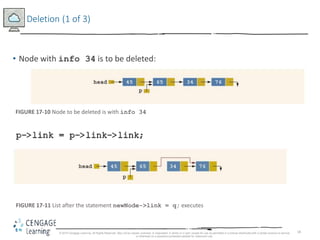
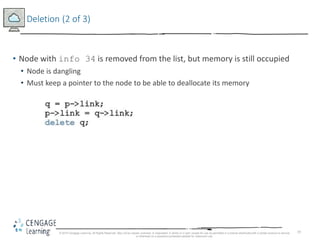
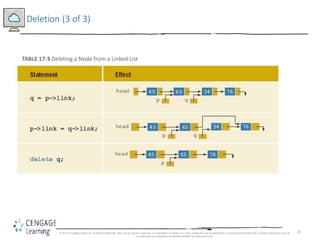
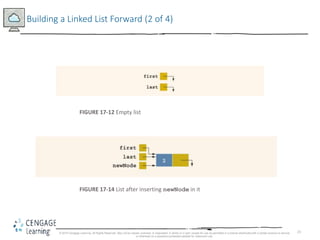
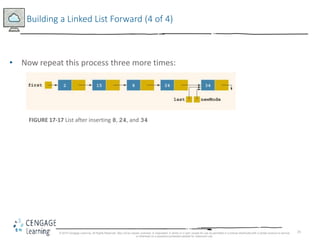
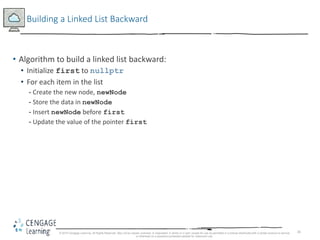
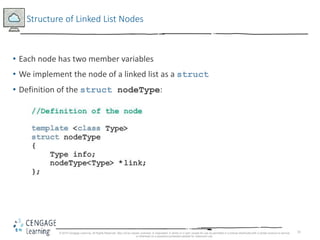
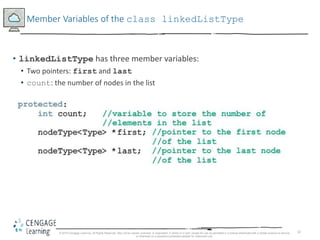
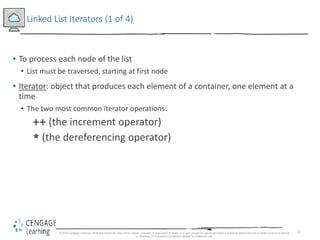
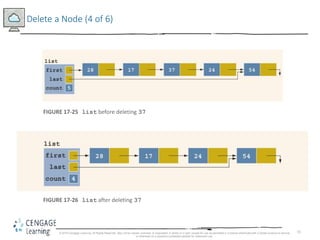
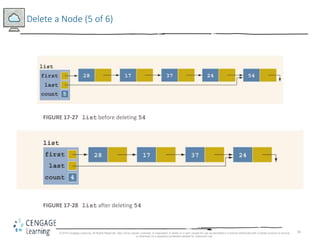
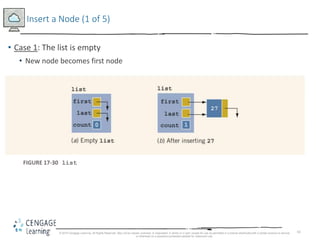
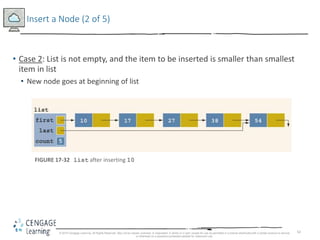
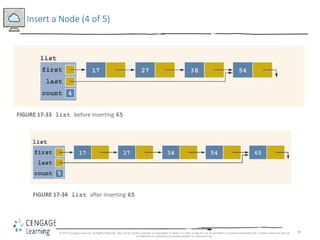
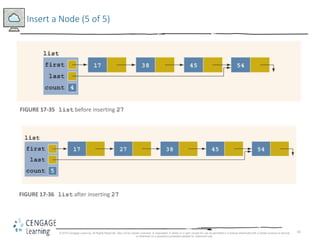
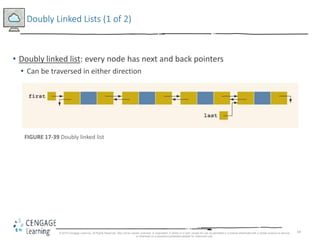
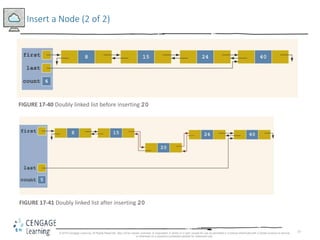
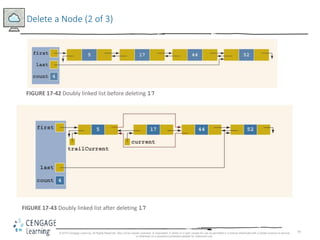
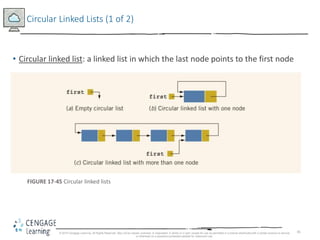
This document discusses linked lists and their implementation in C++. It covers the basic properties of linked lists, including how they are composed of nodes that contain data and a pointer to the next node. The key operations of linked lists are described, such as traversing the list, inserting and deleting nodes, and building the list in both the forward and backward directions. Implementing linked lists as an abstract data type is also covered, including defining iterator classes to iterate through the list.