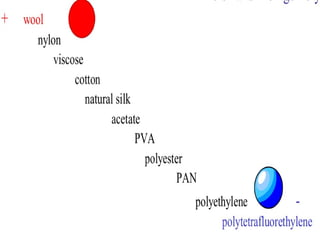
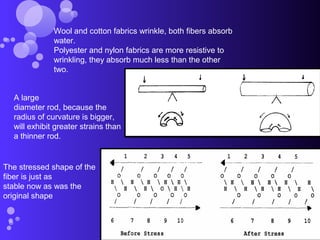
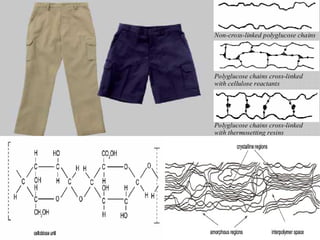
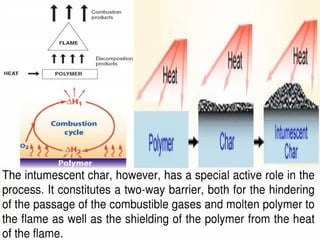
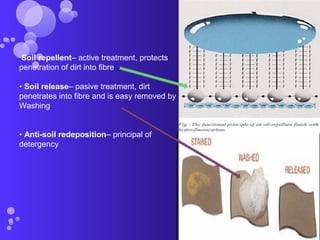
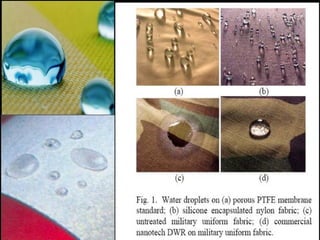
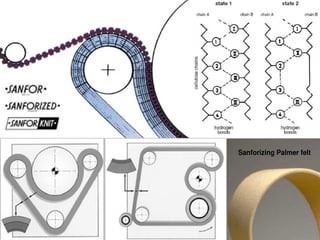
The document discusses various types of fabric finishes including:
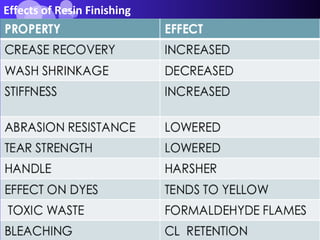
- Resin finishes which increase the intermolecular rigidity of cellulosic fabrics like cotton to reduce creasing.
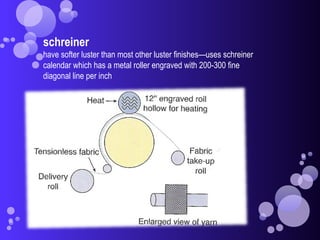
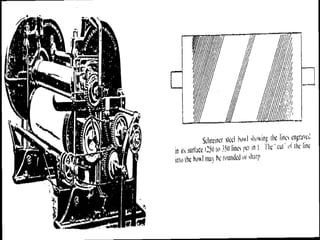
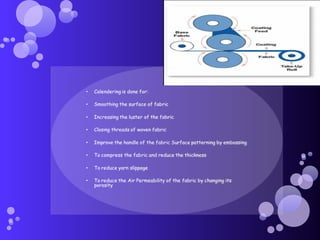
- Glazed finishes which produce a highly polished surface using calendaring.
- Moire finishes which create a wood grain or watermarked appearance.
- Pleated finishes which can be produced by hand folding or using patterned papers and machine blades.
- Embroidered finishes which involve decorating fabrics with surface-applied thread by hand or machine.
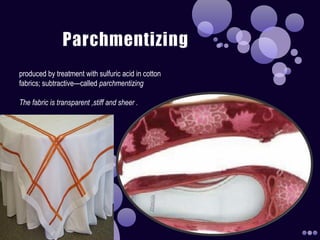
- Parchmentized finishes which make cotton fabrics transparent, stiff and sheer through sulfuric acid treatment.