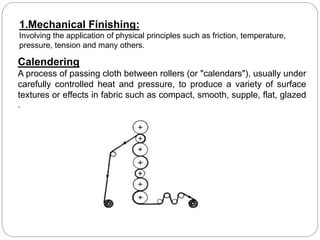
Textile finishing involves mechanical or chemical processes to increase a material's aesthetic and functional properties. It is done to make materials more presentable and durable for customers. There are different types of finishes including aesthetic finishes to modify appearance; functional finishes to improve performance; physical/mechanical finishes using treatments like calendaring and napping; and chemical finishes applied with chemicals and curing. Examples of specific finishes are crease-resistant for wrinkle-free fabrics, water-repellent for outdoor wear, and antimicrobial to protect against microbes. Finishing aims to enhance properties like appearance, feel, durability, and functionality.