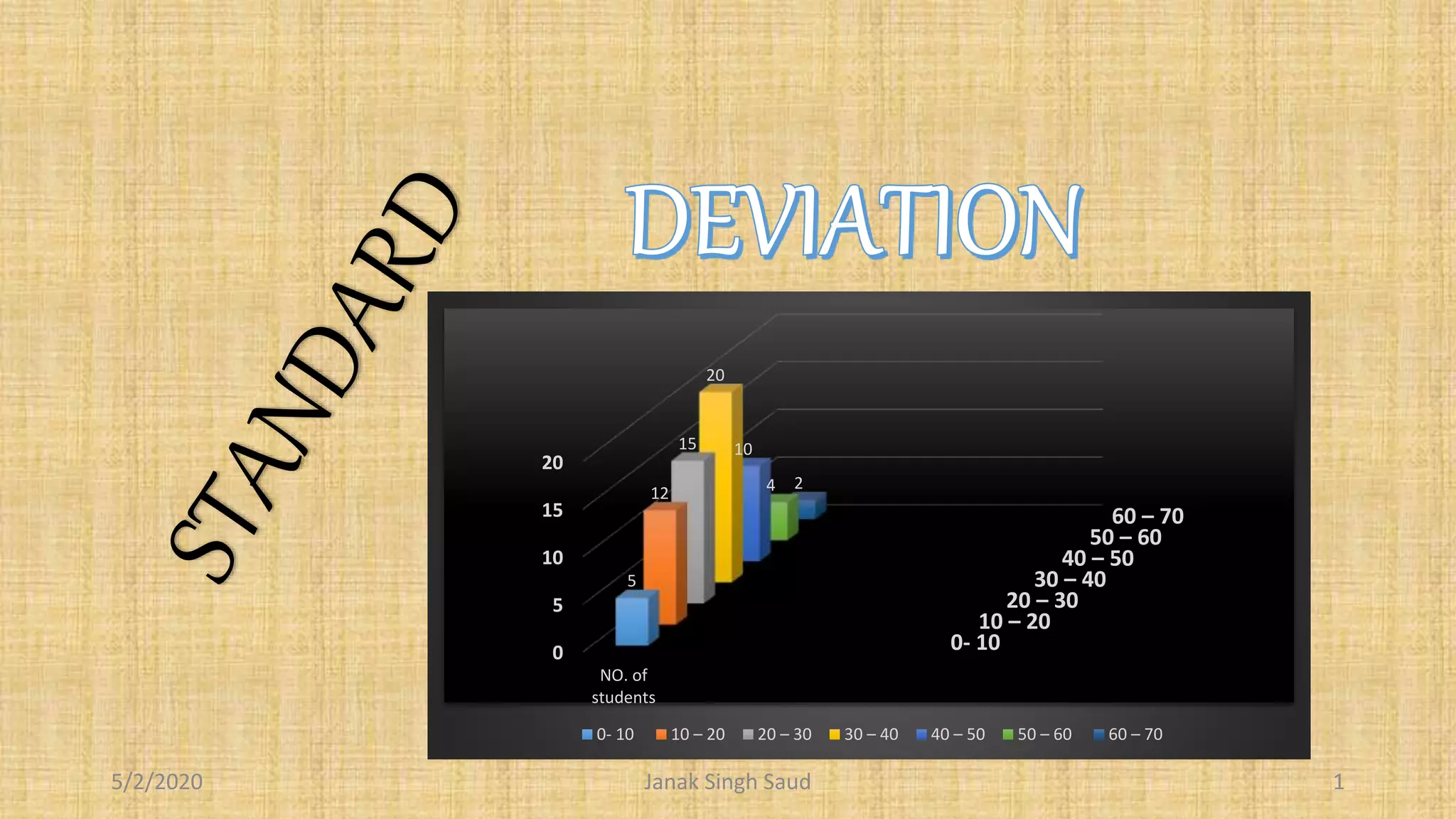
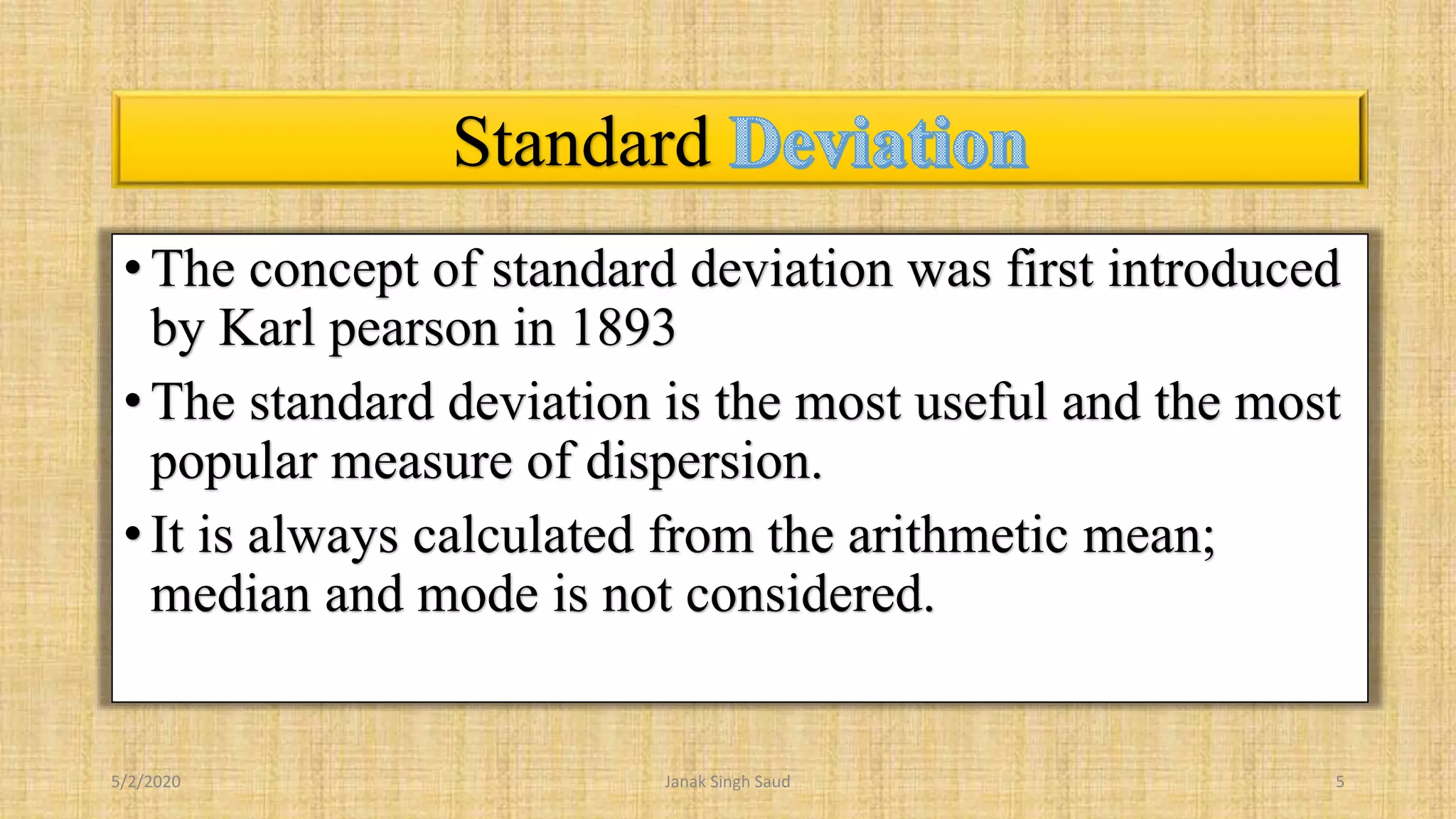
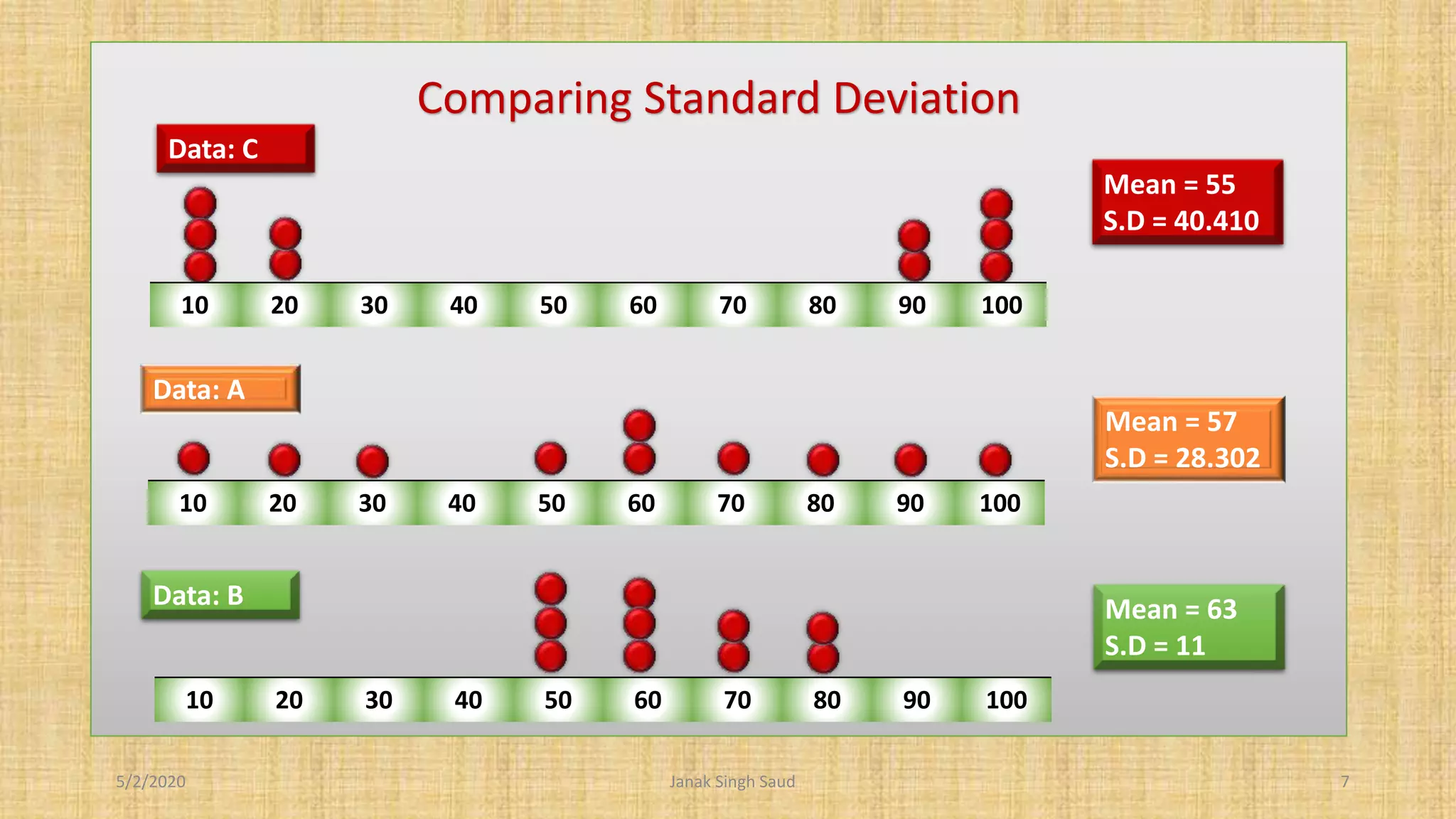
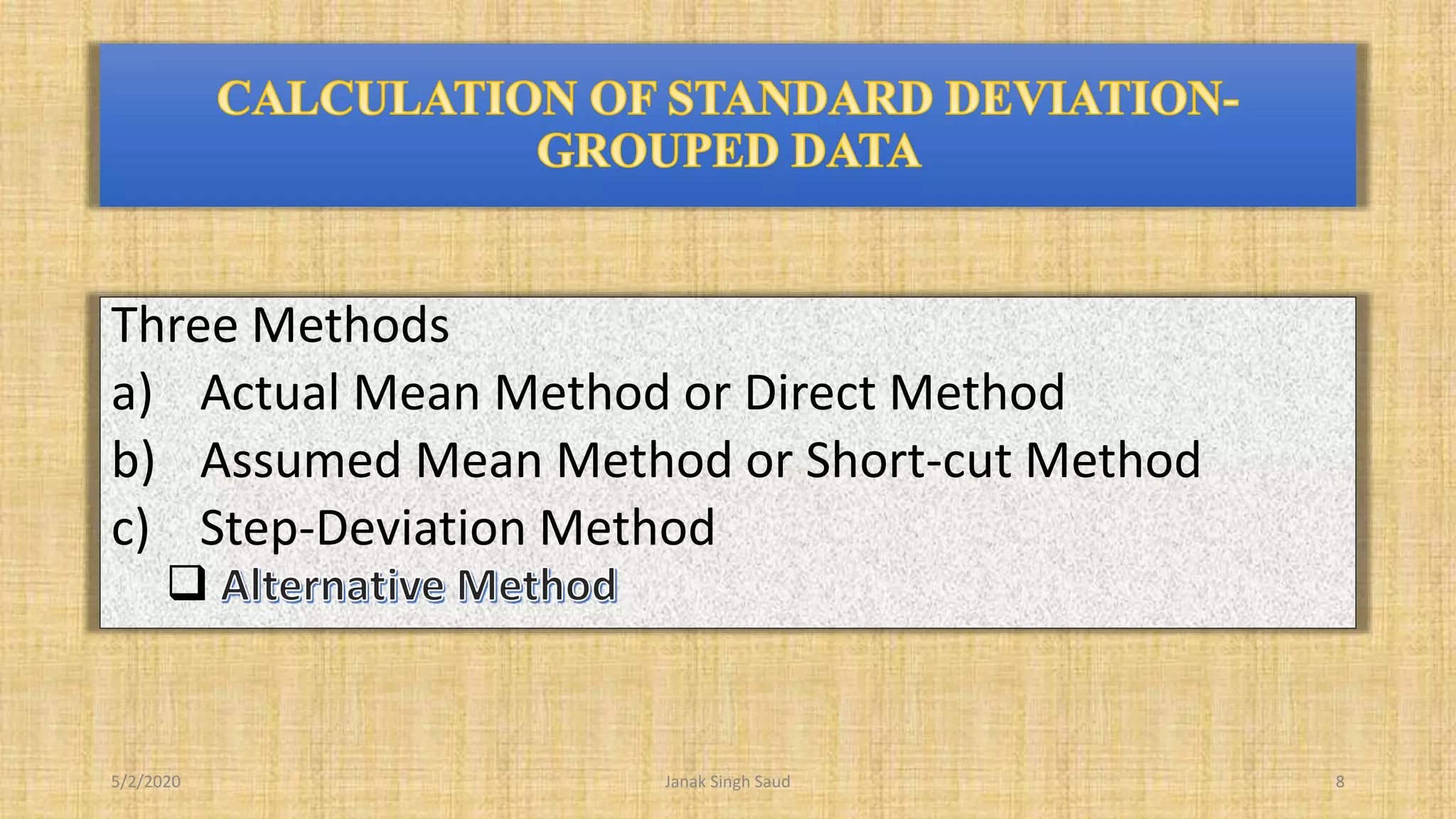
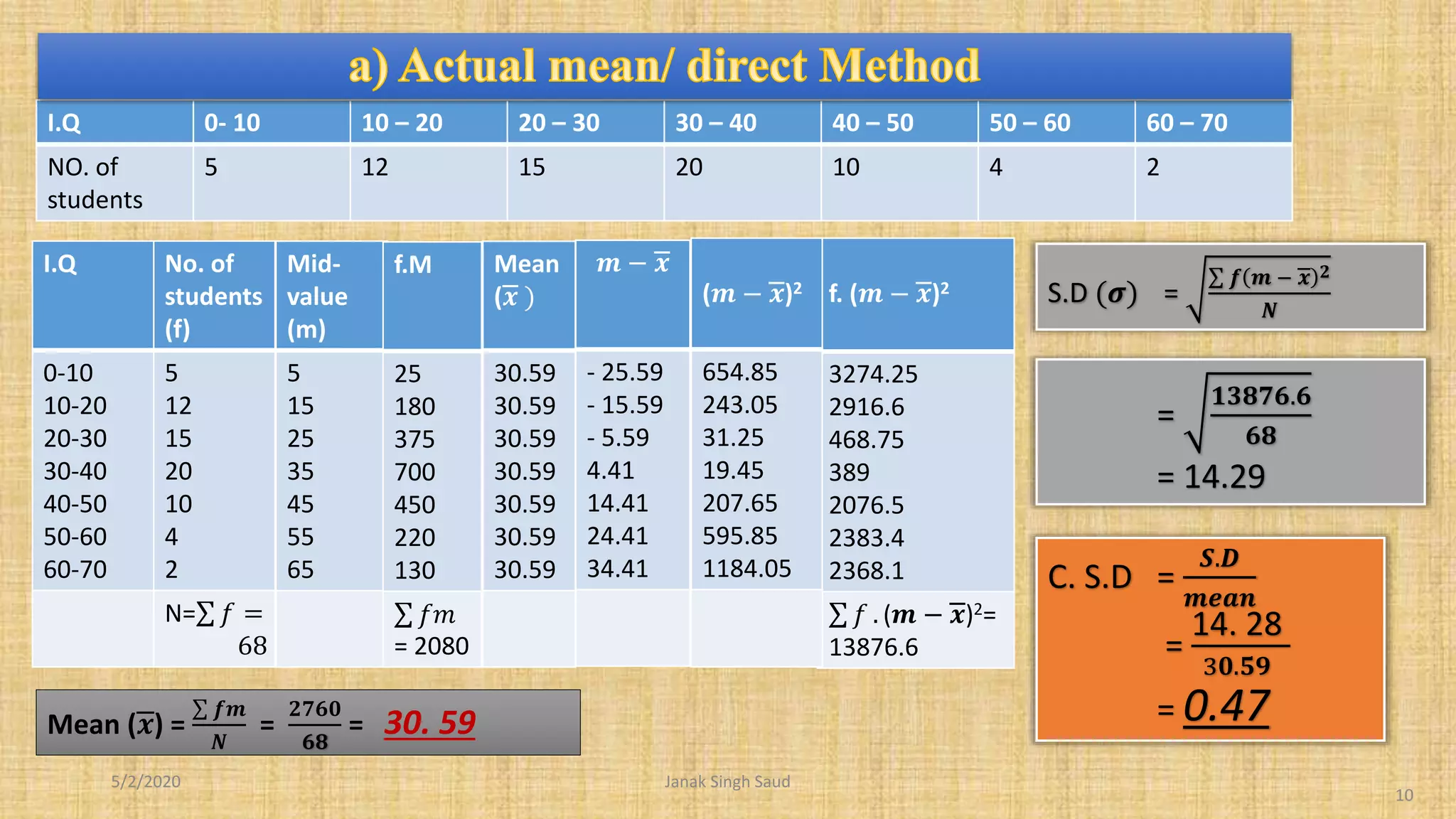
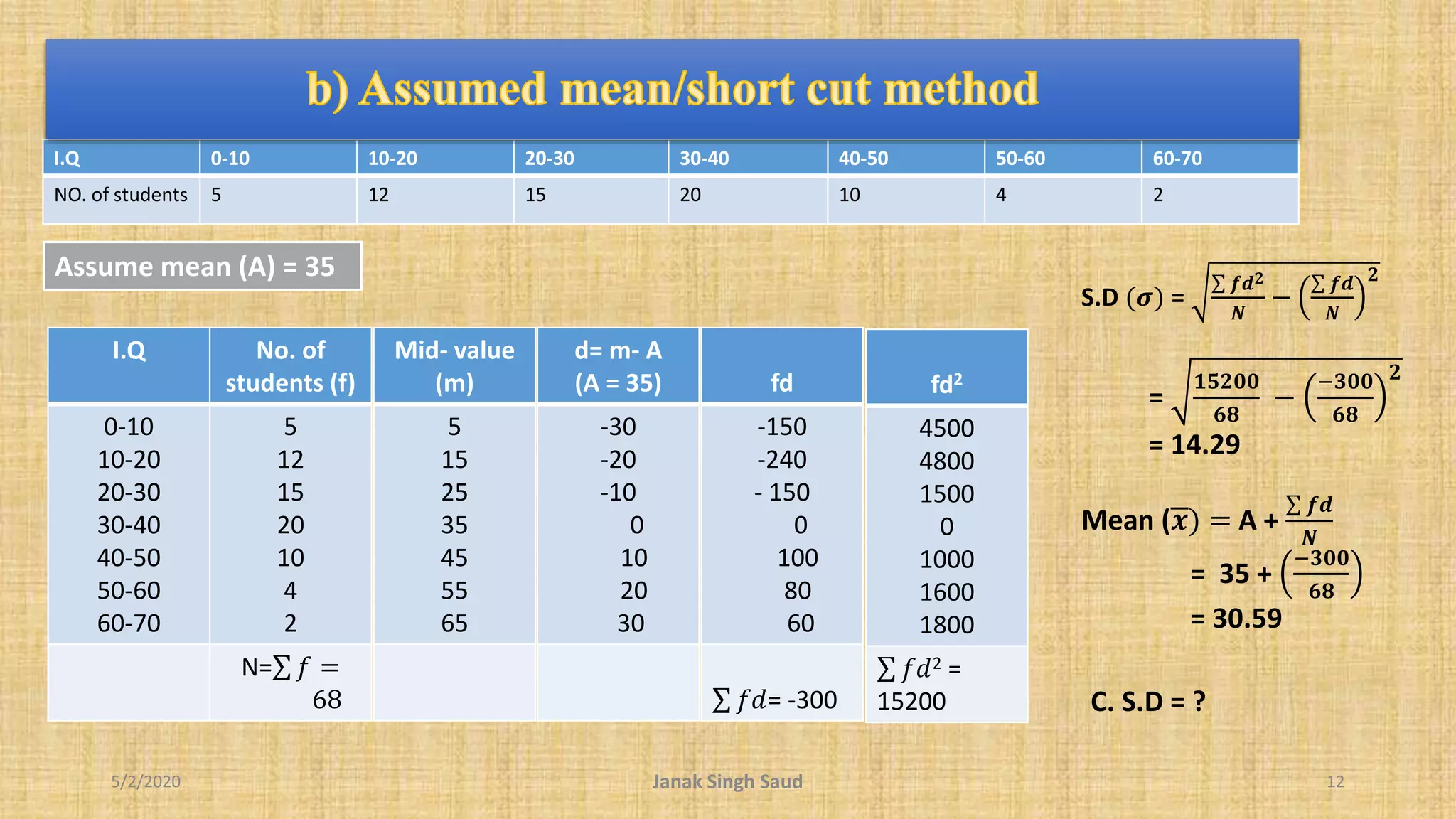
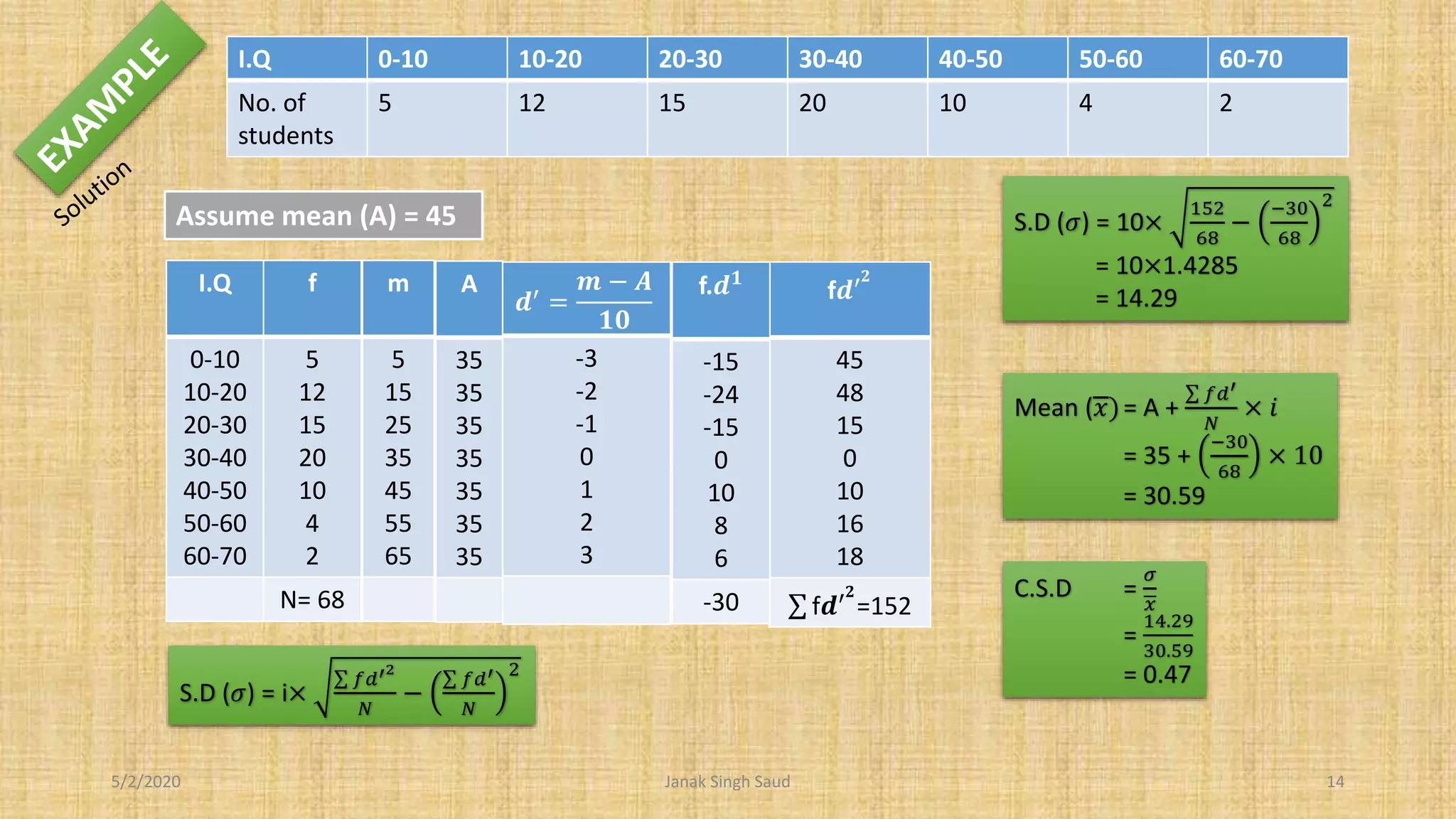
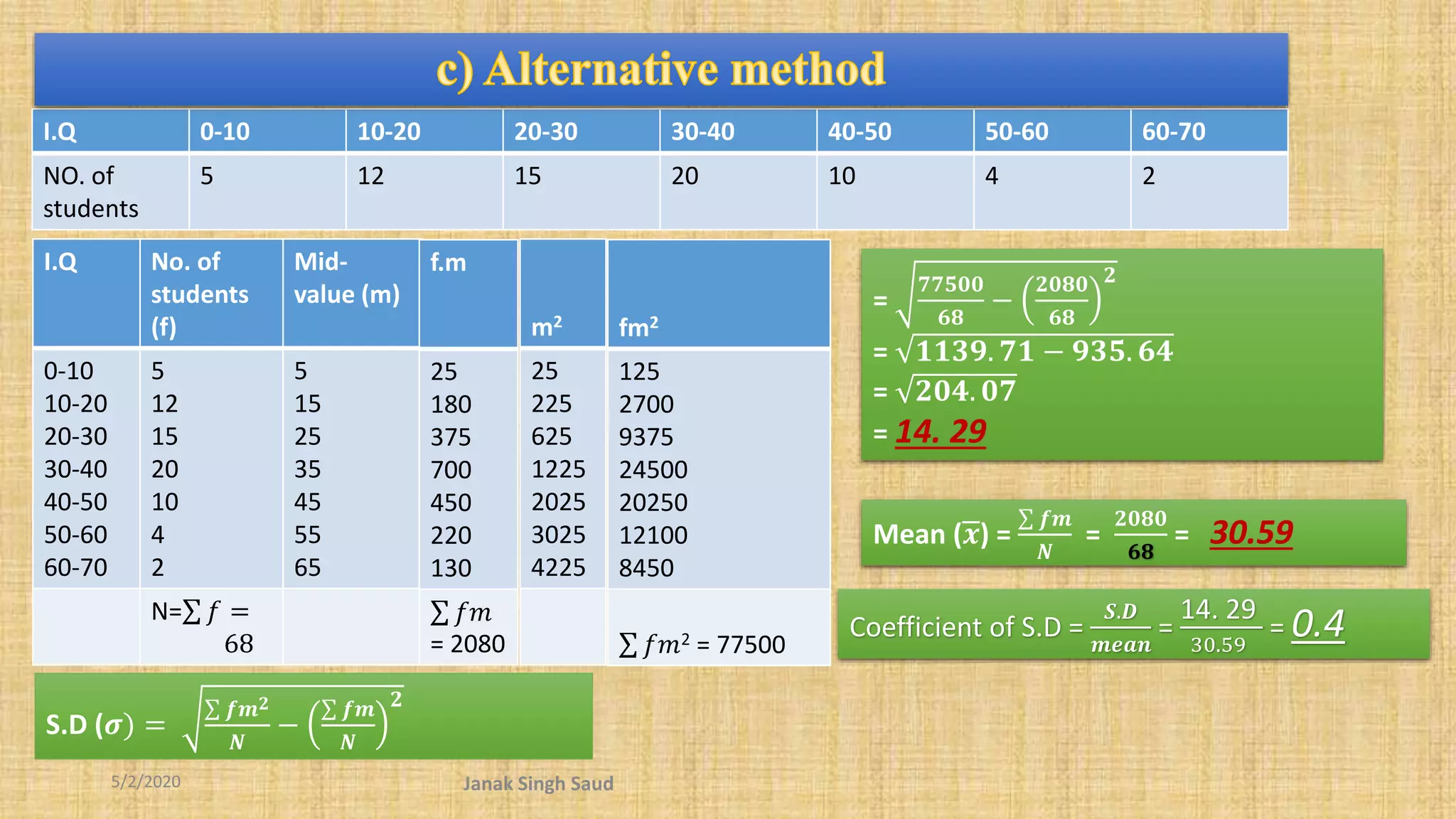
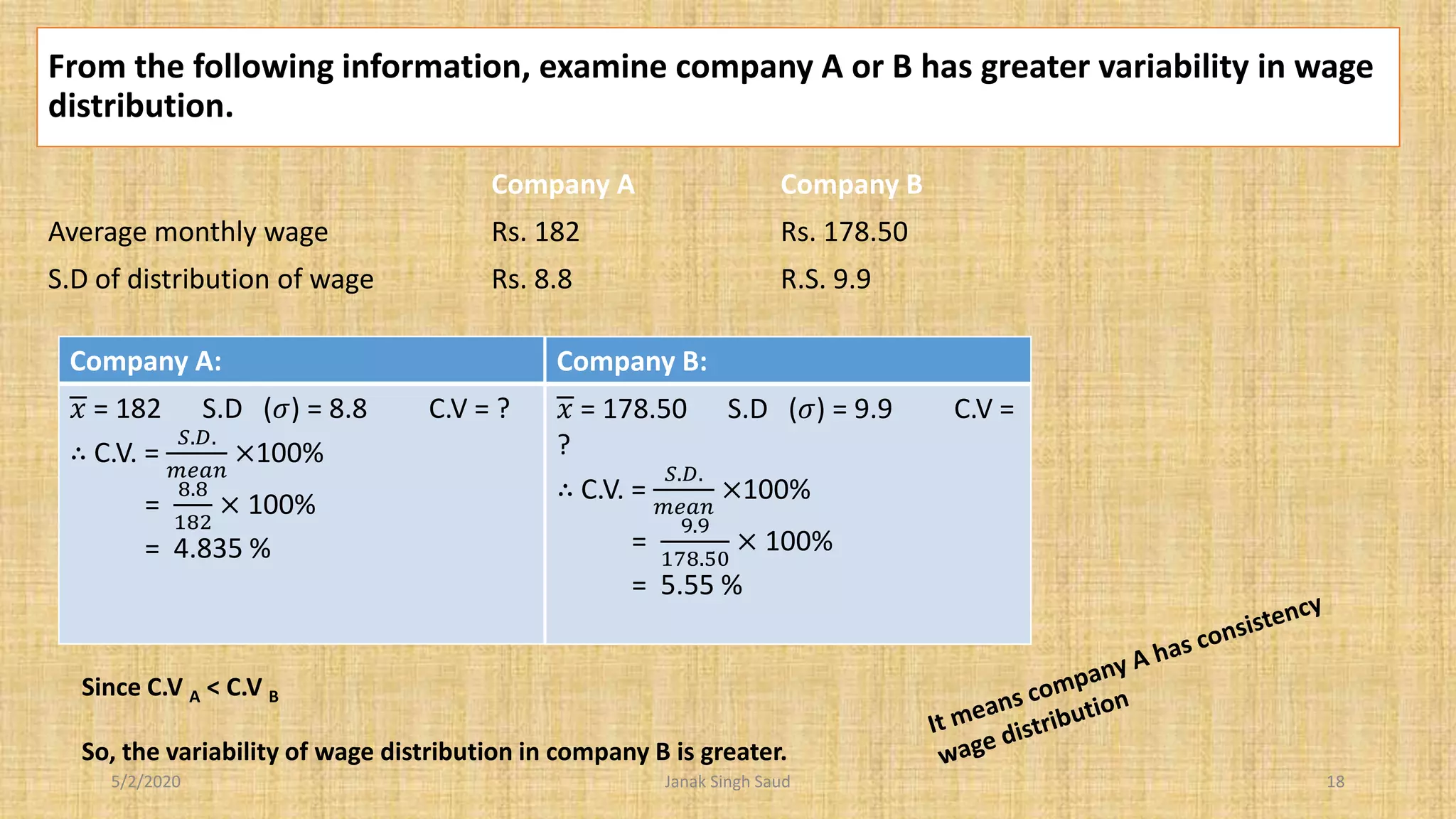
The document outlines methods for calculating standard deviation and its application in comparing the variability of grouped data. It includes formulas for standard deviation, various methods to compute it, and examples demonstrating the comparison of variances in different datasets. Additionally, it discusses the coefficient of variation as a measure of dispersion in wage distributions between two companies.