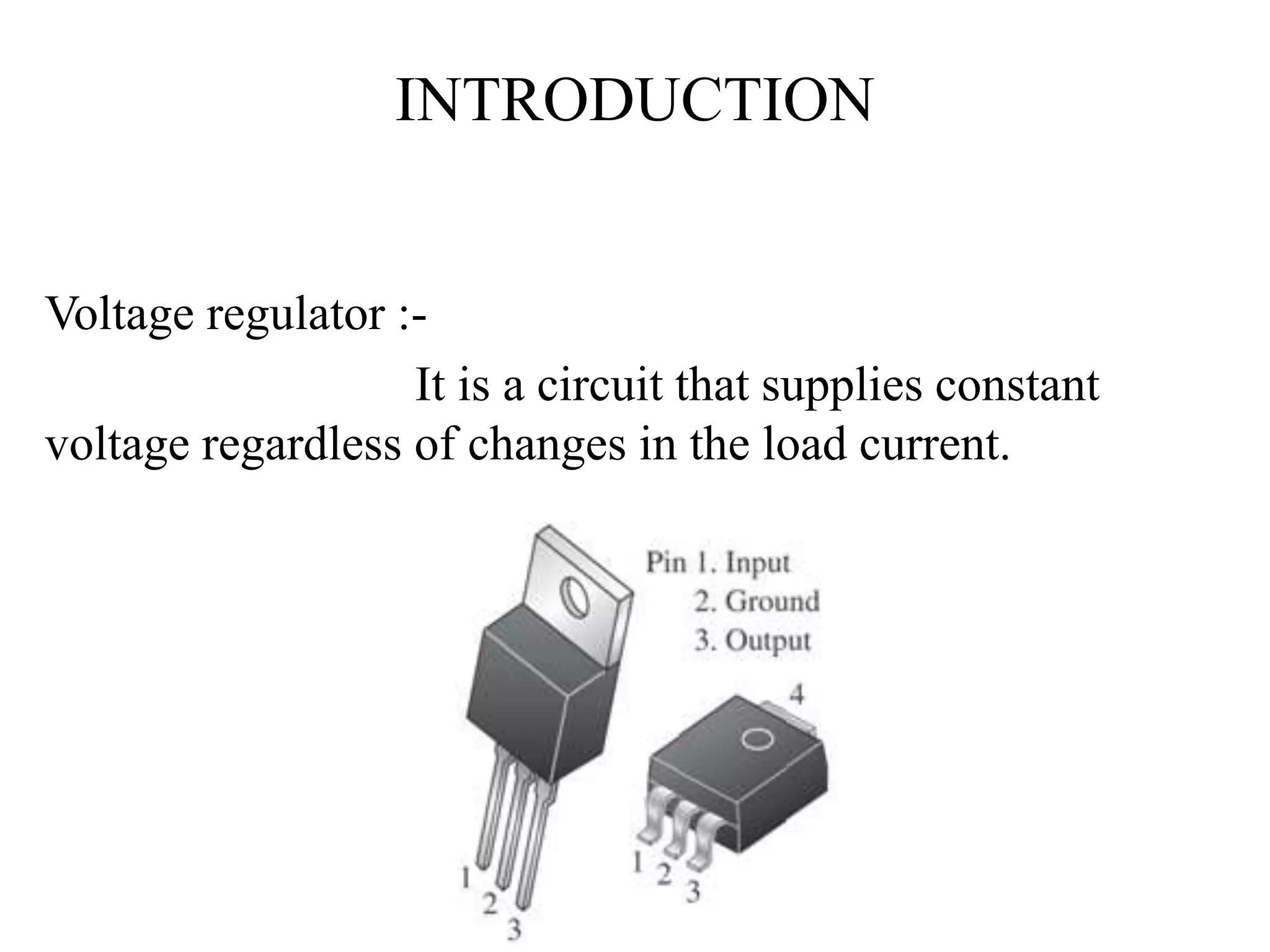
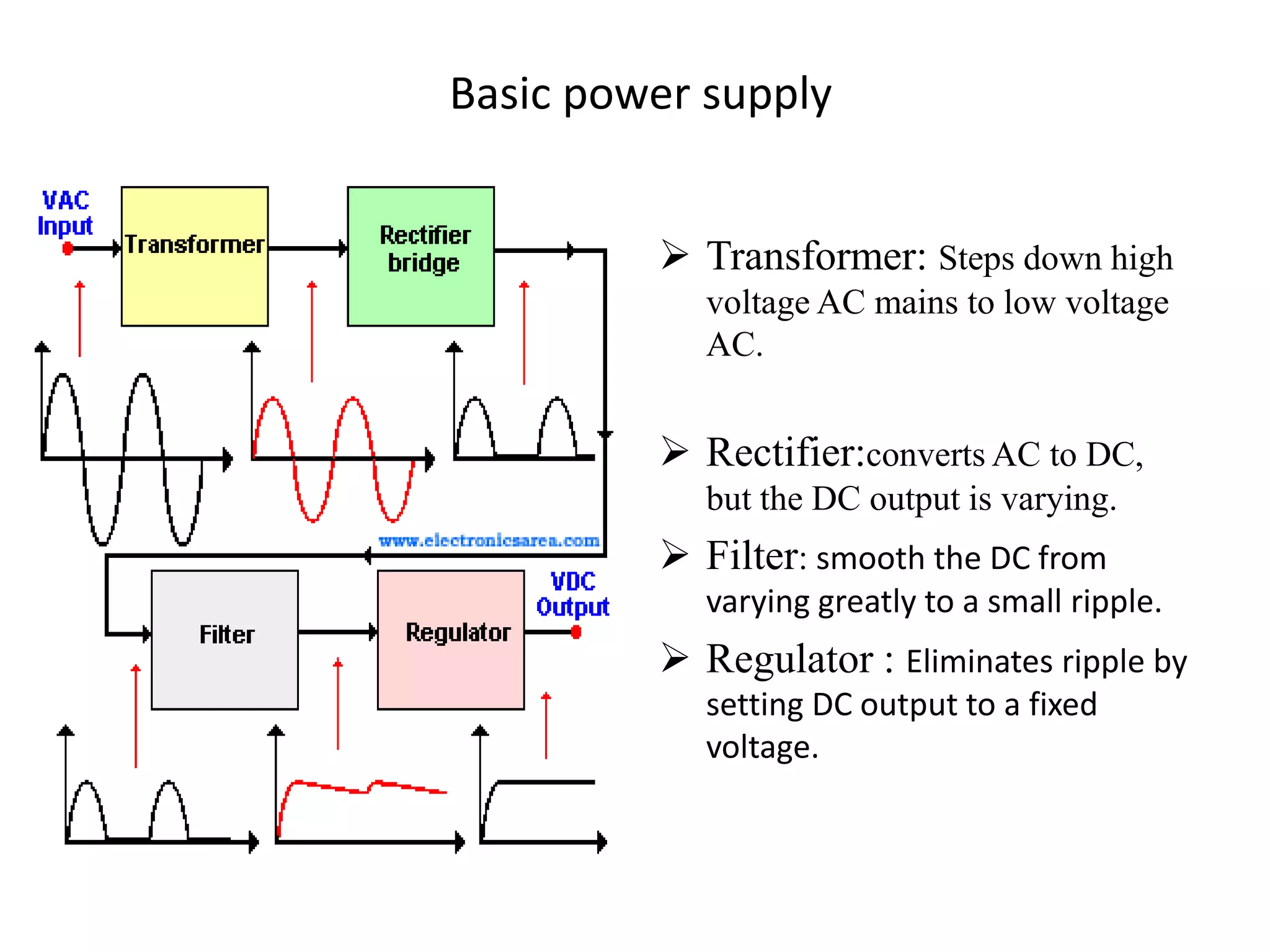
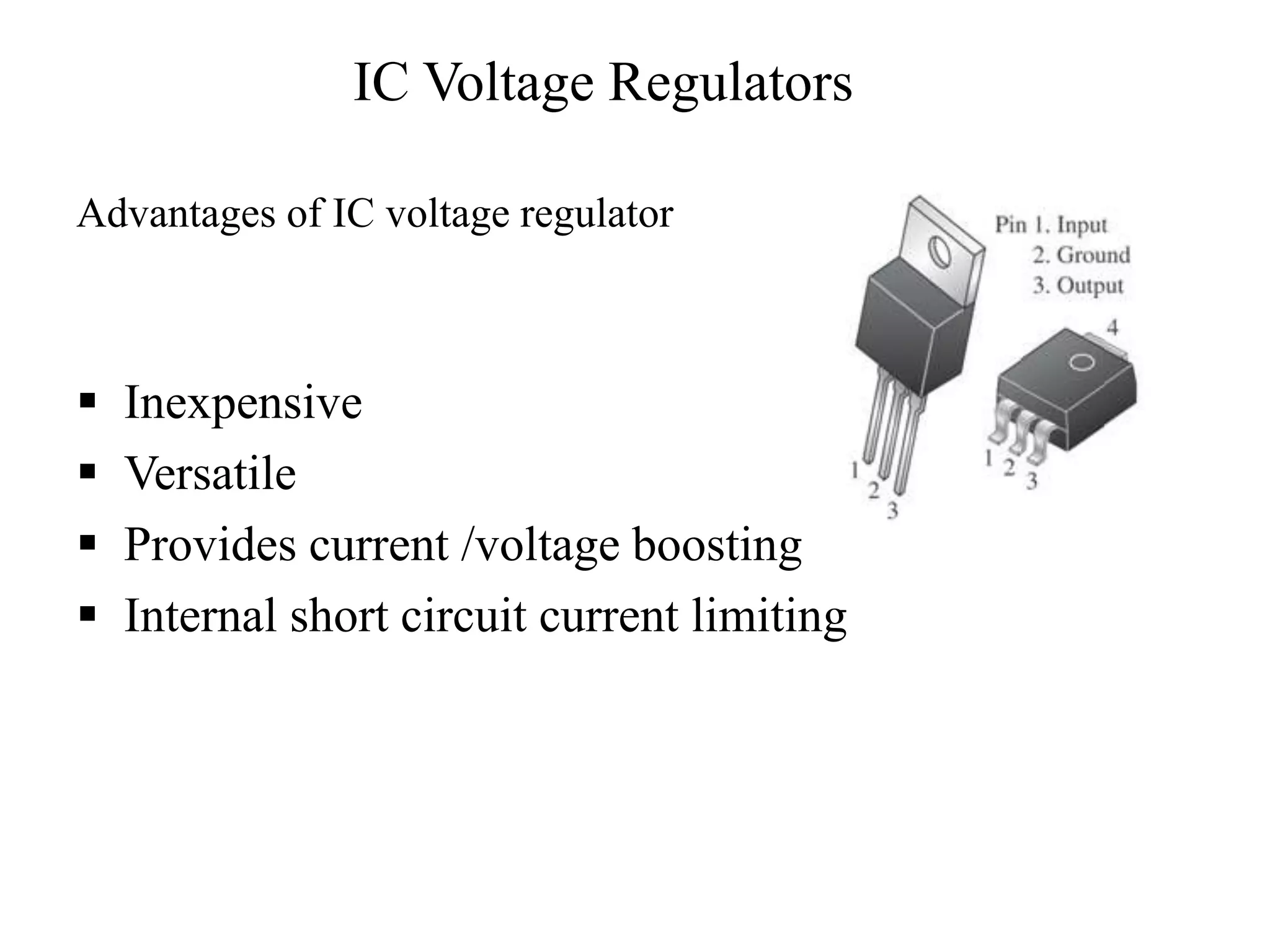
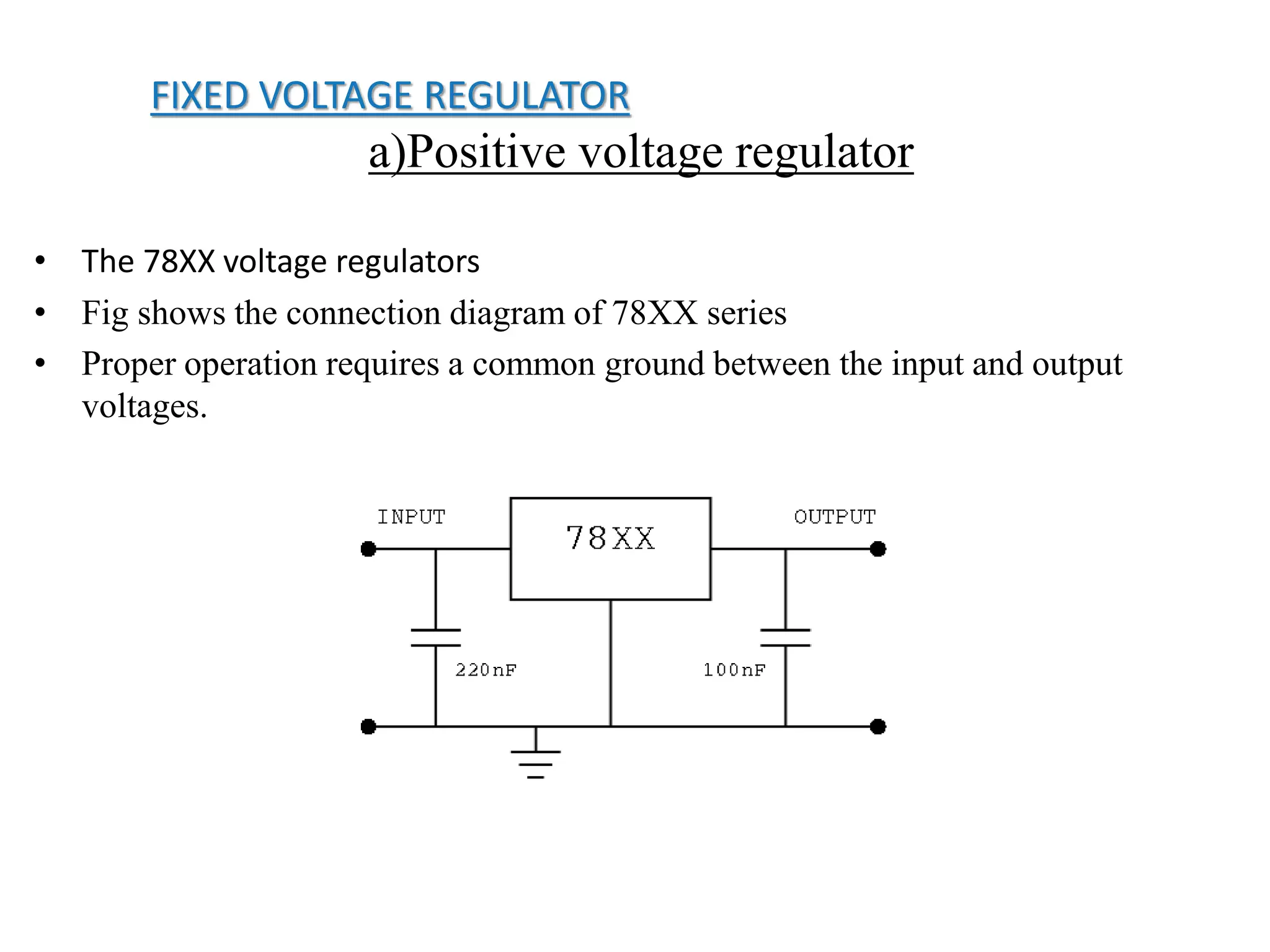
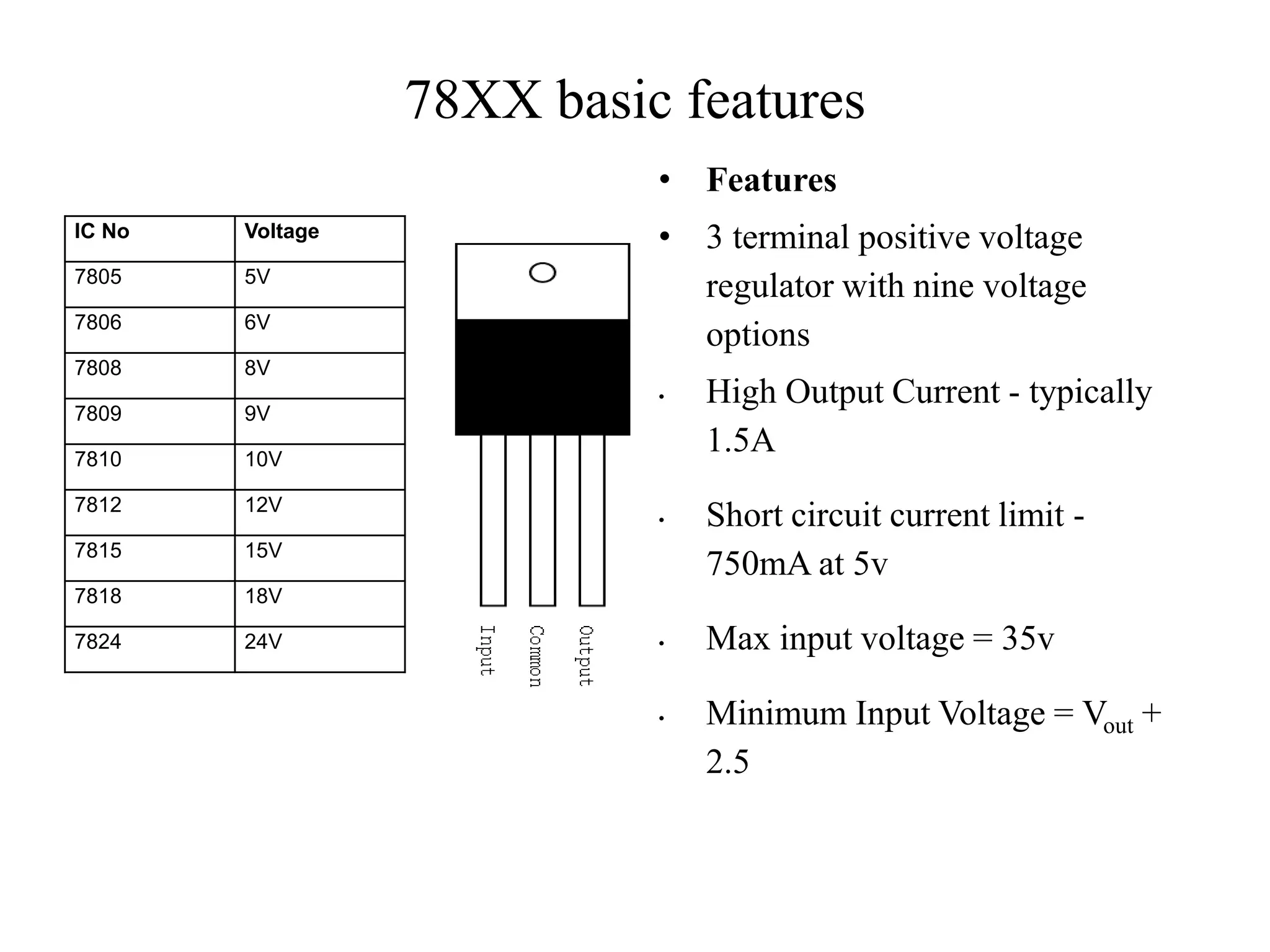
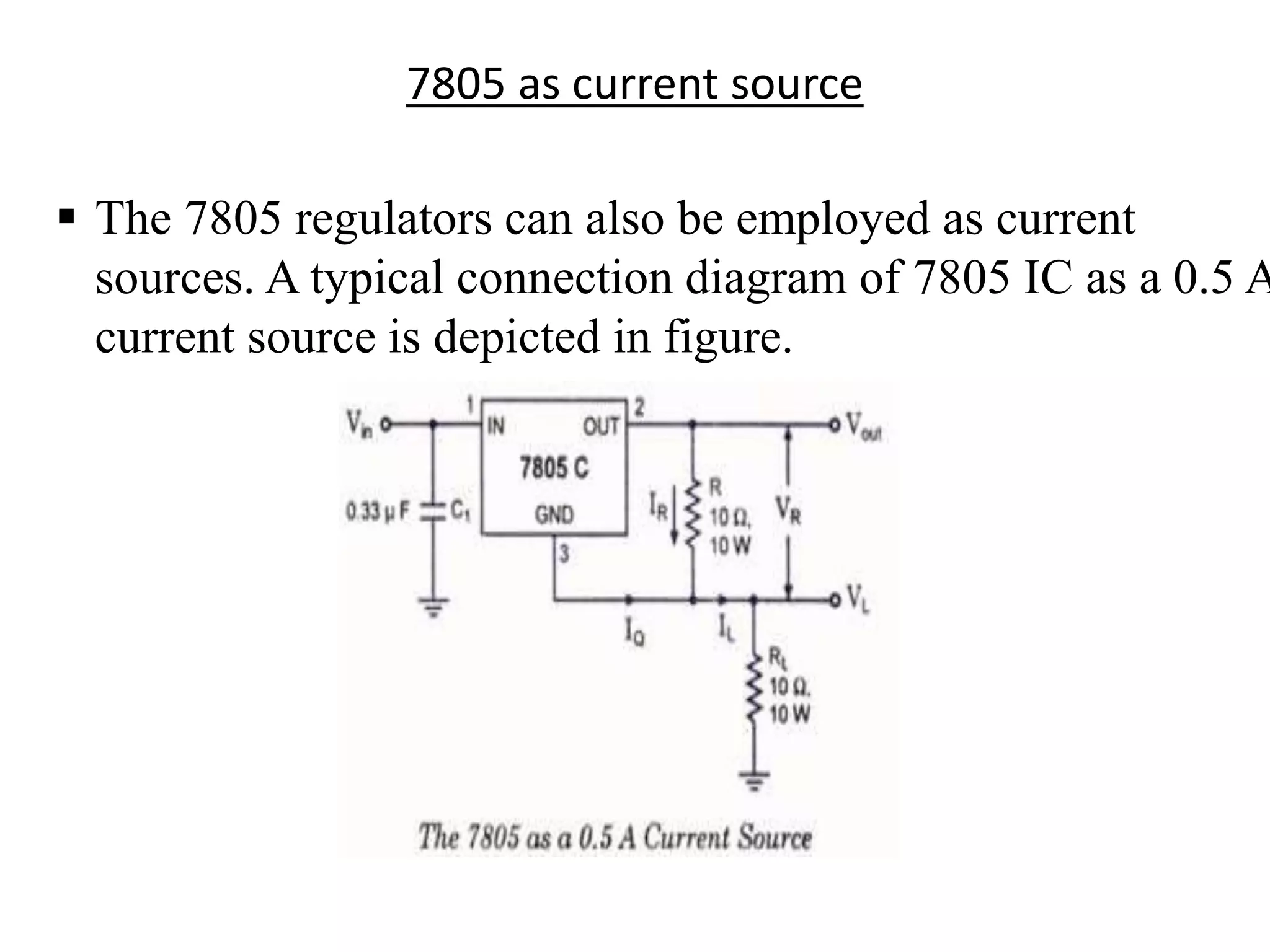
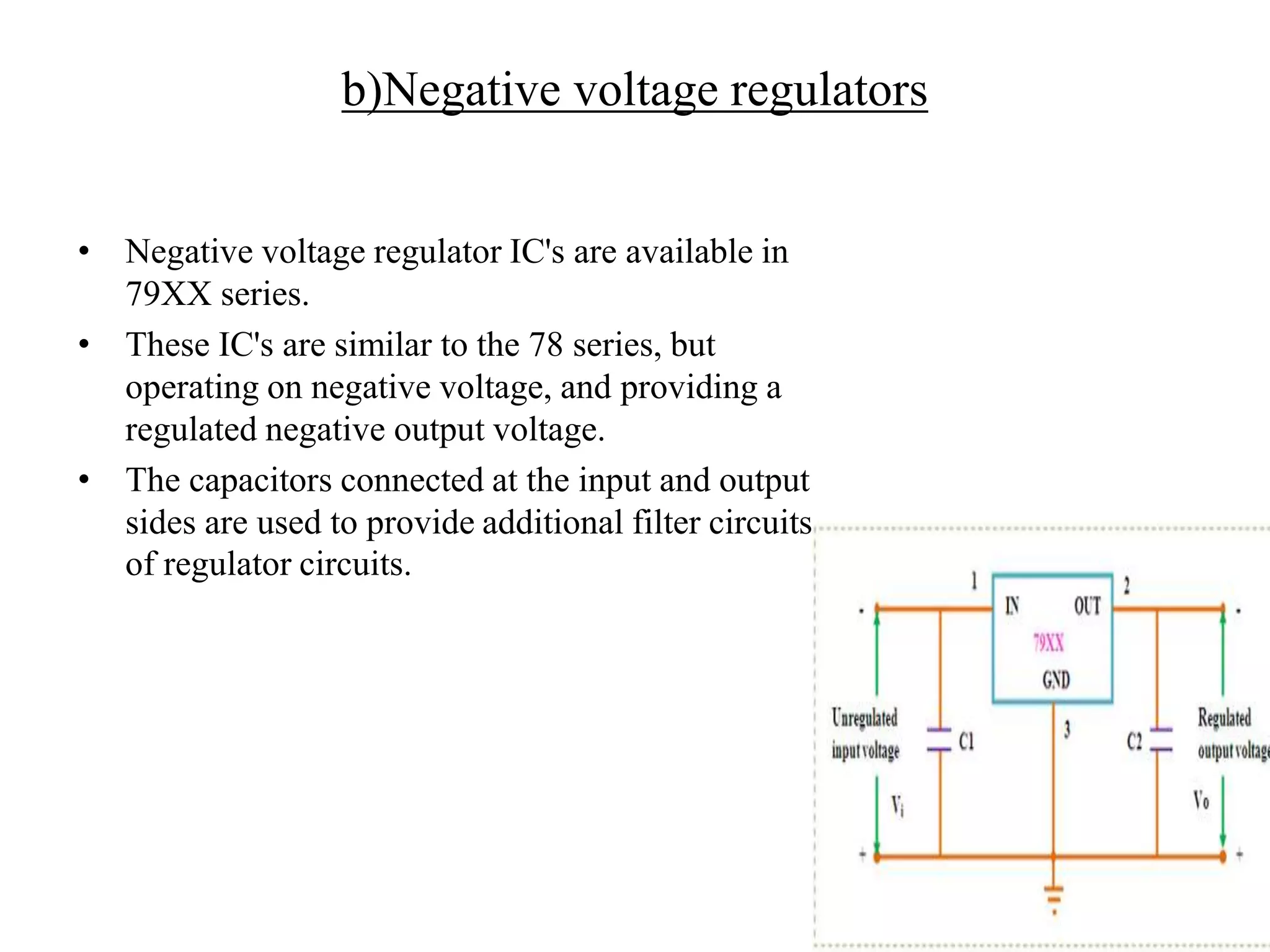
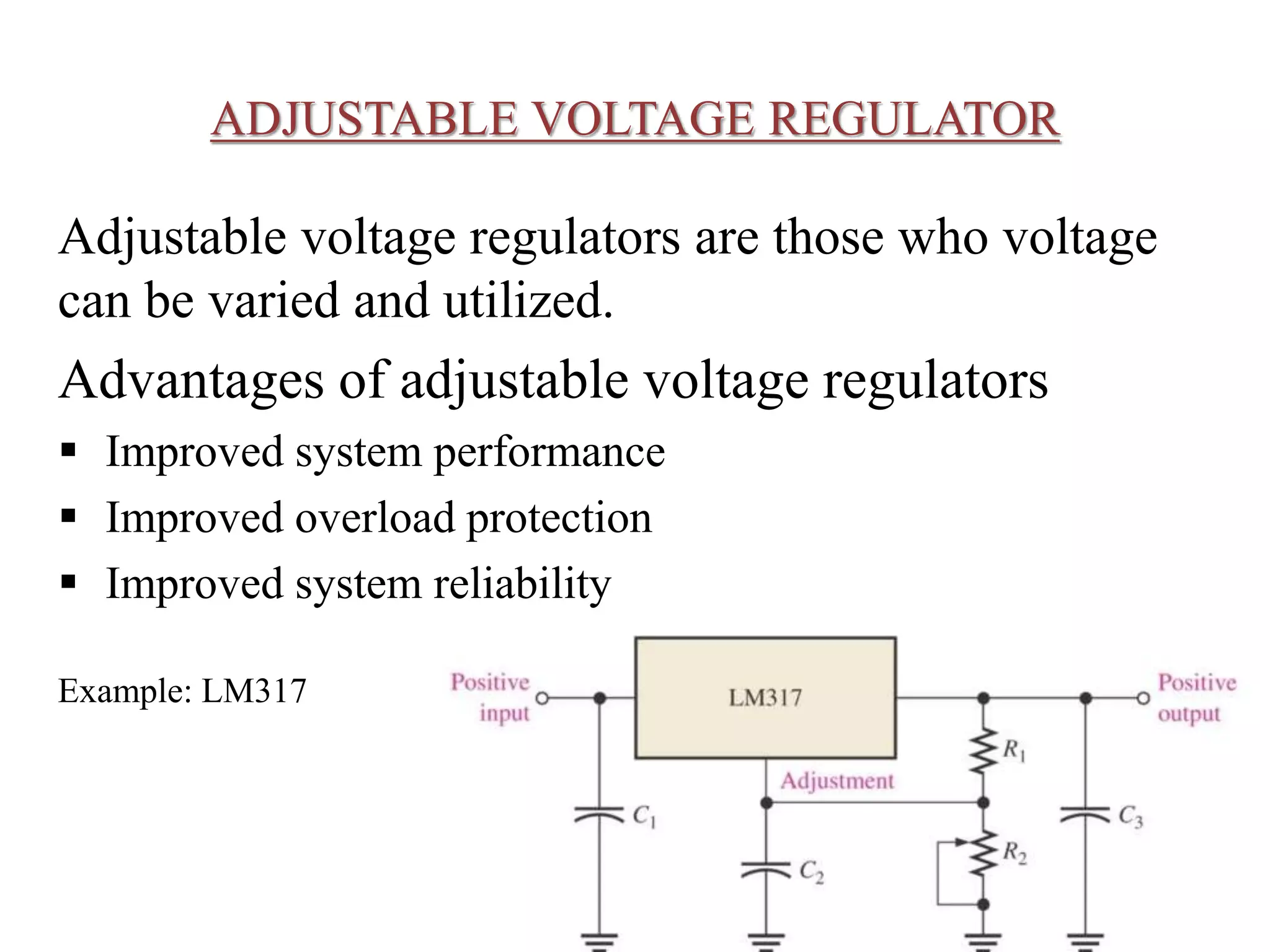
This document presents an overview of integrated circuit voltage regulators. It discusses the need for voltage regulation in circuits to maintain stable potentials. Different types of voltage regulators are described, including fixed output regulators like the 78XX and 79XX series, adjustable output regulators like the LM317, and switching regulators like the MC1723. Key parameters that define regulator performance are also outlined. The document then provides more detailed explanations of specific voltage regulator ICs, their applications, connections, and characteristics.