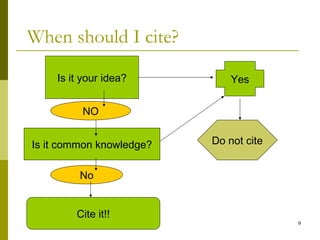
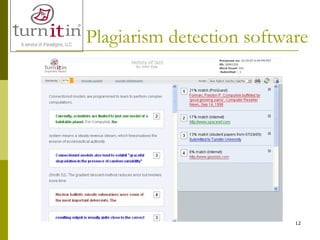
The document discusses plagiarism, defining it as taking and using the thoughts, writings, or inventions of another as one's own without proper citation or credit. It notes that a study found 74% of students admitted to serious test cheating and 72% to plagiarism on written assignments. Plagiarism is problematic as it means students fail to achieve learning outcomes and can be treated as academic misconduct, wasting teachers' time and threatening the reputation of educational institutions. The document provides tips to avoid plagiarism such as using quotes and citations properly, paraphrasing in one's own words, and knowing when common knowledge does not require citation. Severe penalties for plagiarism are outlined for both students and teachers.