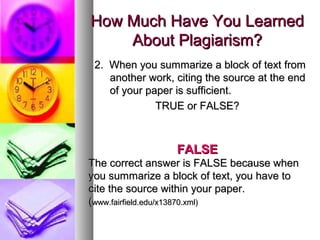
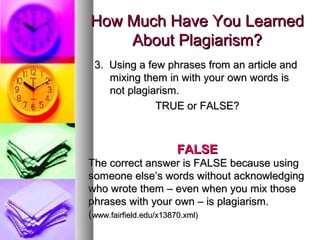
The document discusses plagiarism, defining it as using another's work without proper citation or credit. It notes plagiarism can involve copying text, images, or ideas without attribution. The document outlines how to properly cite sources using a citation style and take notes to avoid plagiarism. It also reviews the consequences of plagiarism such as failing grades or legal punishment. Finally, it provides a short quiz to test the reader's understanding of what actions constitute plagiarism.




![Consequences of Plagiarism
According to Ivy Tech
Community College of Indiana,
“Plagiarism is an issue of
Academic Integrity”:
Students who misrepresent their academic work
violate the rights of their fellow students. […]
The College therefore views any act of
academic dishonesty as a serious offense
requiring disciplinary measures, including failure
for the exam or specific course work, course
failure, suspension, and expulsion from the
College. (Ivy Tech Community College 39)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plagiarism-121024114039-phpapp01/85/Plagiarism-5-320.jpg)



![Quoting a Source
Be careful to quote the text exactly.
A direct quote must be included in
quotations. Use ellipses (…) to show
omitted text and brackets [ ] to show
added phrases.
Quotes must mention the person’s name
and be cited using the format specified by
your instructor.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plagiarism-121024114039-phpapp01/85/Plagiarism-9-320.jpg)