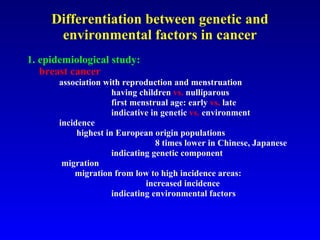
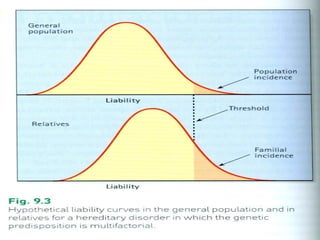
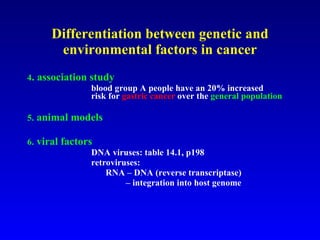
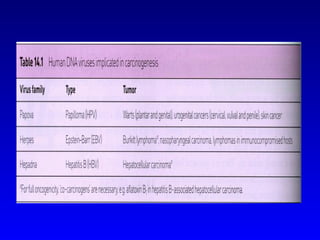
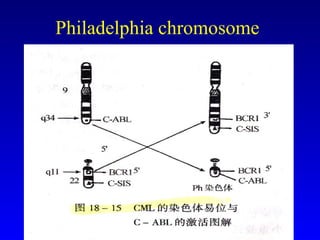
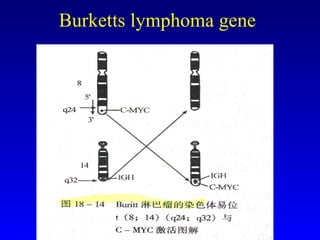
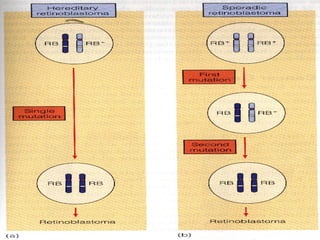
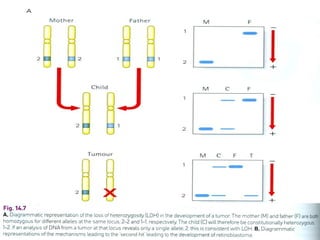
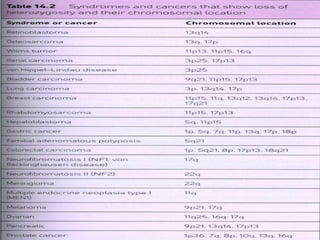
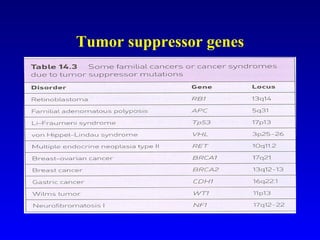
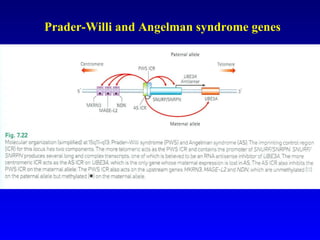
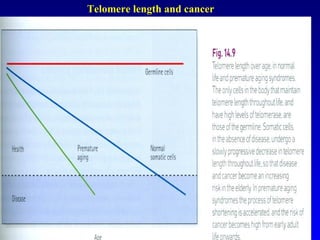
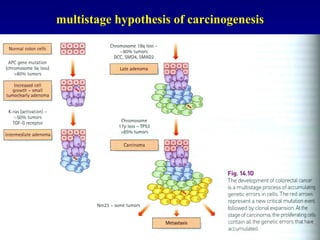
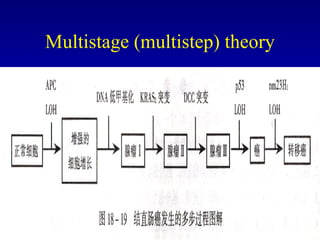
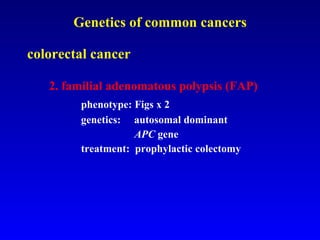
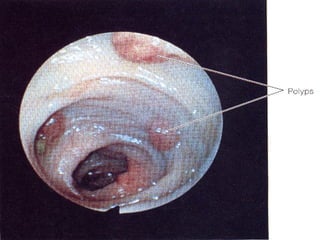
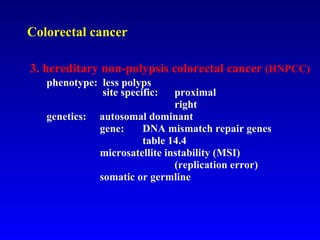
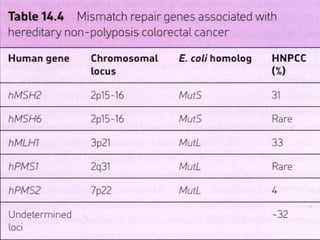
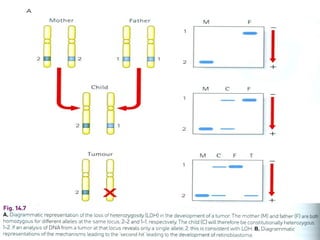
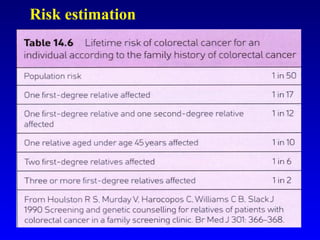
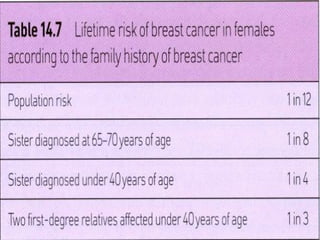
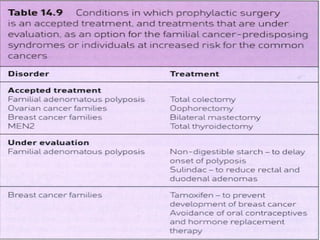
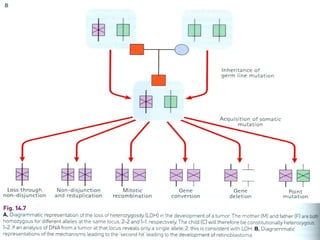
There are genetic and environmental factors that influence cancer development. While some cancers have a strong hereditary component, the majority of cancers are caused by environmental exposures and acquired somatic mutations. Key genetic factors include oncogenes that promote cell growth and tumor suppressor genes whose mutations allow for unchecked cell division. Epigenetic changes like DNA methylation and histone modifications can also influence cancer risk by altering gene expression without changing the underlying DNA sequence.