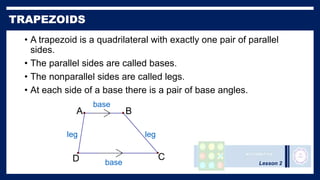
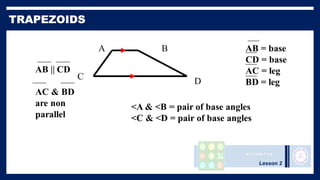
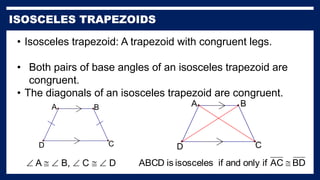
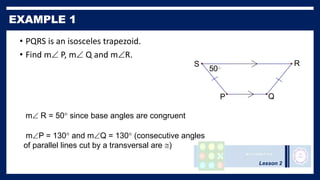
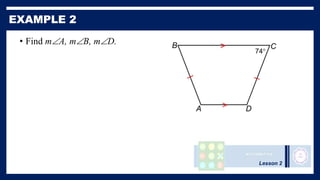
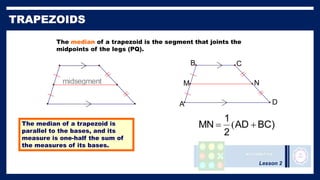
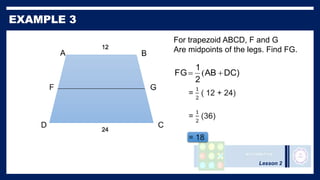
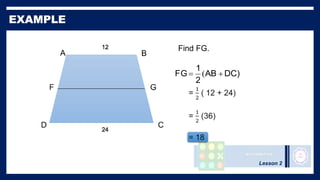
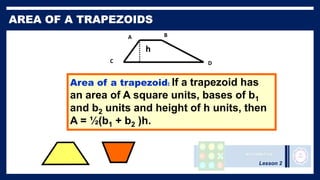
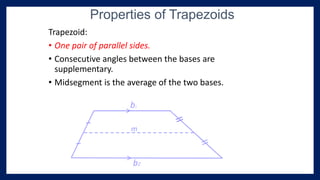
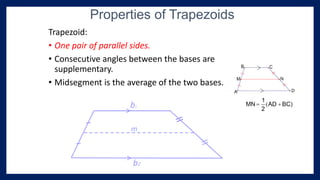
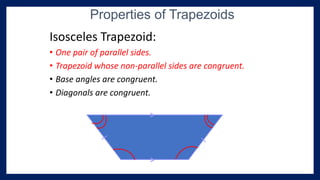
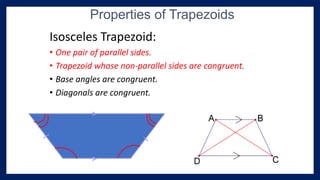
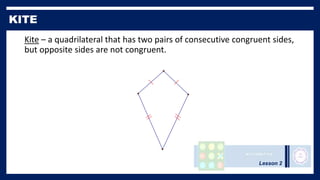
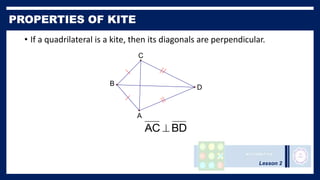
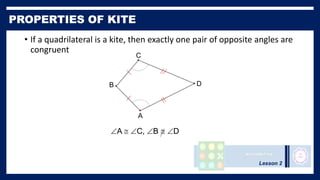
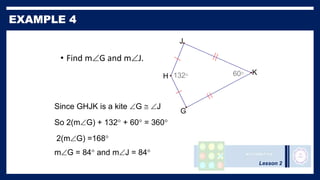
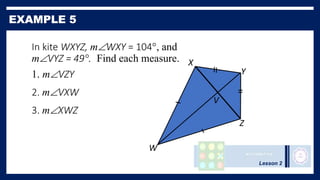
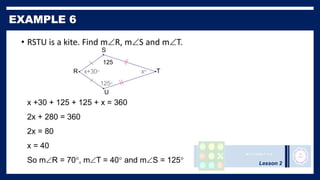
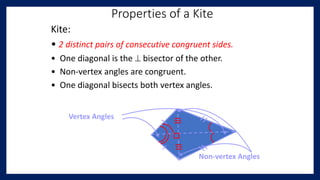
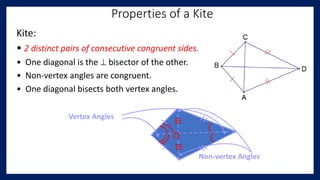
This lesson covers properties of trapezoids and kites. It defines a trapezoid as a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides, and defines properties including that the nonparallel sides are legs and the parallel sides are bases. An isosceles trapezoid has congruent legs. The lesson also defines a kite as a quadrilateral with two pairs of consecutive congruent sides, and defines properties such as perpendicular diagonals and congruent non-vertex angles. Examples of solving problems involving finding angle measures of trapezoids and kites are provided.