Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times



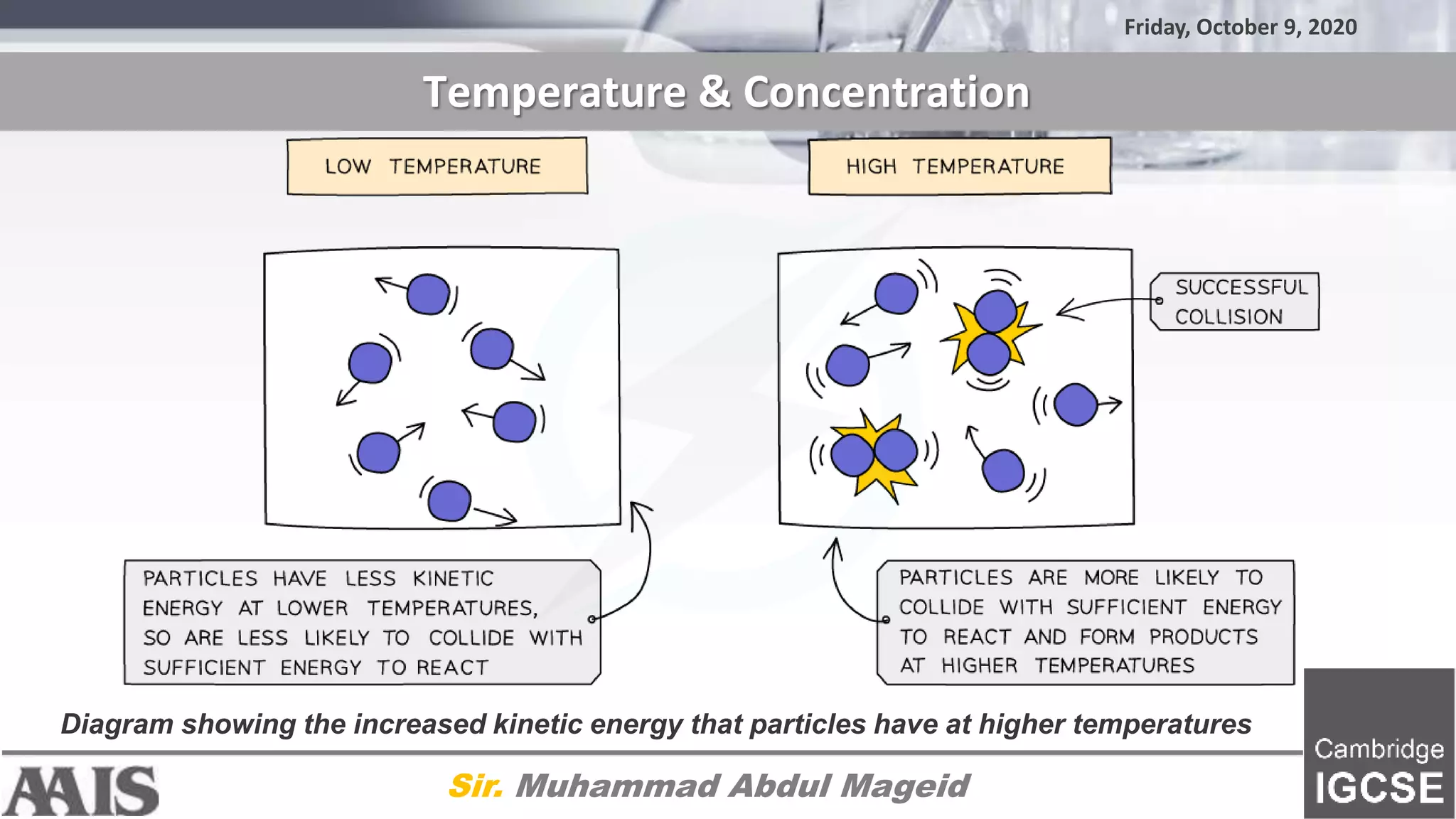
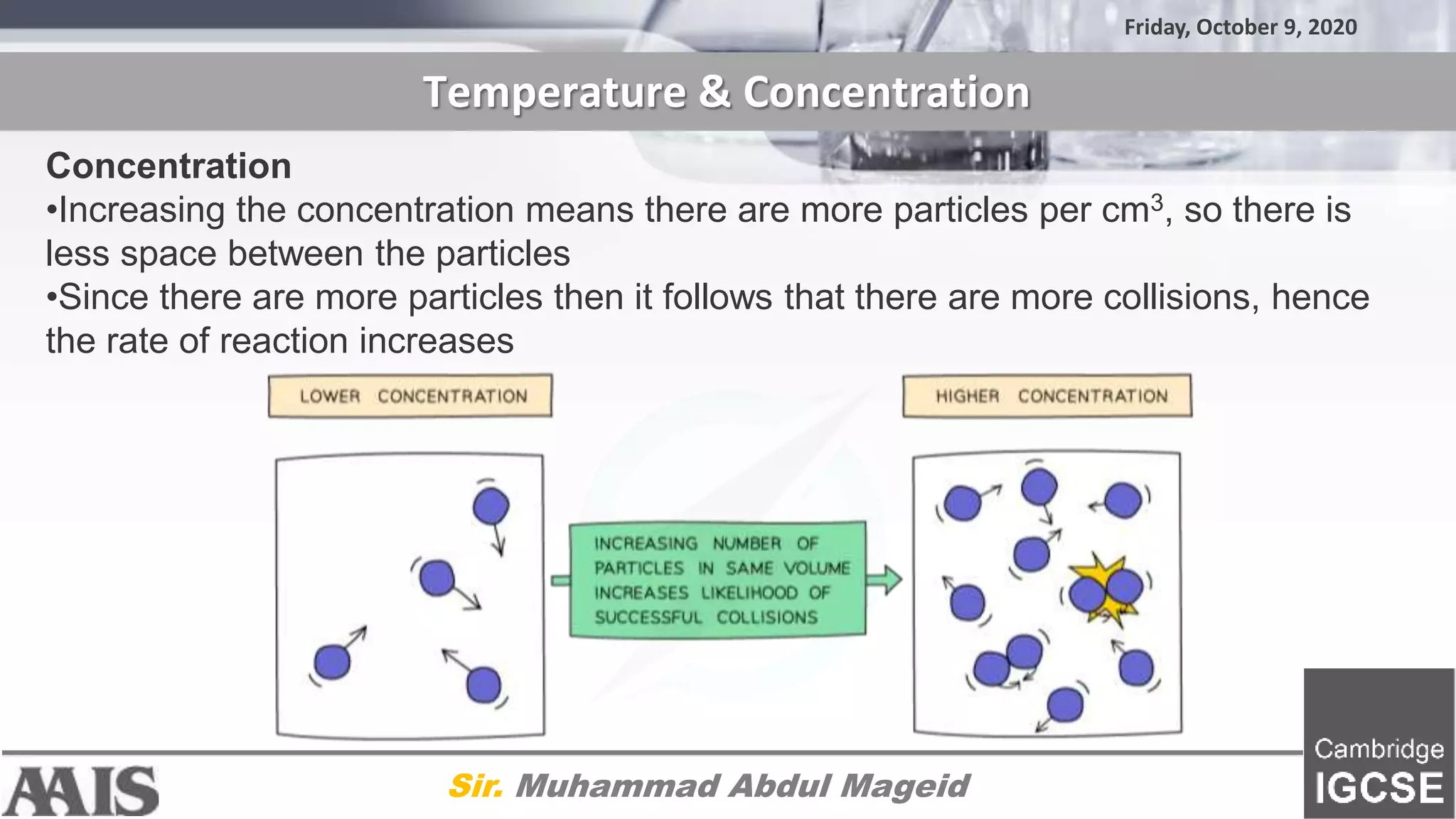

The document discusses factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions, including: 1) Collision theory - reactions only occur during collisions where particles have energy above the activation energy. 2) Higher temperatures lead to more particles with sufficient kinetic energy for reactions. 3) Increasing concentration means less space between particles, leading to more collisions and a faster reaction rate.





