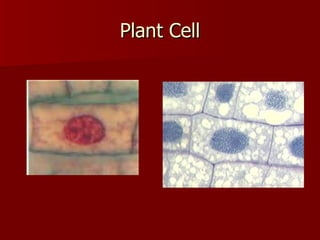
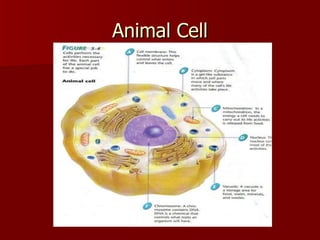
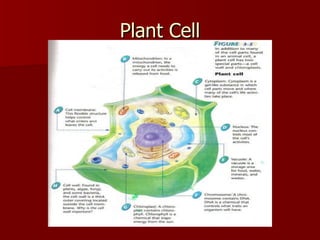
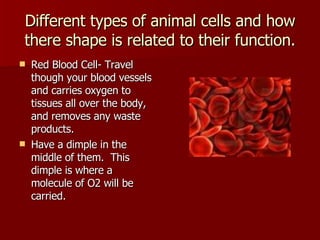
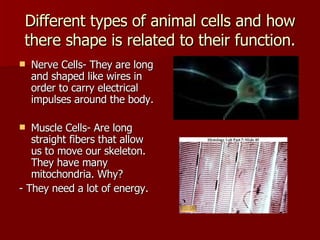
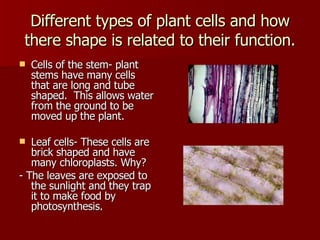
This document discusses cells and their structures. It explains that cells are the basic unit of life, and can only be seen under a microscope. There are plant cells and animal cells, each with their own organelles that perform specific functions. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts, while animal cells do not. The document also describes different types of cells like red blood cells and muscle cells, and how their shapes relate to their functions. Cells combine to form tissues, tissues combine to form organs, and organs combine to form organ systems that make up complete organisms.