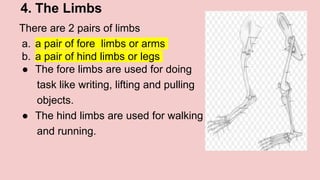
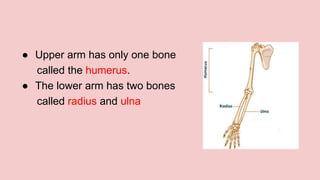
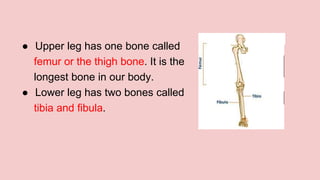
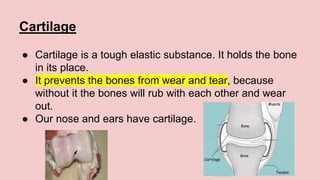
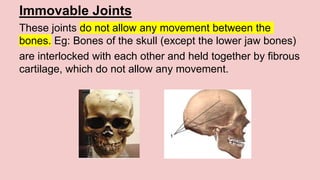
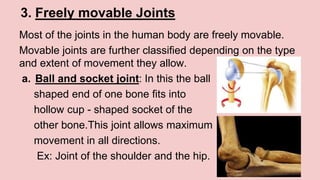
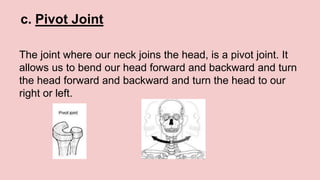
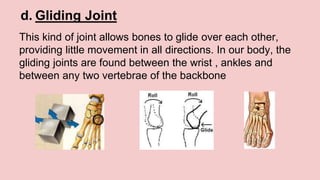
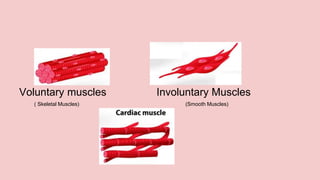
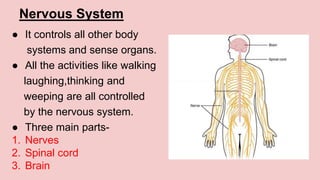
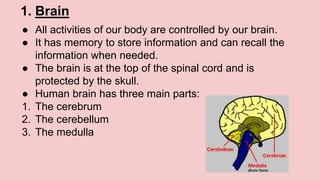
The document describes the skeletal and muscular systems, highlighting the functions of the skeleton, which provides support and protection to the body, and details types of bones and joints. It also explains the muscular system, categorizing muscles into voluntary, involuntary, and cardiac types, and emphasizes the role of tendons in movement. Additionally, it introduces the nervous system, outlining its three main components—brain, spinal cord, and nerves—and explains their functions in controlling body activities and reflex actions.