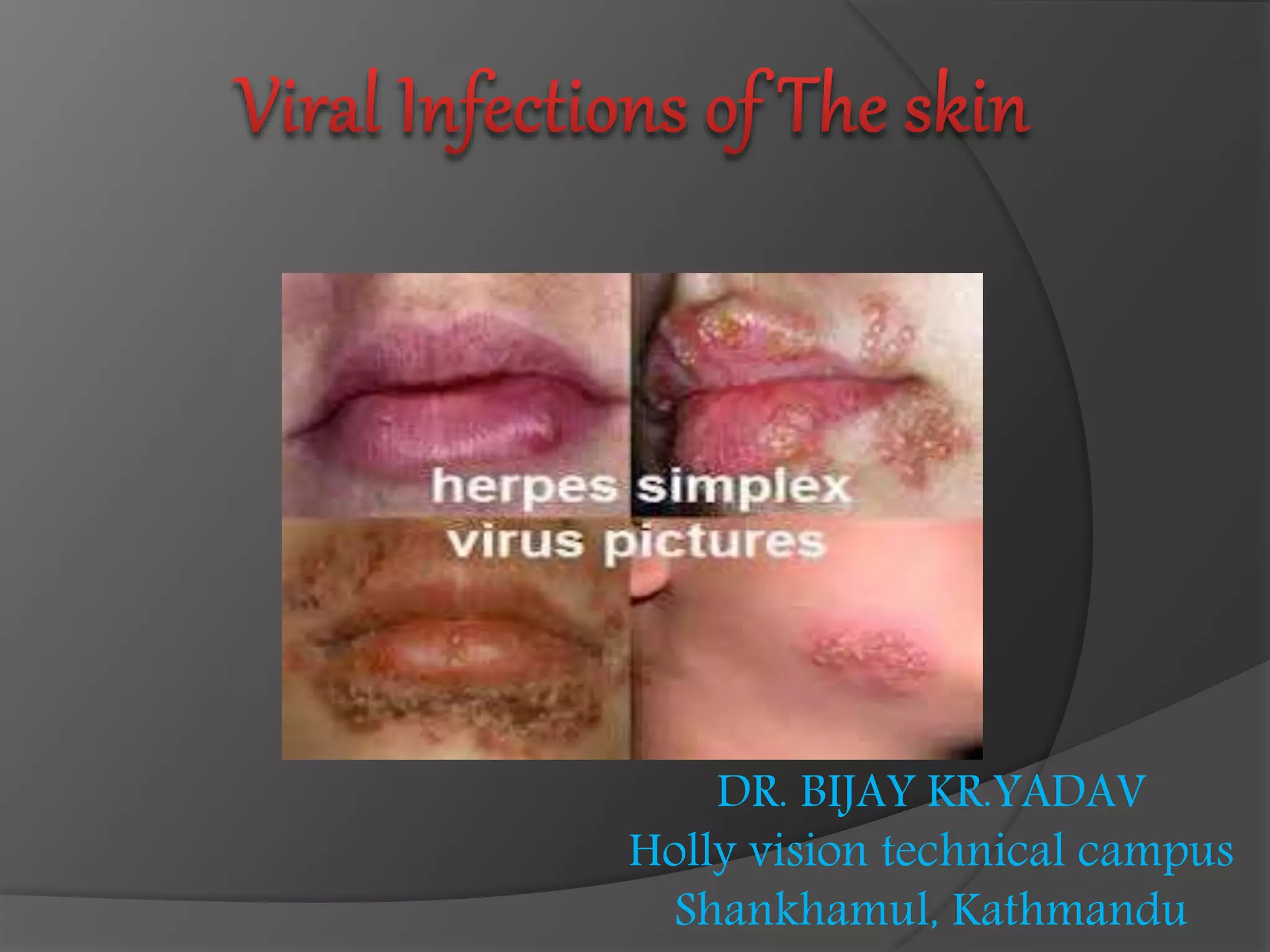
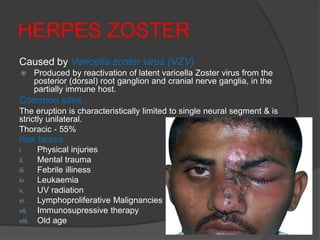
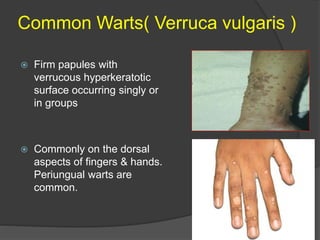
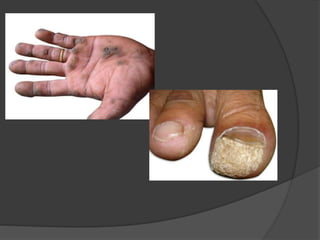
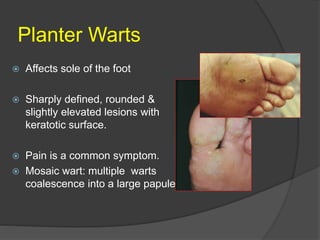
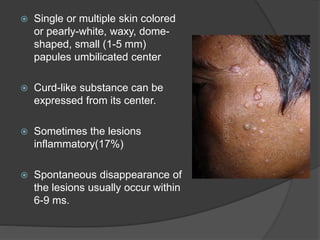
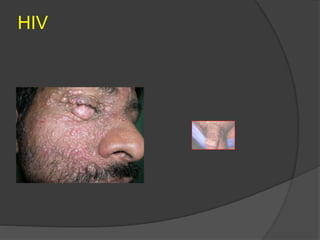
This document discusses several viral infections: Herpes viruses including HSV1, HSV2, varicella zoster virus; human papillomavirus which can cause warts; and molluscum contagiosum virus. It provides details on herpes zoster (shingles) symptoms, risk factors, treatment and warts caused by HPV including common, plantar, and plane warts and their treatments. Molluscum contagiosum is described as a self-limiting skin disease caused by a pox virus, often affecting children and sexually active adults, presenting as small dome shaped papules that can be treated with destruction or antiviral creams.