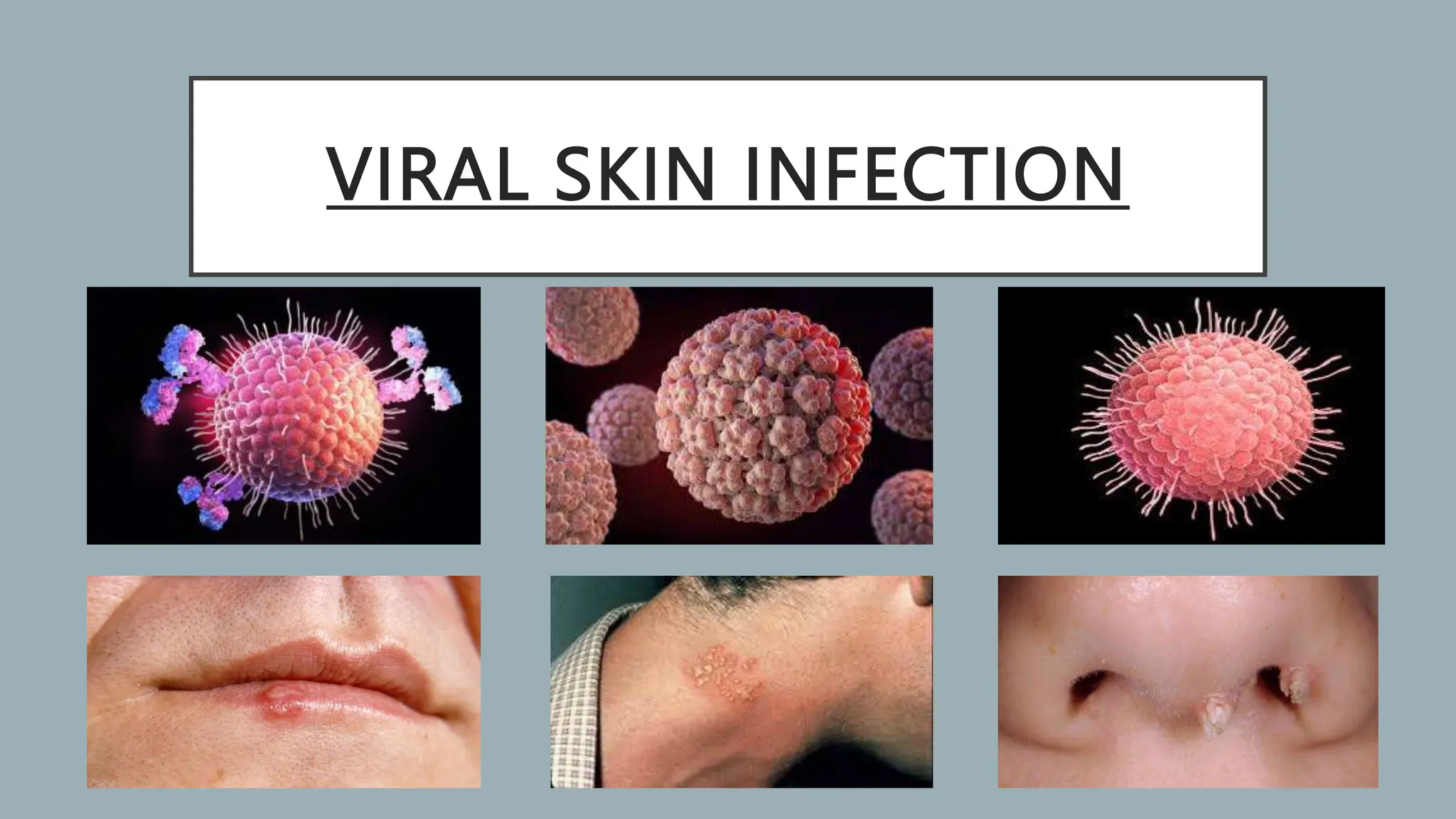
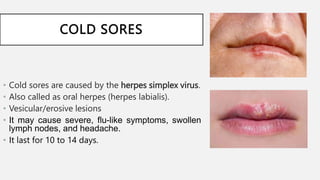
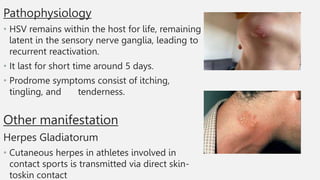
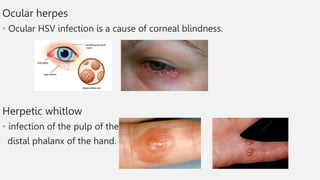
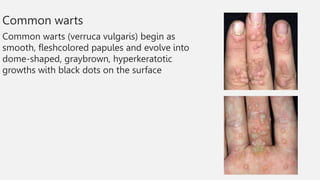
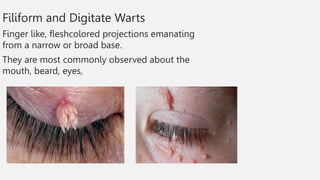
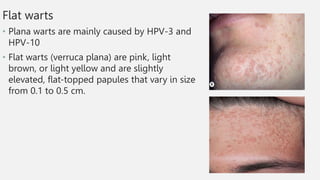
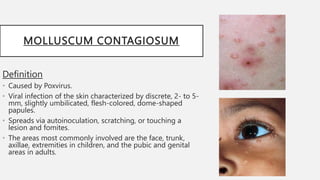
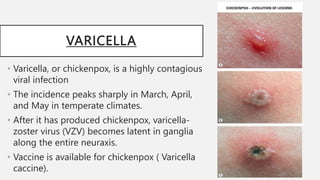
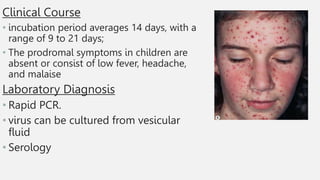
This document summarizes several common viral skin infections: cold sores caused by herpes simplex virus; warts caused by human papillomavirus; molluscum contagiosum caused by a poxvirus; and varicella (chickenpox) caused by varicella-zoster virus. It describes the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of each infection. Common treatments include antiviral medications like acyclovir and valacyclovir as well as cryotherapy or topical medications for warts and molluscum. Vaccines are available to prevent chickenpox.