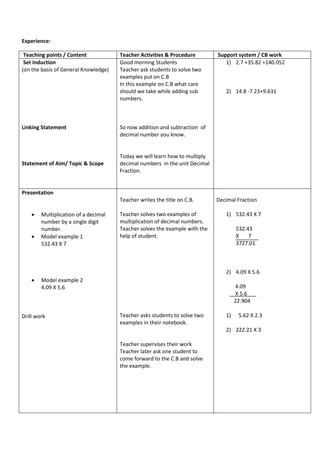
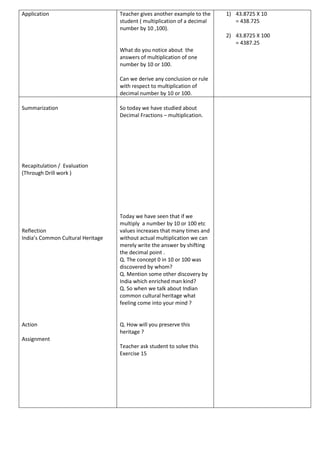
The document outlines a lesson plan for practicing multiplication of decimal fractions for a sixth-grade math class at Ashoka Universal School. It details the objectives, methodology, and instructional activities, including examples and student engagement strategies. Additionally, it includes evaluation components and reflection on India's cultural heritage related to the lesson.