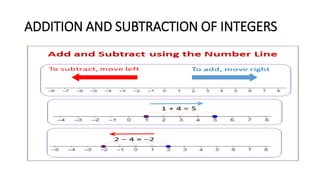
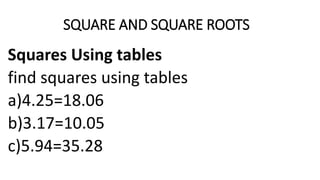
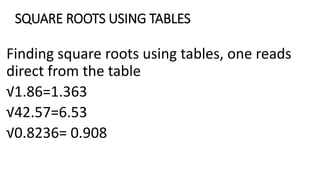
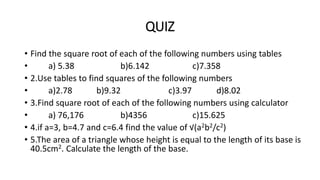
This document provides information about integers, fractions, decimals, squares, and square roots for an 8th grade mathematics strand. It includes specific learning outcomes, definitions of key terms, examples of operations and conversions, and a quiz. The learner is expected to identify integers, represent and operate on them using a number line, and understand their real-world applications. Fractions, decimals, squares, and square roots are similarly defined and examples are provided of related operations and conversions. A quiz at the end assesses these concepts.