The document summarizes key concepts about coordination compounds. It defines coordination compounds as complex inorganic substances where a central metal ion is surrounded by surrounding ligand molecules or ions. The coordination theory proposed by Alfred Werner explains that the central ion occupies a central position and is bonded to surrounding ligand ions or molecules. Properties such as coordination number, isomerism, stability constants, and chemical reactions are also discussed.




![5
For example, the coordination formula of the
complex salt having the composition
PtCl4·2KCl is K2[PtCl6]. Here the inner sphere
consist of a central platinum atom in the
oxidation number +4 and chloride ions, while
the potassium ions are in the outer sphere.
The main characteristic of central ion is the
coordination number. It shows how many
bonds the central ion may forms with ligands.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-5-320.jpg)

![7
Central atom
charge
Coordinative
number
Type of hybrid. Example
+1 2 Sp [Ag(NH3)2]Cl
+2 4,6 sp3
, dsp2
K4[Fe(CN)6]
[Cu(NH3)4]Cl2
+3 6,4 dsp2
K3[Fe(CN)6]
+4 8 d2
sp3
[Pt(NH3)4Cl4]
The Coordination Number](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-7-320.jpg)
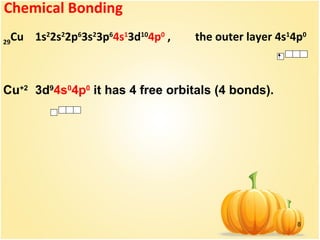
![9
The bonds between central ion and ligands are donor-
acceptor (dative).
27
Co 1s2
2s2
2p6
3s2
3p6
4s2
3d7
4p0
Co+3
[Ar]3d6
4s0
4p0
6 free orbitals remain (6 bonds).
d2
sp3
hybridization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-9-320.jpg)

![11
Classification
I. According to the inner sphere
charge there are:
1.The Anionic complexes - Na2
[NiCl4
]-2
2. The Cationic complexes –
[Zn(NH3
)4
]+2
Cl2
3. The Neutralic complexes –
Pt(NH3
)2
Cl2
]0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-11-320.jpg)
![12
II. According to the nature of the ligands.
1.Ammines – complexes in which ammonia
molecules are the ligands, for instance [Cu(NH3
)4
]SO4
– tetraamminecupper (II) sulfate; [Co(NH3
)6
]Cl3
–
hexaamminecobalt (III) chloride.
2.Aquacomplexes contain water as the ligand:
[Co(H2
O)6
]Cl2
, [Al(H2
O)6
]Cl3
. Hydrated cations in an
aqueous solution contain an aquacomplex as the
central unit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-12-320.jpg)
![13
3.Acidocomplexes. In these complexes, anions
are the ligands. They include complexes of the
double salt type, for example, K2
[PtCl4
], K4
[Fe(CN)6
]
(they can be represented as the product of the
coupling of two salts - PtCl4
·2KCl, Fe(CN)2
·4KCN, etc.),
complex acids – H2
[SiF6
], H2
[CoCl4
],
hydroxocomplexes – Na2
[Zn(OH)4
].
4. Transition series exist between these classes,
which include complexes with different ligands.
K[Pt(NH3
)Cl3
].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-13-320.jpg)

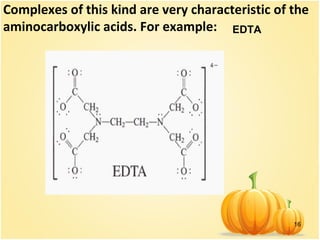
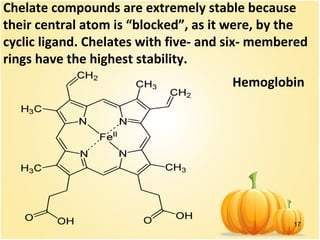
![15
Examples of such complexes are the
oxalate complex of iron (III) [Fe(C2O4)3]3-
and the ethylenediamine complex of
platinum (IV) [PtEn3]4+
. The group of
chelates also includes intracomplex
compounds in which the central atom is
part of a ring, forming covalent bonds
with ligands in various ways – donor–
acceptor mechamism of covalent bond
and bonds at the expense of unpaired
atomic electrons.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-15-320.jpg)








![27
[Pt(NH3
)5
Cl]Br3
pentaamminechloroplatinum(IV) bromide
[Co(H2
NCH2
CH2
NH2
)3
]2
(SO4
)3
tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) sulfate
.K4
[Fe(CN)6
]
potassium hexacyanoferrate(II)
Na2
[NiCl4
]
sodium tetrachloronickelate(II)
Pt(NH3)2Cl4
diamminetetrachloroplatinum(IV)
Fe(CO)5
pentacarbonyliron(0)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-27-320.jpg)
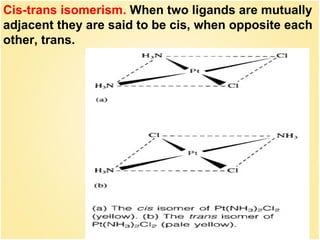
![30
Λ-[Fe(ox)3]3−
Δ-[Fe(ox)3]3−
Λ-cis-[CoCl2(en)2]+
Δ-cis-[CoCl2(en)2]+
Optical isomerism.
Optical isomerism occurs when the mirror image of
a compound is not superimposable with the original
compound. It is so called because such isomers are
optically active, that is, they rotate the plane of
polarized light.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-30-320.jpg)
![31
Stability of Complex Compounds in Solutions.
Constant of Instability.
The aqueous silver forms a complex ion with
ammonia by reacting with NH3
in steps:
Ag+
(aq)
+ NH3 (aq)
[Ag(NH3
)]+
(aq)
Ag(NH3
)+
(aq)
+ NH3 (aq)
[Ag(NH3
)2
]+
(aq)
When we add these equations, we get overall
equation for the formation of the complex ion
Ag(NH3
)2
+
.
Ag+
(aq)
+ 2NH3 (aq)
[Ag(NH3
)2
]+
(aq)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-31-320.jpg)
![32
The formation constant, or stability constant, Kf
, of a
complex ion is the equilibrium constant for the
formation of the complex ion from aqueous metal
ion and the ligands. Thus, the formation constant of
[Ag(NH3
)2
]+
is:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-32-320.jpg)
![33
The value of Kf
for [Ag(NH3
)2
]+
is 1.7×107
.
The ionization constant (Ki
) or (Kd
) for a complex ion
is the inverse value of Kf
. The equation for the
dissociation of [Ag(NH3
)2
]+
is:
[Ag(NH3
)2
]+
(aq)
Ag+
(aq)
+ 2NH3 (aq)
and its equlibrium constant is](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-33-320.jpg)
![34
Chemical Properties.
I. Without destruction of inner sphere.
1.(NH4
)2
[Hg(SCN)4
] + ZnSO4
→ (NH4
)SO4
+
+ Zn[Hg(SCN)4
]↓
2. 2K4
[Fe(CN)6
] + H2
O2
→ 2K3
[Fe(CN)6
] + 2KOH
2 [Fe(CN)│ 6
]4-
- ℮ → [Fe(CN)6
]3-
1 H│ 2
O2
+ 2℮ → 2OH-
2[Fe(CN)6
]4-
+H2
O2
→ 2[Fe(CN)6
]3-
+ 2OH-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-34-320.jpg)
![35
II. With destruction of inner sphere.
1.[Ag(NH3
)2
]Cl + 2HNO3
→ AgCl↓ + 2NH4
NO3
2.H2
[SnCl6
] + Zn → ZnCl2
+ SnCl2
+ 2HCl
1 [SnCl6]│ 2-
+ 2℮ → Sn2+
+ 6Cl-
1 Zn│ 0
- 2℮ → Zn2+
[SnCl6
]2-
+ Zn0
→ Sn2+
+ 6Cl-
+ Zn2+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6coordinativecomp-151203093956-lva1-app6892/85/6-coordinative-comp-35-320.jpg)
