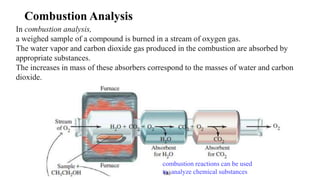
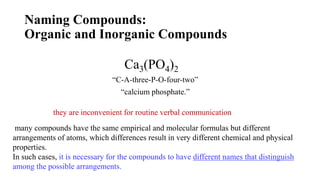
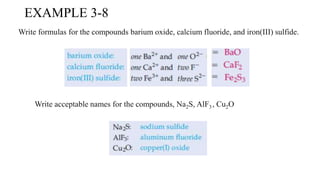
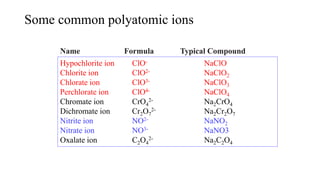
This document discusses chemical concepts related to combustion analysis, oxidation states, assigning oxidation states, naming inorganic compounds, binary compounds, polyatomic ions, and oxoacids. It provides examples and rules for determining oxidation states, naming inorganic compounds based on their formulas, and identifying common polyatomic ions and their names. Key points include that combustion analysis can be used to analyze chemical substances, oxidation states are related to electrons gained or lost by atoms, and there are systematic rules for naming inorganic compounds and identifying polyatomic ions based on their structures and formulas.