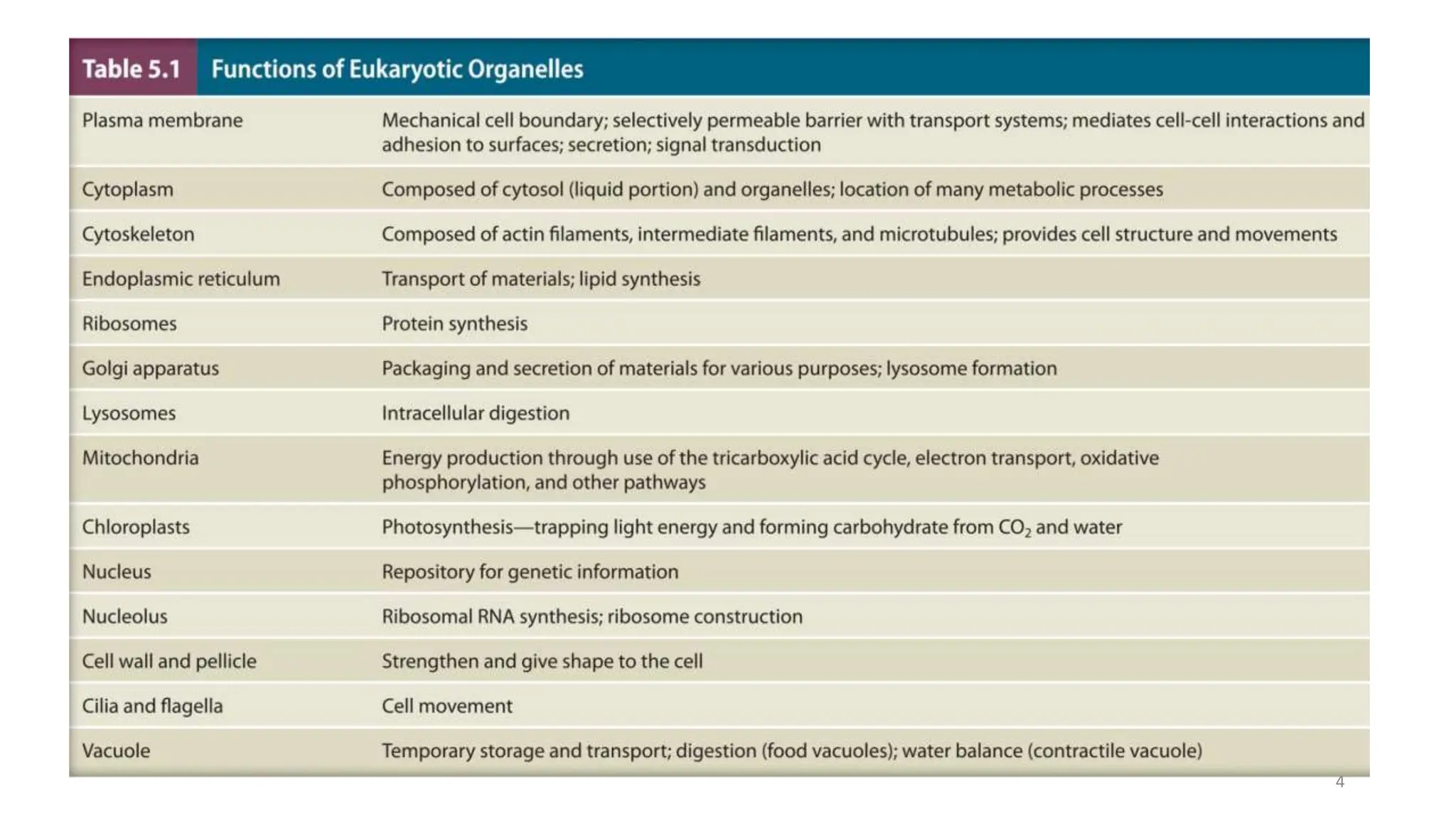
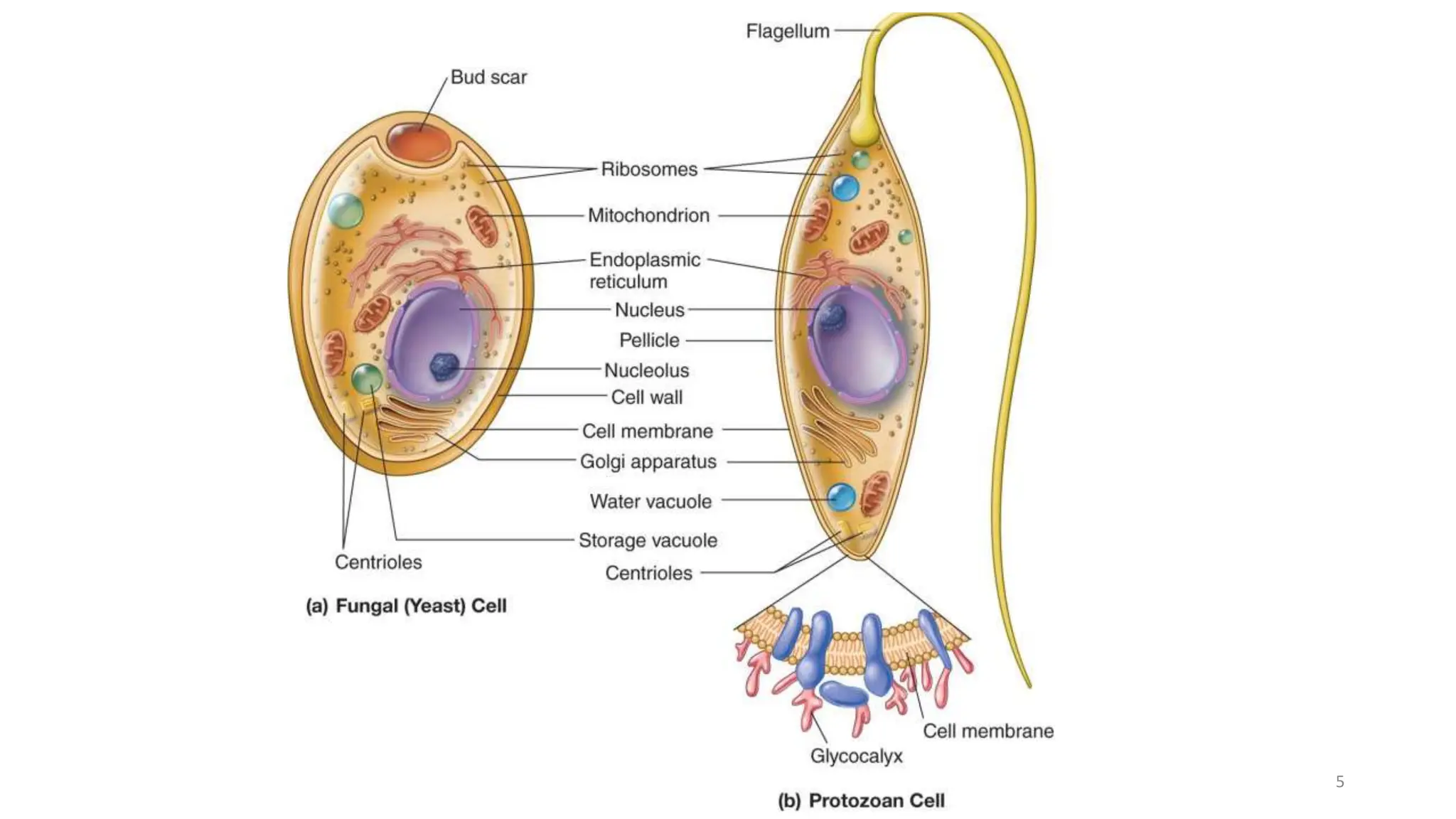
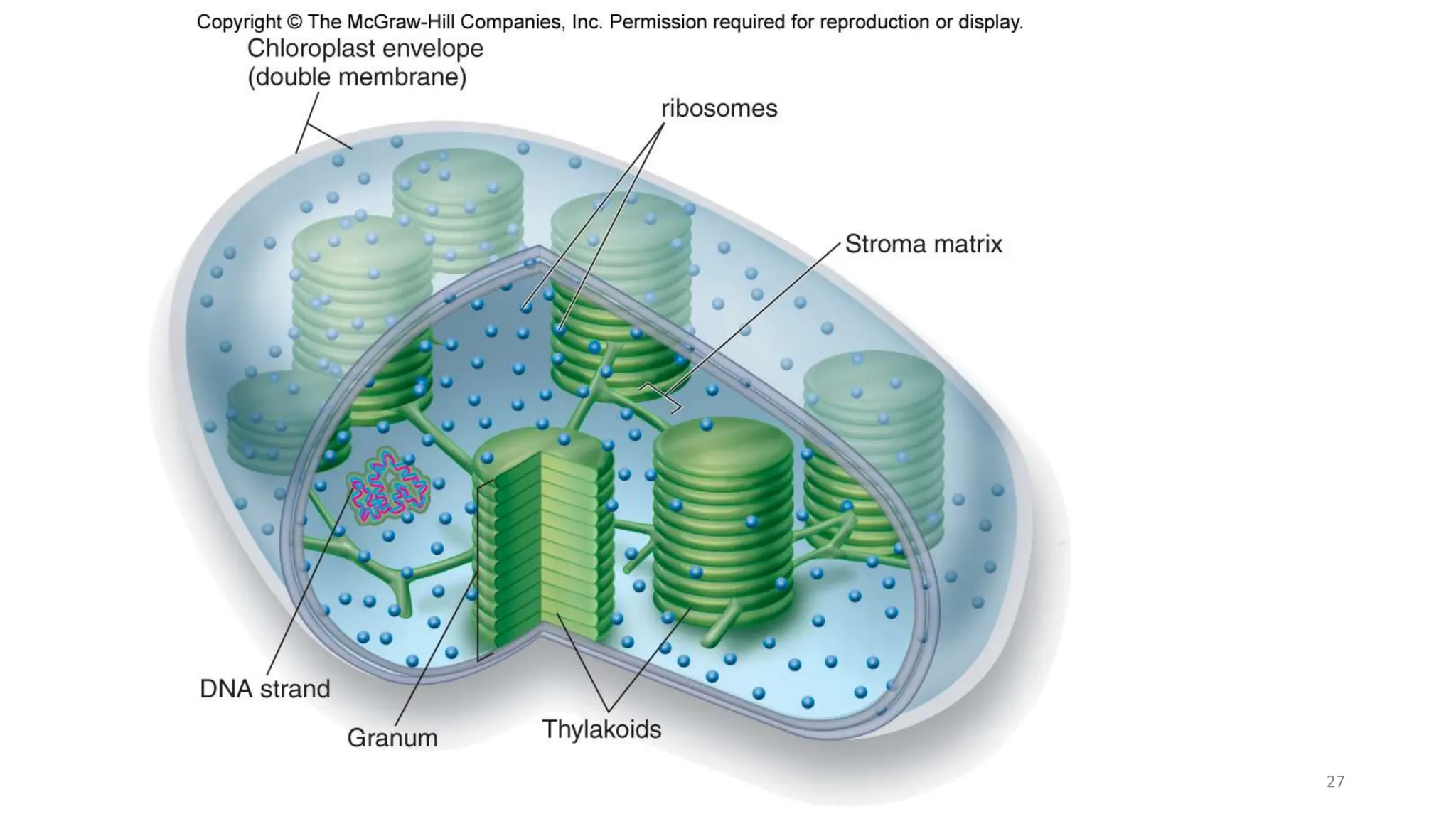
Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. They contain membrane-bound organelles and have a cytoskeleton that provides structure and aids transport. Key organelles include the nucleus, which houses genetic material, and mitochondria, which generate energy. The endomembrane system includes the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and lysosomes, and facilitates protein transport and modification. Other structures are chloroplasts for photosynthesis and cilia or flagella for motility. Eukaryotic cells have a more complex organization than prokaryotes and can perform more specialized processes and functions.