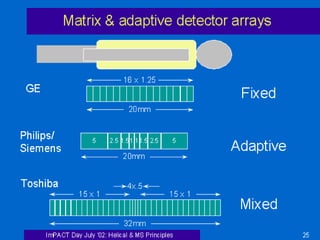
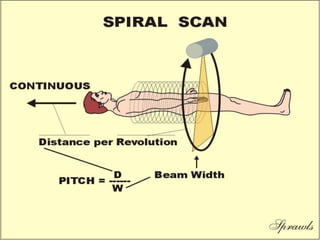
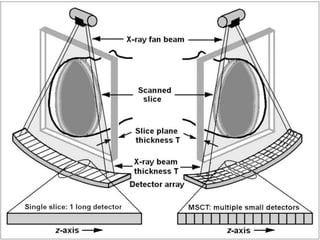
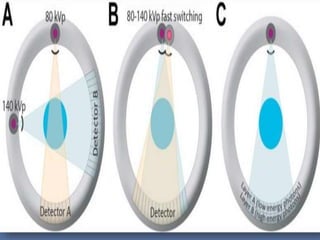
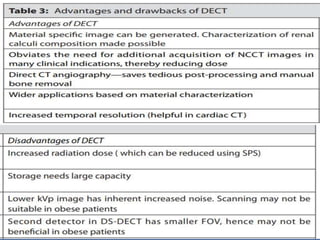
This document discusses different types of computed tomography (CT) scanning technologies, including multi-slice CT (MSCT), dual-energy CT (DECT), and various configurations for DECT scanning using single- or dual-xray sources. It provides details on the technical aspects and principles of each technology, as well as their advantages and disadvantages. Common clinical applications of DECT are also listed and include characterization of renal calculi, cysts, and masses as well as evaluation of hepatic and pulmonary conditions.