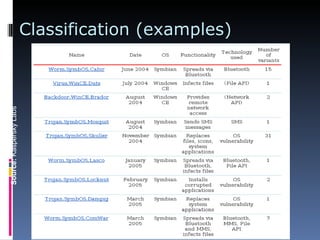
The document discusses threats from mobile malware and viruses and provides strategies for protecting smartphones. It notes that as smartphones have become pocket computers, they are now susceptible to many of the same threats as computers like viruses, worms and trojans. These threats can spread via the internet, Bluetooth, MMS and more. The document then examines some specific examples of early mobile viruses and worms. It concludes by recommending security best practices like using passcodes, enabling auto-lock, being wary of Bluetooth and downloads, and maintaining awareness of social engineering threats.