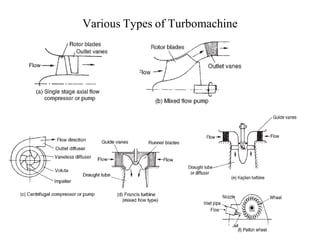
A turbomachine is defined as a device that transfers energy to or from a continuously flowing fluid using one or more moving blade rows. Turbomachines are classified into two main categories - those that absorb power to increase fluid pressure like compressors and pumps, and those that produce power by expanding fluid to a lower pressure like turbines. They are further categorized based on the flow path, which can be axial, radial, or mixed, and by the compressibility and pressure changes in the fluid flow through the rotor.