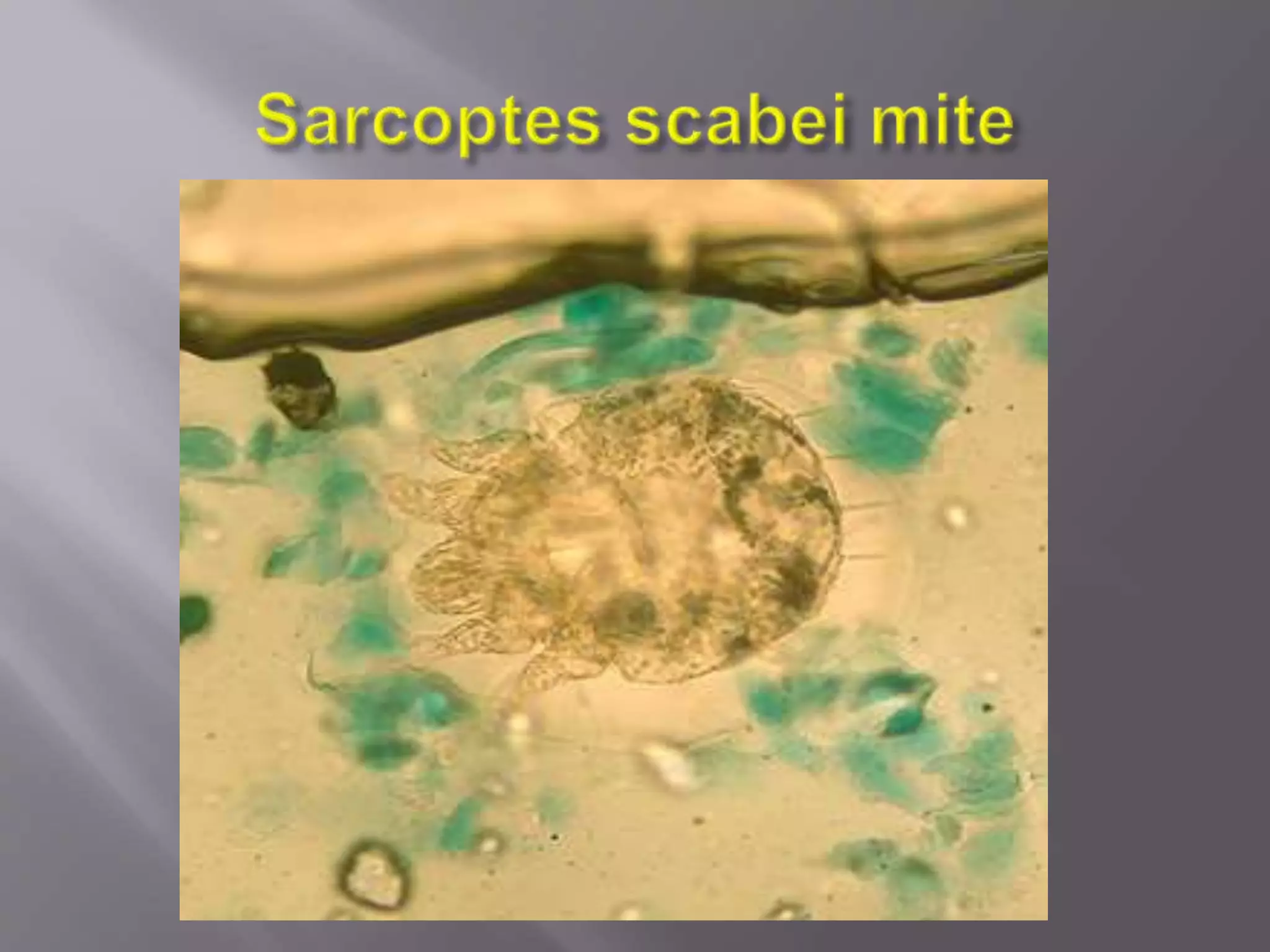
This document discusses scabies, which is an infestation of the skin caused by the scabies mite Sarcoptes scabies. The mite burrows into the epidermis and lives its entire 30-day lifecycle in the skin. It is commonly transmitted through intimate contact. Symptoms include severe itching, papules or vesicles usually worst at night. Diagnosis is usually made through visual examination finding burrows or mites. Treatment involves application of benzene hexachloride or permethrin cream, with additional medications for secondary infections or itching. Proper hygiene and treatment of cases and contacts is important to prevent spread.