This document discusses probability and provides examples of calculating probabilities of events. Some key points covered include:
- Probability allows quantifying the variability in outcomes of experiments with uncertain results.
- Key concepts like sample space, events, outcomes, mutually exclusive events, independent events are defined.
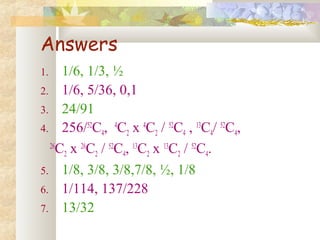
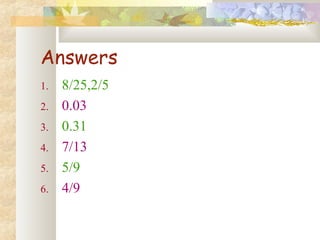
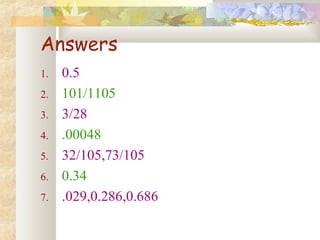
- Probability is calculated as the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of outcomes.
- Examples of probability calculations involving dice rolls, card draws, and coin tosses are provided.
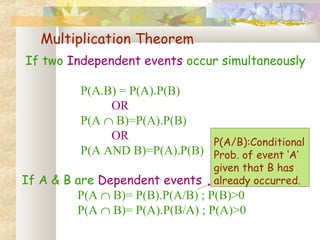
- Theorems like addition rule, multiplication rule, and conditional probability are discussed.