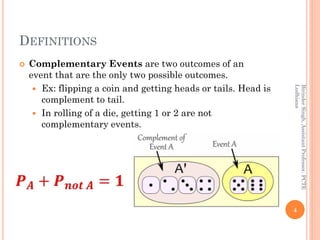
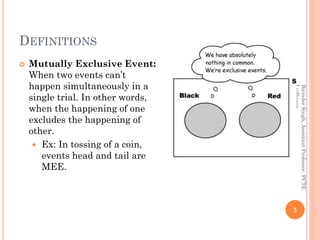
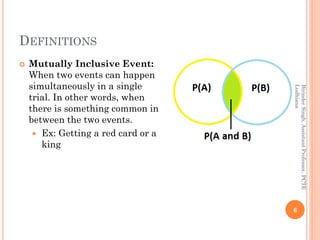
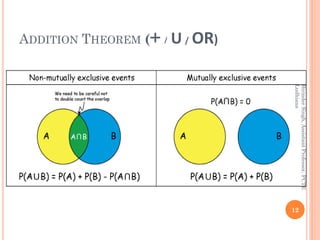
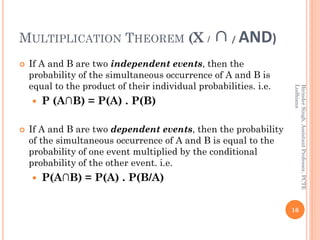
The document provides definitions and concepts related to probability, including experiments, events, complementary and mutually exclusive events, sample spaces, and the basic principles of calculating probabilities. It outlines various theorems such as the addition and multiplication theorems, along with practical problems for applying these concepts in real-world scenarios. Additionally, it addresses the use of Bayes' theorem and includes practice problems to reinforce the understanding of probability.